Wi-Fi Direct enables devices to connect directly for file sharing and communication without a router, while Miracast specializes in wireless screen mirroring and media streaming between compatible devices. Explore the rest of the article to understand which technology best suits your connectivity needs.
Table of Comparison
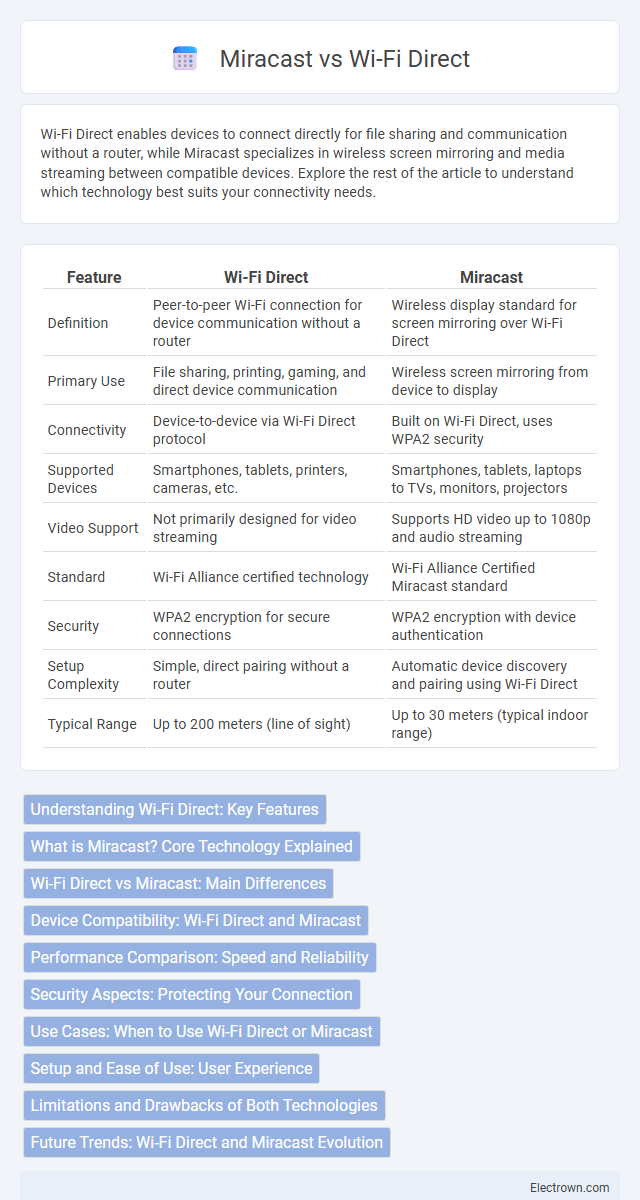
| Feature | Wi-Fi Direct | Miracast |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Peer-to-peer Wi-Fi connection for device communication without a router | Wireless display standard for screen mirroring over Wi-Fi Direct |
| Primary Use | File sharing, printing, gaming, and direct device communication | Wireless screen mirroring from device to display |
| Connectivity | Device-to-device via Wi-Fi Direct protocol | Built on Wi-Fi Direct, uses WPA2 security |
| Supported Devices | Smartphones, tablets, printers, cameras, etc. | Smartphones, tablets, laptops to TVs, monitors, projectors |
| Video Support | Not primarily designed for video streaming | Supports HD video up to 1080p and audio streaming |
| Standard | Wi-Fi Alliance certified technology | Wi-Fi Alliance Certified Miracast standard |
| Security | WPA2 encryption for secure connections | WPA2 encryption with device authentication |
| Setup Complexity | Simple, direct pairing without a router | Automatic device discovery and pairing using Wi-Fi Direct |
| Typical Range | Up to 200 meters (line of sight) | Up to 30 meters (typical indoor range) |
Understanding Wi-Fi Direct: Key Features
Wi-Fi Direct enables devices to connect directly without a wireless access point, supporting peer-to-peer communication for file sharing, printing, and multiplayer gaming. It uses WPA2 security to ensure encrypted connections, providing a fast and secure method for device pairing. Wi-Fi Direct supports simultaneous connections with multiple devices, enhancing flexibility in various wireless communication scenarios.
What is Miracast? Core Technology Explained
Miracast is a wireless display standard that allows you to mirror your device's screen directly to a compatible TV or monitor using Wi-Fi Direct technology. It creates a peer-to-peer Wi-Fi connection without requiring a traditional network or router, enabling real-time streaming of audio and video content. Your device uses Miracast to transmit high-definition media with minimal latency, making it ideal for presentations, gaming, and media playback.
Wi-Fi Direct vs Miracast: Main Differences
Wi-Fi Direct establishes a peer-to-peer wireless connection between devices, enabling file sharing and device communication without a traditional Wi-Fi network. Miracast uses Wi-Fi Direct technology specifically for screen mirroring, allowing one device to wirelessly display its screen on another, such as from a smartphone to a TV. Unlike Wi-Fi Direct's broad device compatibility, Miracast is designed primarily for video and audio streaming between compatible display devices.
Device Compatibility: Wi-Fi Direct and Miracast
Wi-Fi Direct supports a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and printers, enabling peer-to-peer connections without a traditional Wi-Fi network. Miracast, primarily designed for screen mirroring, is compatible with many Windows and Android devices but has limited support on iOS and older hardware. Your choice depends on the specific devices you own and the connection type you need for seamless compatibility.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Reliability
Wi-Fi Direct offers higher data transfer speeds up to 250 Mbps, ensuring faster and more stable connections compared to Miracast, which typically maxes out around 150 Mbps. Miracast relies on Wi-Fi Direct technology but often experiences more latency and interference due to screen mirroring compression and real-time streaming demands. For applications requiring low latency and consistent reliability, such as gaming or HD video streaming, Wi-Fi Direct provides superior performance over Miracast.
Security Aspects: Protecting Your Connection
Wi-Fi Direct and Miracast both offer secure wireless connections using WPA2 encryption to protect your data from unauthorized access. Wi-Fi Direct provides device-to-device communication with built-in PIN code authentication, enhancing security during the pairing process. Miracast's use of Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) ensures encrypted streaming between compatible devices, safeguarding your connection against potential eavesdropping.
Use Cases: When to Use Wi-Fi Direct or Miracast
Wi-Fi Direct is ideal for peer-to-peer file sharing, gaming, and printing without requiring a wireless access point, supporting direct device connections for faster data transfer. Miracast excels in screen mirroring applications such as streaming videos or displaying presentations wirelessly from smartphones, tablets, or PCs to larger displays like TVs or projectors. Choosing Wi-Fi Direct suits scenarios demanding flexible device communication, while Miracast is preferred for real-time media sharing and extended screen casting.
Setup and Ease of Use: User Experience
Wi-Fi Direct offers simple and quick peer-to-peer connections without requiring a wireless router, making setup straightforward for users seeking direct device communication. Miracast, built on Wi-Fi Direct technology, adds screen mirroring capabilities but often involves slightly more complex pairing processes and device compatibility checks. Your user experience will depend on the ease of detecting and connecting devices, where Wi-Fi Direct typically excels in speed, while Miracast prioritizes seamless media sharing.
Limitations and Drawbacks of Both Technologies
Wi-Fi Direct faces limitations in range and device compatibility, often requiring devices to support the standard explicitly, which restricts seamless connectivity. Miracast struggles with latency issues and inconsistent video quality due to varying hardware and software implementations, affecting real-time streaming performance. Both technologies also face challenges with security vulnerabilities, as improper configurations or lack of updates can expose connections to unauthorized access.
Future Trends: Wi-Fi Direct and Miracast Evolution
Wi-Fi Direct continues to evolve with enhanced security protocols and faster transfer speeds, supporting a wider range of IoT devices for seamless peer-to-peer connectivity. Miracast is advancing through integration with newer display standards and improved latency reduction techniques, allowing your streaming experience to become smoother and more reliable. Both technologies are converging towards broader compatibility and energy-efficient performance, shaping the future of wireless content sharing and device interconnectivity.
Wi-Fi Direct vs Miracast Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com