FDM and SLA are two prominent 3D printing technologies with distinct advantages: FDM uses thermoplastic filaments ideal for durable prototypes and functional parts, while SLA employs resin and laser curing to create high-resolution, detailed models with smooth finishes. Explore the rest of the article to discover which technology best suits your 3D printing needs.
Table of Comparison
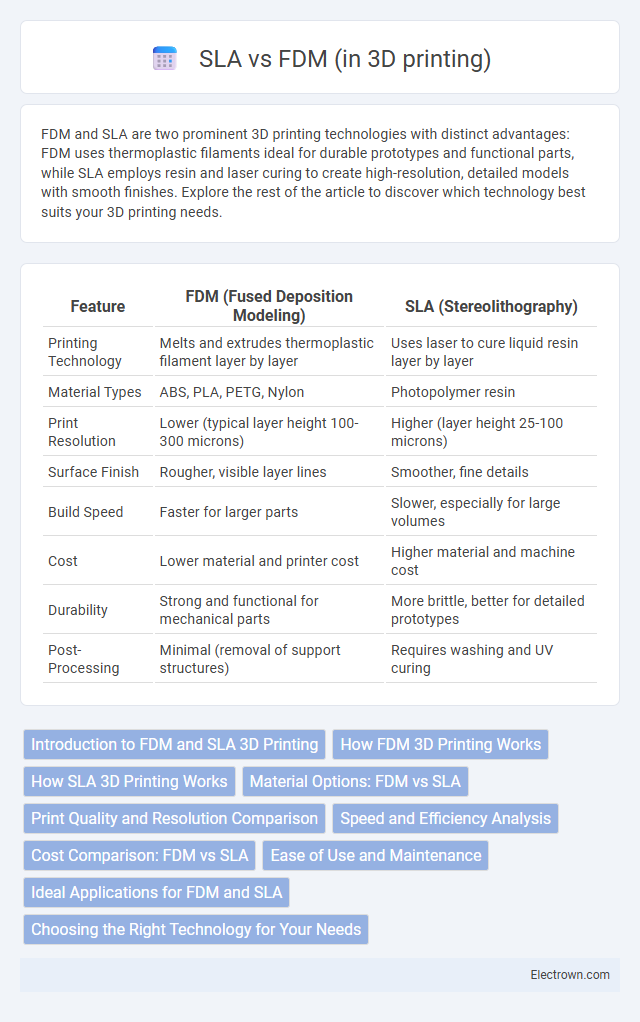
| Feature | FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) | SLA (Stereolithography) |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Technology | Melts and extrudes thermoplastic filament layer by layer | Uses laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer |
| Material Types | ABS, PLA, PETG, Nylon | Photopolymer resin |
| Print Resolution | Lower (typical layer height 100-300 microns) | Higher (layer height 25-100 microns) |
| Surface Finish | Rougher, visible layer lines | Smoother, fine details |
| Build Speed | Faster for larger parts | Slower, especially for large volumes |
| Cost | Lower material and printer cost | Higher material and machine cost |
| Durability | Strong and functional for mechanical parts | More brittle, better for detailed prototypes |
| Post-Processing | Minimal (removal of support structures) | Requires washing and UV curing |
Introduction to FDM and SLA 3D Printing
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printing involves melting and extruding thermoplastic filaments layer by layer to create objects, offering affordability and ease of use for prototyping and functional parts. SLA (Stereolithography) employs a UV laser to cure photopolymer resin with high precision, producing smooth surface finishes and intricate details ideal for dental, jewelry, and engineering applications. Both technologies serve distinct purposes in additive manufacturing, balancing speed, resolution, and material properties.
How FDM 3D Printing Works
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printing operates by melting thermoplastic filament and extruding it layer-by-layer through a heated nozzle to build objects. The printer follows a computer-generated 3D model, precisely depositing material on a build platform that moves downward as each layer solidifies. This method is known for its accessibility, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with common materials like PLA and ABS.
How SLA 3D Printing Works
SLA 3D printing uses a laser to cure liquid resin layer by layer, producing high-resolution and smooth surface finishes ideal for detailed prototypes and complex geometries. Your design is transformed as the laser precisely solidifies the resin in specific areas, allowing for intricate features unattainable with FDM's filament extrusion process. This technology excels in creating parts with superior accuracy and fine details compared to the layered texture often seen in FDM prints.
Material Options: FDM vs SLA
FDM 3D printing typically uses thermoplastic filaments like PLA, ABS, and PETG, offering a wide range of affordable and durable material options suitable for prototyping and functional parts. SLA printing employs photopolymer resins that provide superior detail, smooth surface finishes, and specialized options such as flexible, castable, or biocompatible resins, ideal for high-precision applications. Your choice depends on the required material properties, with FDM favoring robustness and cost-efficiency while SLA excels in fine detail and material versatility.
Print Quality and Resolution Comparison
SLA (Stereolithography) offers superior print quality and higher resolution, achieving layer heights as fine as 25 microns, resulting in intricate details and smooth surface finishes. FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) typically produces lower resolution prints with visible layer lines and a minimum layer height of around 100 microns, making it less ideal for highly detailed models. The photopolymer resin used in SLA cures with precision, whereas FDM relies on thermoplastic filament extrusion, impacting overall surface smoothness and accuracy.
Speed and Efficiency Analysis
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) generally offers faster prototyping due to its straightforward layer-by-layer extrusion process, making it efficient for larger, less detailed models. SLA (Stereolithography), while slower because of its intricate photopolymer curing method, delivers higher precision and smoother surface finishes, which reduces post-processing time for detailed parts. Speed efficiency in FDM is favored for quick, functional prototypes; SLA excels in applications requiring fine resolution and minimal finishing.
Cost Comparison: FDM vs SLA
FDM 3D printing typically offers lower upfront costs and affordable filament materials, making it ideal for budget-conscious prototyping and hobbyist projects. SLA printers involve higher initial investment and resin material costs but deliver superior detail and surface finish, justifying expenses for professional-grade models. Your choice depends on balancing cost efficiency with the desired print quality and application requirements.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
FDM 3D printers are generally easier to use and maintain due to their straightforward mechanics and widely available filament materials, making them suitable for beginners and hobbyists. SLA printers require more specialized knowledge to handle resin materials safely and necessitate routine cleaning of resin tanks and post-processing, which can complicate maintenance. The ease of use in FDM contrasts with SLA's need for careful resin management, impacting user preference based on skill level and maintenance willingness.
Ideal Applications for FDM and SLA
FDM is ideal for rapid prototyping, functional parts, and large-scale models due to its cost-effectiveness and ability to print durable thermoplastics like ABS and PLA. SLA excels in producing highly detailed, smooth-surfaced parts, making it perfect for intricate jewelry designs, dental models, and precise engineering prototypes. Both technologies serve different needs: FDM for robust, practical uses and SLA for fine-detail, high-resolution applications.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) offers affordable, durable parts suitable for functional prototypes and large-scale models, while SLA (Stereolithography) delivers high-resolution, detailed prints ideal for intricate designs and smooth surface finishes. Your choice depends on factors like budget, required precision, material properties, and production speed. Evaluating these parameters ensures you select the 3D printing technology best aligned with your project requirements.
FDM vs SLA (in 3D printing) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com