NFC payment offers faster, contactless transactions by simply tapping your device on a reader, while QR payment requires scanning a code, making it more accessible on devices without NFC capabilities. Explore the full article to understand which payment method best suits your needs and lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
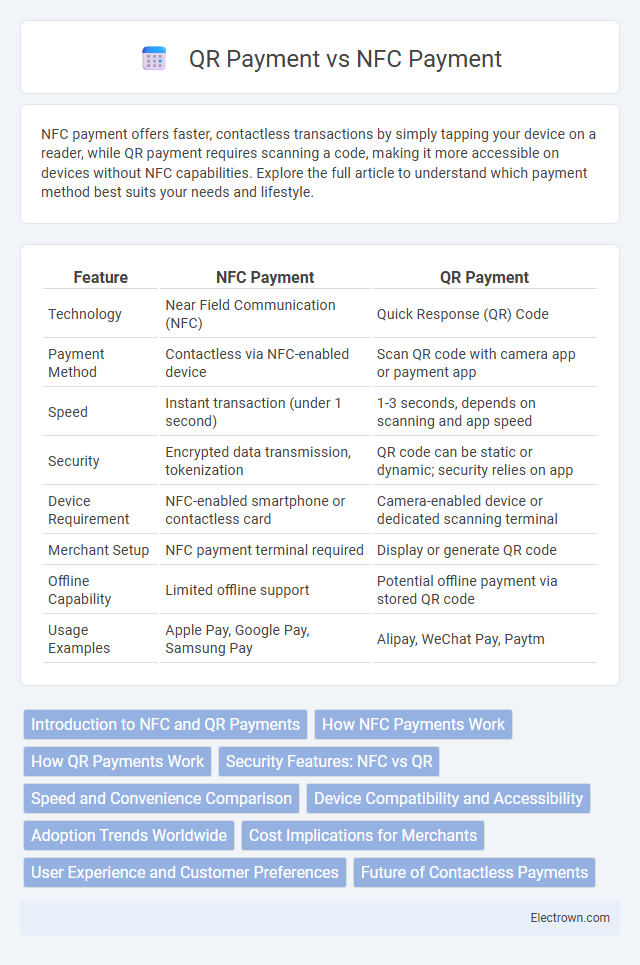
| Feature | NFC Payment | QR Payment |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Near Field Communication (NFC) | Quick Response (QR) Code |
| Payment Method | Contactless via NFC-enabled device | Scan QR code with camera app or payment app |
| Speed | Instant transaction (under 1 second) | 1-3 seconds, depends on scanning and app speed |
| Security | Encrypted data transmission, tokenization | QR code can be static or dynamic; security relies on app |
| Device Requirement | NFC-enabled smartphone or contactless card | Camera-enabled device or dedicated scanning terminal |
| Merchant Setup | NFC payment terminal required | Display or generate QR code |
| Offline Capability | Limited offline support | Potential offline payment via stored QR code |
| Usage Examples | Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay | Alipay, WeChat Pay, Paytm |
Introduction to NFC and QR Payments
NFC (Near Field Communication) payment uses contactless technology that allows two devices to communicate wirelessly within a short range, enabling secure transactions through smartphones or contactless cards. QR (Quick Response) payment involves scanning a unique code displayed by the merchant or user, which directs your mobile payment app to process the transaction. Both methods offer convenient alternatives to cash, with NFC emphasizing tap-to-pay speed and QR focusing on versatile, camera-based interaction.
How NFC Payments Work
NFC payments utilize near-field communication technology to enable secure, contactless transactions by allowing devices like smartphones or contactless cards to communicate with payment terminals within a few centimeters. When a user taps their device on an NFC-enabled terminal, encrypted payment data is transmitted instantly, facilitating quick authorization through tokenization and secure elements embedded in the device. The technology supports seamless integration with digital wallets such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, enhancing user convenience and transaction speed.
How QR Payments Work
QR payments operate by scanning a machine-readable QR code displayed on a merchant's device or printed material using a smartphone camera or payment app. The scanned QR code contains encrypted transaction information, which is transmitted to the payment gateway to authenticate and process the payment securely. This method leverages internet connectivity and real-time data exchange, allowing seamless, contactless transactions without requiring specialized hardware like NFC-enabled terminals.
Security Features: NFC vs QR
NFC payment utilizes encrypted communication and tokenization to secure transactions, significantly reducing the risk of data interception or fraud. QR payments rely on scanning static or dynamic codes, which can be susceptible to phishing attacks or code tampering without proper encryption and verification methods. Your choice between NFC and QR payment security should consider the level of encryption and fraud prevention each method employs.
Speed and Convenience Comparison
NFC payment transactions typically complete within milliseconds by simply tapping a device or card on a reader, offering near-instantaneous speed ideal for high-traffic environments. QR payment requires users to open an app, scan a code, and confirm the payment, usually taking longer and involving multiple steps. NFC's contactless nature enhances convenience by eliminating the need to unlock phones or align cameras, making it faster and more seamless than QR code payment methods.
Device Compatibility and Accessibility
NFC payment technology works seamlessly on smartphones and wearable devices equipped with NFC chips, offering contactless and instant transactions across various platforms like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay. QR payment systems rely on the device's camera capability to scan codes, making them accessible to a wider range of smartphones, including older models without NFC. While NFC provides faster and more secure processing, QR payments excel in device compatibility, especially in regions where NFC adoption is limited.
Adoption Trends Worldwide
NFC payment adoption is rapidly increasing worldwide, especially in developed markets like the US, Europe, and parts of Asia, driven by the rise of contactless cards and mobile wallets such as Apple Pay and Google Pay. QR payment systems dominate in regions like China and India, where they offer a low-cost, easy-to-implement solution for both merchants and consumers, with platforms like Alipay and Paytm leading the charge. Your choice between NFC and QR payments should consider regional consumer behavior, infrastructure availability, and the growing preference for secure, fast contactless transactions.
Cost Implications for Merchants
NFC payment systems require merchants to invest in specialized contactless payment terminals and may involve higher transaction fees due to proprietary technology licensing. QR payment solutions typically lower upfront costs as they can be integrated with standard smartphone cameras and printed QR codes, reducing hardware expenses. However, QR payments might incur higher processing fees depending on the payment service provider's structure and transaction volume.
User Experience and Customer Preferences
NFC payment provides a seamless and faster user experience by enabling tap-to-pay technology that reduces transaction time and enhances convenience at checkout. QR payment requires users to open a scanning app or camera, adding extra steps and potentially slowing down the payment process, which some customers find less intuitive. Customer preferences often favor NFC payment for its ease of use and speed, while QR payment remains popular in regions with lower NFC adoption due to its accessibility on any smartphone without specialized hardware.
Future of Contactless Payments
NFC payment technology offers faster, more secure transactions with encrypted data exchange, making it ideal for high-volume retail environments. QR payment systems provide versatility and lower implementation costs, especially in emerging markets where smartphone penetration is key. Your choice between NFC and QR payments should consider scalability, user convenience, and evolving consumer preferences in the contactless payment landscape.
NFC Payment vs QR Payment Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com