Choosing between 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi depends on your need for range versus speed, with 2.4GHz offering broader coverage and better penetration through walls, while 5GHz provides faster speeds over shorter distances. Explore the rest of the article to understand which frequency band suits your Wi-Fi setup for optimal performance.
Table of Comparison
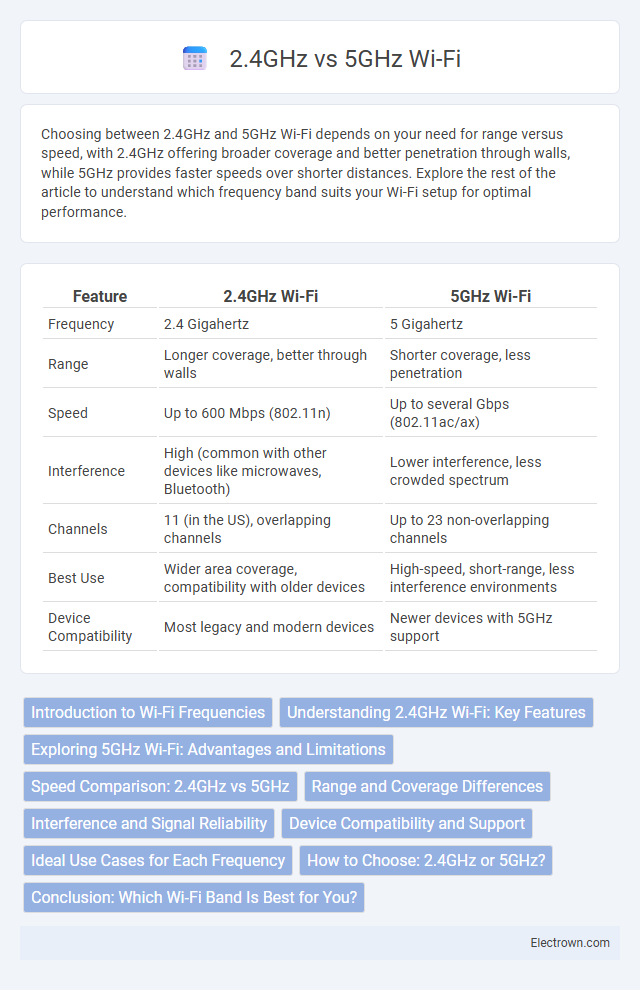
| Feature | 2.4GHz Wi-Fi | 5GHz Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 Gigahertz | 5 Gigahertz |
| Range | Longer coverage, better through walls | Shorter coverage, less penetration |
| Speed | Up to 600 Mbps (802.11n) | Up to several Gbps (802.11ac/ax) |
| Interference | High (common with other devices like microwaves, Bluetooth) | Lower interference, less crowded spectrum |
| Channels | 11 (in the US), overlapping channels | Up to 23 non-overlapping channels |
| Best Use | Wider area coverage, compatibility with older devices | High-speed, short-range, less interference environments |
| Device Compatibility | Most legacy and modern devices | Newer devices with 5GHz support |
Introduction to Wi-Fi Frequencies
2.4GHz and 5GHz are the primary Wi-Fi frequency bands used in wireless networking, each offering distinct advantages for connectivity. The 2.4GHz band provides broader coverage and better wall penetration, making it ideal for larger areas and older devices, while 5GHz offers faster speeds and less interference due to its higher frequency and wider channels. Understanding these frequency characteristics helps optimize Wi-Fi performance based on specific environment and device needs.
Understanding 2.4GHz Wi-Fi: Key Features
2.4GHz Wi-Fi operates on a lower frequency band with better range and wall penetration, making it ideal for larger areas and devices farther from the router. It supports slower data rates compared to 5GHz but offers greater compatibility with older devices and more widespread network access. Interference is common due to crowded channels from household devices like microwaves and Bluetooth gadgets, which can impact connection stability.
Exploring 5GHz Wi-Fi: Advantages and Limitations
5GHz Wi-Fi offers faster data transfer speeds and reduced interference compared to 2.4GHz, making it ideal for high-bandwidth activities like HD streaming and online gaming. However, its shorter range and limited wall penetration reduce coverage in larger or obstructed spaces. Devices supporting 5GHz deliver improved performance in dense environments but may require closer proximity to the router for optimal connectivity.
Speed Comparison: 2.4GHz vs 5GHz
The 5GHz Wi-Fi band offers significantly higher speeds compared to the 2.4GHz band, often delivering up to 1300 Mbps versus the 450 Mbps typically supported by 2.4GHz. This speed advantage is due to 5GHz's ability to support wider channels and less interference, making it ideal for high-bandwidth activities like streaming and gaming. The 2.4GHz band, while slower, provides better range and penetration through walls, making it more suitable for larger areas or environments with many obstacles.
Range and Coverage Differences
The 2.4GHz Wi-Fi band offers better range and coverage due to its lower frequency, allowing signals to penetrate walls and obstacles more effectively. In contrast, the 5GHz band provides higher data speeds but has a shorter range, making it ideal for smaller areas with less interference. Choosing the right band can improve your network's performance by balancing distance and speed according to your environment.
Interference and Signal Reliability
The 2.4GHz Wi-Fi band often faces more interference due to its crowded frequency, as many household devices like microwaves and Bluetooth gadgets operate around the same spectrum, leading to potential signal disruptions. In contrast, the 5GHz band experiences less interference, offering a more stable and reliable connection with faster speeds, especially in environments dense with Wi-Fi networks. You can enhance your network's signal reliability by choosing 5GHz when interference is a concern, but 2.4GHz remains effective for greater range and penetration through walls.
Device Compatibility and Support
Most modern devices support both 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi bands, but older gadgets may be limited to 2.4GHz only, which offers wider compatibility. The 2.4GHz band is favored for its longer range and better penetration through walls, making it suitable for devices like smart home devices and IoT gadgets. In contrast, 5GHz provides faster speeds and less interference, preferred by newer smartphones, laptops, and gaming consoles but with a shorter coverage area.
Ideal Use Cases for Each Frequency
2.4GHz Wi-Fi is ideal for larger areas with multiple walls and obstacles, offering better range and penetration suitable for browsing, emailing, and smart home devices. 5GHz Wi-Fi provides faster speeds and lower latency, making it optimal for gaming, HD video streaming, and high-bandwidth applications within shorter distances. Devices requiring stable and high-speed connections benefit most from 5GHz, while 2.4GHz supports devices needing broader coverage with less speed.
How to Choose: 2.4GHz or 5GHz?
Choosing between 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi depends on your priority for range or speed. The 2.4GHz band offers broader coverage and better wall penetration, ideal for larger spaces or devices far from the router, while 5GHz provides faster speeds and less interference, suitable for gaming, streaming, or video calls in close proximity. Assess your environment and device compatibility to optimize your network performance for your specific needs.
Conclusion: Which Wi-Fi Band Is Best for You?
Choosing between 2.4GHz and 5GHz Wi-Fi depends on your specific needs for range and speed; 2.4GHz offers better coverage and penetration through walls, making it ideal for larger spaces or older devices. The 5GHz band provides faster speeds and less interference, perfect for activities like gaming or streaming in close proximity to the router. Your best Wi-Fi band aligns with whether you prioritize extended range or higher performance for your connected devices.
2.4GHz vs 5GHz Wi-Fi Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com