PCIe SSDs deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to SATA SSDs, enhancing overall system performance for gaming, video editing, and intensive applications. Explore the full article to understand which SSD type best suits your storage needs and budget.
Table of Comparison
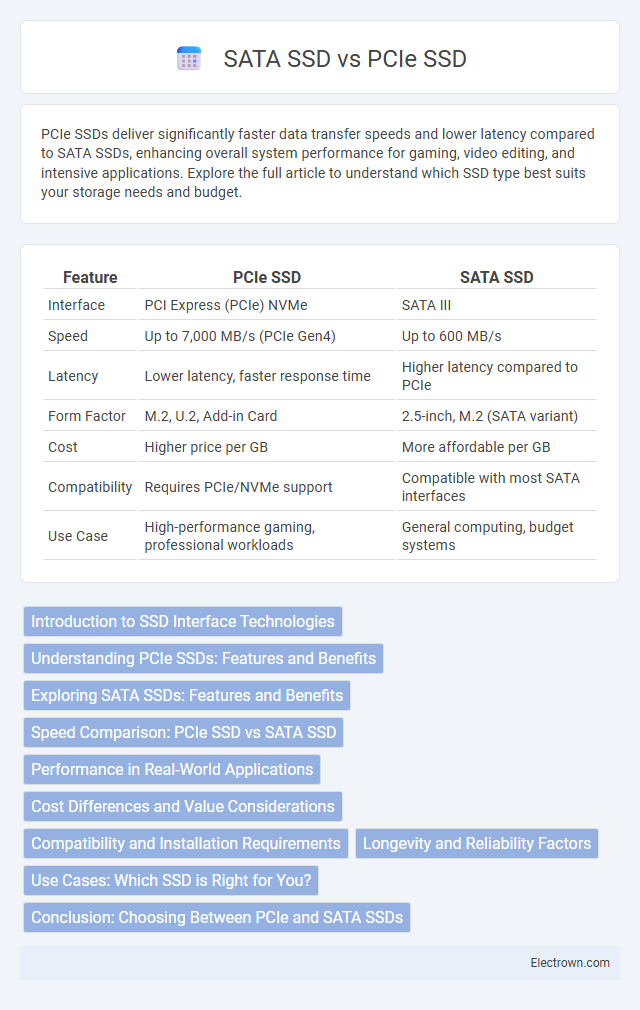
| Feature | PCIe SSD | SATA SSD |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | PCI Express (PCIe) NVMe | SATA III |
| Speed | Up to 7,000 MB/s (PCIe Gen4) | Up to 600 MB/s |
| Latency | Lower latency, faster response time | Higher latency compared to PCIe |
| Form Factor | M.2, U.2, Add-in Card | 2.5-inch, M.2 (SATA variant) |
| Cost | Higher price per GB | More affordable per GB |
| Compatibility | Requires PCIe/NVMe support | Compatible with most SATA interfaces |
| Use Case | High-performance gaming, professional workloads | General computing, budget systems |
Introduction to SSD Interface Technologies
PCIe SSDs leverage the PCI Express interface, offering significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs, which rely on the older SATA interface originally designed for hard drives. PCIe SSDs utilize multiple lanes for high bandwidth and low latency, making them ideal for demanding tasks like gaming, video editing, and large data processing. Your choice between PCIe and SATA SSD will impact overall system performance, with PCIe providing superior speed and efficiency for modern computing needs.
Understanding PCIe SSDs: Features and Benefits
PCIe SSDs leverage the Peripheral Component Interconnect Express interface to deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs, offering bandwidth up to 4x higher. These drives utilize NVMe protocol, reducing latency and enhancing performance for intensive tasks like gaming, video editing, and large file transfers. Your system benefits from quicker boot times and improved overall responsiveness when upgrading to a PCIe SSD over a traditional SATA SSD.
Exploring SATA SSDs: Features and Benefits
SATA SSDs offer a cost-effective upgrade with widespread compatibility across older and budget-friendly systems. Utilizing the SATA III interface, these drives provide read/write speeds up to 600 MB/s, significantly improving boot times and application loading over traditional HDDs. Their lower power consumption and reliable performance make SATA SSDs an ideal choice for everyday computing and moderate data transfer needs.
Speed Comparison: PCIe SSD vs SATA SSD
PCIe SSDs deliver significantly faster data transfer speeds compared to SATA SSDs, with PCIe Gen 4 SSDs reaching up to 7,000 MB/s, while SATA SSDs max out around 600 MB/s due to interface limitations. PCIe SSDs utilize multiple lanes for simultaneous data transmission, enabling lower latency and improved IOPS, critical for high-performance computing and gaming applications. In contrast, SATA SSDs remain suitable for cost-effective upgrades where ultra-high speed is not a priority.
Performance in Real-World Applications
PCIe SSDs deliver significantly faster data transfer rates, often exceeding 3,500 MB/s, compared to SATA SSDs, which typically max out around 600 MB/s, resulting in quicker boot times and faster file transfers in real-world applications. This superior speed enhances performance in demanding tasks such as 4K video editing, gaming, and large database operations, where reduced latency and increased bandwidth are critical. SATA SSDs remain suitable for everyday computing needs but fall short in scenarios requiring high-speed data access and intensive workflow efficiency.
Cost Differences and Value Considerations
PCIe SSDs generally cost more than SATA SSDs due to faster data transfer rates and advanced NVMe technology, providing superior performance for high-demand applications. SATA SSDs offer a more affordable option with sufficient speed for everyday computing tasks, making them a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious users. When evaluating value, PCIe SSDs deliver enhanced speed and future-proofing benefits, while SATA SSDs balance price and performance for typical storage needs.
Compatibility and Installation Requirements
PCIe SSDs require motherboards with M.2 or PCIe slots and support NVMe protocols, offering faster data transfer speeds but demanding greater compatibility considerations than SATA SSDs, which fit standard SATA ports and connectors commonly found in most systems. Installation of PCIe SSDs may necessitate updated BIOS versions and specific slot configurations, while SATA SSDs generally involve simpler plug-and-play installation through SATA cables and power connectors. Your choice impacts system compatibility and installation complexity, with PCIe SSDs geared toward high-performance builds and SATA SSDs providing broad compatibility and ease of use.
Longevity and Reliability Factors
PCIe SSDs typically offer superior longevity and reliability due to advanced NAND flash management and higher-quality controllers compared to SATA SSDs, which often use older interfaces and less efficient error correction. The increased bandwidth and reduced latency in PCIe SSDs result in lower wear on memory cells, extending your drive's lifespan under heavy workloads. SATA SSDs may still provide reliable performance for everyday use but tend to have shorter endurance ratings, making PCIe SSDs a better choice for demanding applications requiring long-term durability.
Use Cases: Which SSD is Right for You?
PCIe SSDs deliver superior speed and low latency, making them ideal for high-performance tasks like gaming, video editing, and large database operations where rapid data access is crucial. SATA SSDs offer reliable performance at a lower cost, fitting well for everyday computing, web browsing, and office applications that don't require maximum throughput. Understanding your workload demands helps determine if the enhanced speed of a PCIe SSD justifies the investment or if a SATA SSD meets your storage needs efficiently.
Conclusion: Choosing Between PCIe and SATA SSDs
PCIe SSDs offer significantly faster data transfer speeds and lower latency compared to SATA SSDs, making them ideal for high-performance tasks like gaming, video editing, and large file transfers. SATA SSDs remain a cost-effective option for everyday computing needs and provide reliable performance for most users. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize speed and future-proofing with PCIe or value affordability and widespread compatibility with SATA.
PCIe SSD vs SATA SSD Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com