S/PDIF and TOSLINK are two common audio interface standards used for transmitting digital audio signals, with S/PDIF typically utilizing coaxial cables and TOSLINK using optical fiber for reduced interference. Understanding the differences in cable types, signal quality, and compatibility can help you choose the best option for your audio setup; continue reading to explore their features in detail and find out which suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
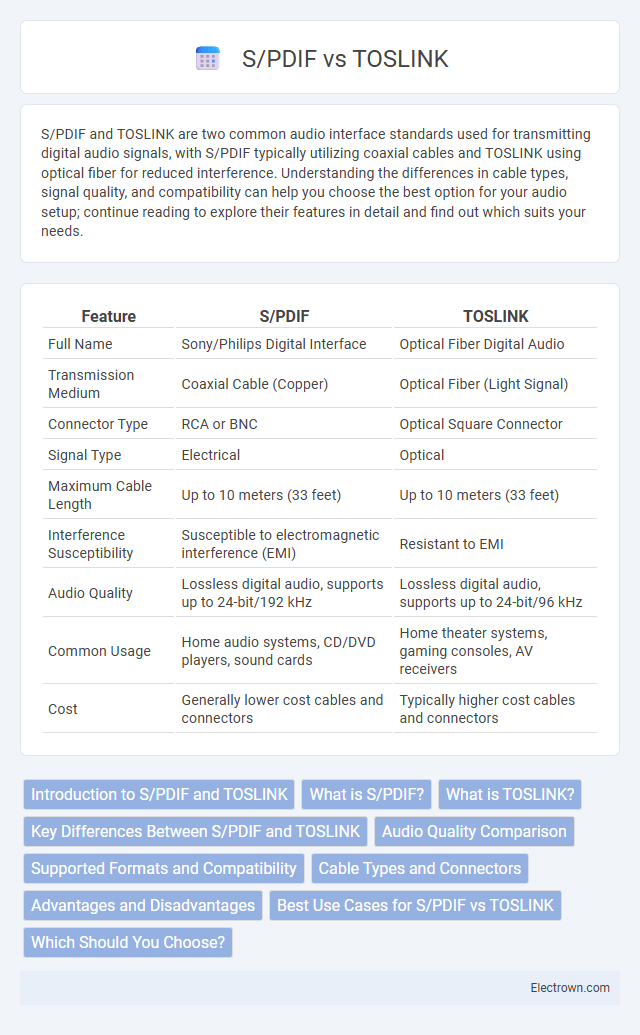
| Feature | S/PDIF | TOSLINK |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Sony/Philips Digital Interface | Optical Fiber Digital Audio |
| Transmission Medium | Coaxial Cable (Copper) | Optical Fiber (Light Signal) |
| Connector Type | RCA or BNC | Optical Square Connector |
| Signal Type | Electrical | Optical |
| Maximum Cable Length | Up to 10 meters (33 feet) | Up to 10 meters (33 feet) |
| Interference Susceptibility | Susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) | Resistant to EMI |
| Audio Quality | Lossless digital audio, supports up to 24-bit/192 kHz | Lossless digital audio, supports up to 24-bit/96 kHz |
| Common Usage | Home audio systems, CD/DVD players, sound cards | Home theater systems, gaming consoles, AV receivers |
| Cost | Generally lower cost cables and connectors | Typically higher cost cables and connectors |
Introduction to S/PDIF and TOSLINK
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a digital audio transfer protocol designed for transmitting high-quality audio signals between devices using coaxial or optical cables. TOSLINK, a specific type of S/PDIF connection, utilizes fiber optic cables to transmit digital audio signals via light pulses, reducing electromagnetic interference. Both standards support stereo and multichannel surround sound, with TOSLINK commonly preferred for its noise immunity and durability in home audio setups.
What is S/PDIF?
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format) is a digital audio transfer protocol that transmits high-quality stereo or multichannel signals between devices using coaxial or optical cables. It supports two main types of physical connections: coaxial cables with RCA connectors and optical fibers known as TOSLINK. S/PDIF enables lossless audio transmission, making it essential for home theater systems, CD players, and digital audio processors.
What is TOSLINK?
TOSLINK is an optical fiber digital audio interface that transmits sound signals using light pulses, reducing electromagnetic interference compared to traditional electrical connections. It primarily supports S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format) audio signals, delivering high-quality stereo and multichannel sound for home theater systems and professional audio equipment. TOSLINK cables use fiber optic strands, providing reliable and noise-free transmission over distances typically up to 10 meters.
Key Differences Between S/PDIF and TOSLINK
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) transmits digital audio signals through either coaxial cable using electrical impulses or optical fiber via TOSLINK connectors, which utilize light signals for data transfer. The key difference lies in the medium--S/PDIF supports both coaxial and optical connections, whereas TOSLINK is exclusive to optical transmission, reducing EMI and ground loop noise. Coaxial S/PDIF typically offers more robust signal integrity over longer distances compared to TOSLINK, which may suffer from signal degradation beyond 5 meters without repeaters.
Audio Quality Comparison
S/PDIF and TOSLINK both transmit high-quality digital audio signals with minimal loss, ensuring excellent sound fidelity for your audio setup. S/PDIF uses electrical coaxial cables, which can be susceptible to electromagnetic interference, potentially affecting audio clarity over long distances. TOSLINK employs optical fiber, eliminating electrical noise and maintaining consistent audio quality, especially useful in environments with high electronic interference.
Supported Formats and Compatibility
S/PDIF supports both coaxial and optical interfaces, accommodating digital audio formats like PCM, Dolby Digital, and DTS, ensuring broad compatibility with home theater systems and audio devices. TOSLINK exclusively uses optical fiber and supports standard stereo PCM as well as compressed formats such as Dolby Digital and DTS, but may not handle higher-resolution audio formats like Dolby TrueHD or DTS-HD Master Audio. Compatibility varies with device capabilities and the type of connection, with S/PDIF offering more flexibility across various digital audio sources.
Cable Types and Connectors
S/PDIF supports both coaxial cables with RCA connectors and optical cables with TOSLINK connectors, offering flexibility depending on your audio setup. Coaxial cables use copper wiring to transmit electrical signals, providing durability and resistance to interference, while TOSLINK cables use fiber optic strands for transmitting digital audio as light, minimizing electromagnetic interference. Choosing between these depends on your device compatibility and preference for signal transmission, with TOSLINK favored for its immunity to electrical noise.
Advantages and Disadvantages
S/PDIF supports both coaxial and optical connections, offering flexibility with coaxial cables providing superior durability and longer cable runs compared to TOSLINK's optical fibers, which are immune to electromagnetic interference. TOSLINK excels in noise-free digital audio transmission but is more susceptible to physical damage and signal degradation over longer distances. S/PDIF coaxial cables are typically more affordable and easier to terminate, whereas TOSLINK connectors reduce ground loop issues but require careful handling to avoid fiber damage.
Best Use Cases for S/PDIF vs TOSLINK
S/PDIF excels in professional audio environments and setups requiring electrical signal transmission over coaxial cables, offering superior resistance to interference and higher bandwidth capabilities for uncompressed audio. TOSLINK is ideal for consumer electronics and home theater systems, utilizing optical fiber to provide electrical isolation, prevent ground loops, and ensure noise-free digital audio transmission over moderate distances. Choosing between S/PDIF and TOSLINK depends on the specific application environment, with S/PDIF favored for studio reliability and TOSLINK preferred for simplicity and EMI immunity in residential use.
Which Should You Choose?
Choosing between S/PDIF and TOSLINK depends on your audio setup and connection preferences. S/PDIF offers both coaxial and optical formats, with coaxial providing slightly better durability and signal integrity, while TOSLINK uses optical fiber to minimize electrical interference and ground loop issues. For high-fidelity home audio systems, S/PDIF coaxial is preferred, but TOSLINK is ideal for environments with high electronic noise or when isolating audio devices is necessary.
S/PDIF vs TOSLINK Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com