Dual band Wi-Fi operates on two frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) offering reliable performance for everyday internet use, while tri-band Wi-Fi adds an extra 5 GHz band to support more devices simultaneously and reduce network congestion. Explore this article to discover which Wi-Fi setup best suits your home or office needs.
Table of Comparison
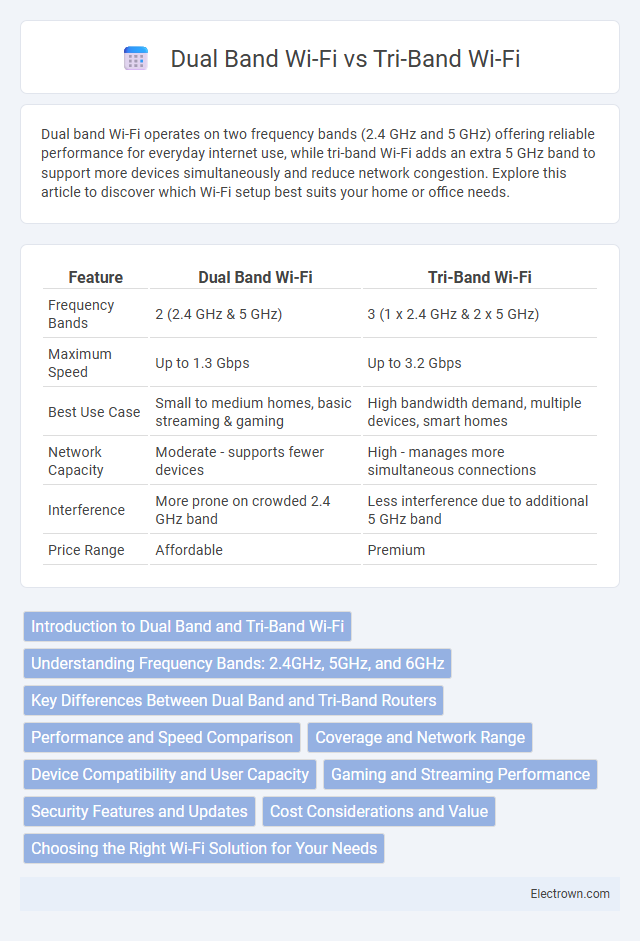
| Feature | Dual Band Wi-Fi | Tri-Band Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Bands | 2 (2.4 GHz & 5 GHz) | 3 (1 x 2.4 GHz & 2 x 5 GHz) |
| Maximum Speed | Up to 1.3 Gbps | Up to 3.2 Gbps |
| Best Use Case | Small to medium homes, basic streaming & gaming | High bandwidth demand, multiple devices, smart homes |
| Network Capacity | Moderate - supports fewer devices | High - manages more simultaneous connections |
| Interference | More prone on crowded 2.4 GHz band | Less interference due to additional 5 GHz band |
| Price Range | Affordable | Premium |
Introduction to Dual Band and Tri-Band Wi-Fi
Dual Band Wi-Fi operates on two frequency bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, offering balanced coverage and speed suitable for most home networks. Tri-Band Wi-Fi adds an extra 5 GHz band, enhancing capacity and reducing congestion in environments with multiple connected devices. Choosing between Dual Band and Tri-Band Wi-Fi depends on Your need for higher bandwidth and simultaneous device connections, with Tri-Band providing better performance in busy networks.
Understanding Frequency Bands: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz
Dual Band Wi-Fi operates on 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands, offering a balance between range and speed ideal for most home networks. Tri-Band Wi-Fi adds a third band, often a 6GHz frequency, enhancing network capacity and reducing congestion for devices supporting Wi-Fi 6E. Understanding these frequency bands helps optimize Your wireless connectivity by leveraging 2.4GHz for longer range, 5GHz for faster speeds, and 6GHz for ultra-high throughput with minimal interference.
Key Differences Between Dual Band and Tri-Band Routers
Dual Band Wi-Fi routers operate on two frequency bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, providing balanced speed and range suitable for moderate device use, while Tri-Band Wi-Fi routers add an extra 5 GHz band to handle more devices and reduce network congestion. Dual Band routers typically offer speeds up to 1.9 Gbps, whereas Tri-Band routers can exceed 3 Gbps, making them ideal for high-bandwidth activities like 4K streaming and online gaming on multiple devices simultaneously. Tri-Band networks improve overall performance in busy environments by dynamically distributing devices across three bands to minimize interference and maximize throughput.
Performance and Speed Comparison
Dual Band Wi-Fi operates on two frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), offering solid performance for most home networks with speeds up to 1.3 Gbps on 5 GHz. Tri-Band Wi-Fi adds an extra 5 GHz band, significantly improving performance and speed by reducing network congestion and increasing overall bandwidth, ideal for households with multiple high-demand devices. This extra band enables tri-band routers to deliver faster speeds and better handling of simultaneous data streams, resulting in smoother streaming, gaming, and large file transfers compared to dual-band systems.
Coverage and Network Range
Dual Band Wi-Fi operates on two frequency bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, providing good coverage with a balance between range and speed, ideal for most home environments. Tri-Band Wi-Fi adds an additional 5 GHz band, enhancing network range by reducing congestion and improving performance in larger spaces or homes with many connected devices. Optimizing your network coverage depends on your home's size and device density, with Tri-Band Wi-Fi offering better range and connectivity in high-demand scenarios.
Device Compatibility and User Capacity
Dual Band Wi-Fi operates on two frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), supporting compatibility with most devices and offering efficient performance for moderate user capacity, typically handling up to 20-30 connected devices effectively. Tri-Band Wi-Fi includes an additional 5 GHz band, enhancing device compatibility for newer, high-performance gadgets and significantly increasing user capacity by managing up to 50 or more devices simultaneously with reduced network congestion. This difference makes Tri-Band ideal for smart homes or offices with multiple high-bandwidth devices, whereas Dual Band suits smaller setups with fewer connected devices.
Gaming and Streaming Performance
Tri-Band Wi-Fi offers enhanced gaming and streaming performance by utilizing an additional 5GHz band, reducing network congestion and providing more consistent low-latency connections compared to Dual Band Wi-Fi. Gamers benefit from minimized ping spikes and faster data rates, while 4K streaming experiences less buffering and higher video quality due to increased bandwidth availability. Dual Band Wi-Fi supports moderate traffic but may struggle in environments with multiple simultaneous high-demand devices during intense gaming sessions or streaming marathons.
Security Features and Updates
Dual Band Wi-Fi routers typically support WPA3 encryption and receive regular firmware updates to enhance security features and patch vulnerabilities. Tri-Band Wi-Fi devices, designed for higher performance, often include advanced security protocols like WPA3 and may offer more frequent updates from manufacturers to address potential threats. Your choice between Dual Band and Tri-Band Wi-Fi should consider the security features and update policies to protect your network effectively.
Cost Considerations and Value
Dual Band Wi-Fi routers generally offer a more affordable option, providing sufficient performance for most home networks with two frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz). Tri-Band Wi-Fi routers, which include an additional 5 GHz band, come at a higher cost but deliver enhanced capacity and reduced congestion, benefiting environments with many connected devices or heavy streaming demands. Weighing cost considerations against network needs, Dual Band offers solid value for typical users, while Tri-Band represents a premium investment for maximizing speed and device handling in complex or high-usage scenarios.
Choosing the Right Wi-Fi Solution for Your Needs
Dual Band Wi-Fi operates on 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies, offering reliable performance for everyday internet use with moderate device connectivity. Tri-Band Wi-Fi adds an extra 5 GHz band, ideal for households or offices with multiple high-demand devices requiring faster speeds and reduced interference. Your choice depends on your network size and usage patterns, with Tri-Band providing enhanced capacity and smoother streaming for heavy multitasking environments.
Dual Band Wi-Fi vs Tri-Band Wi-Fi Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com