Quick Charge and USB Power Delivery are two prominent fast-charging technologies that differ in compatibility, charging speed, and power management, with Quick Charge primarily used in Qualcomm devices and USB Power Delivery offering broader device support including laptops and smartphones. Understanding these distinctions can help You choose the best charging method for your device, so continue reading to discover which technology suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
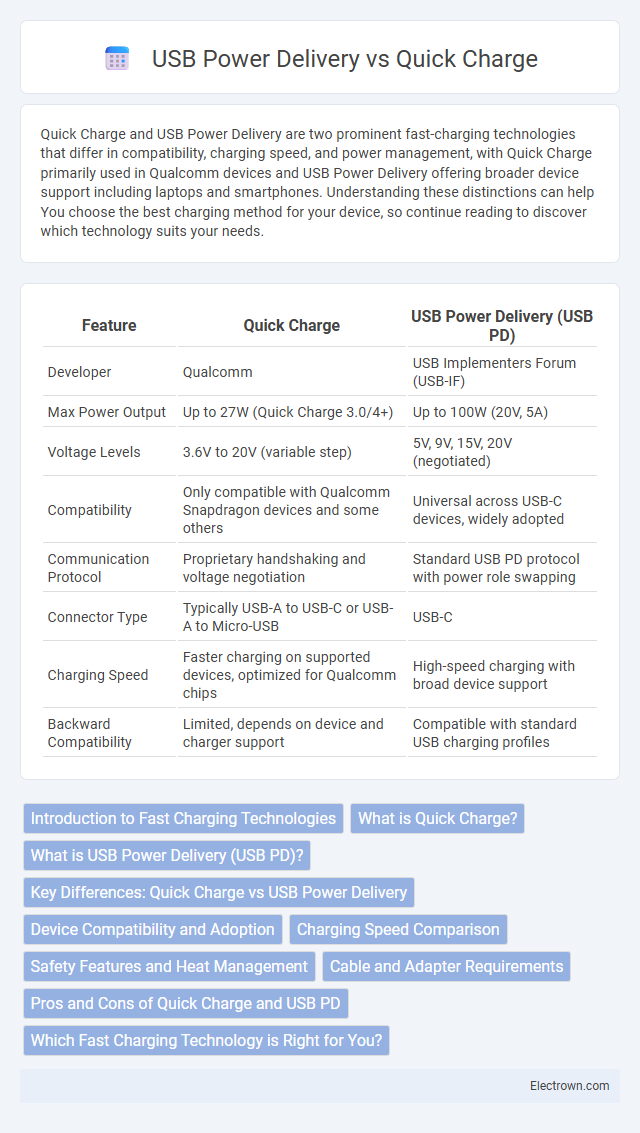
| Feature | Quick Charge | USB Power Delivery (USB PD) |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | Qualcomm | USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) |
| Max Power Output | Up to 27W (Quick Charge 3.0/4+) | Up to 100W (20V, 5A) |
| Voltage Levels | 3.6V to 20V (variable step) | 5V, 9V, 15V, 20V (negotiated) |
| Compatibility | Only compatible with Qualcomm Snapdragon devices and some others | Universal across USB-C devices, widely adopted |
| Communication Protocol | Proprietary handshaking and voltage negotiation | Standard USB PD protocol with power role swapping |
| Connector Type | Typically USB-A to USB-C or USB-A to Micro-USB | USB-C |
| Charging Speed | Faster charging on supported devices, optimized for Qualcomm chips | High-speed charging with broad device support |
| Backward Compatibility | Limited, depends on device and charger support | Compatible with standard USB charging profiles |
Introduction to Fast Charging Technologies
Fast charging technologies like Quick Charge and USB Power Delivery significantly reduce charging time by increasing power output beyond standard USB limits. Quick Charge, developed by Qualcomm, supports variable voltage and current levels up to 20W or higher for compatible devices, optimizing charging speed through efficient power management. USB Power Delivery, an open standard managed by the USB Implementers Forum, delivers up to 100W of power with smart negotiation between devices, making it widely compatible with phones, tablets, and laptops.
What is Quick Charge?
Quick Charge is a proprietary fast-charging technology developed by Qualcomm that significantly reduces the time needed to charge compatible devices by increasing voltage and current output. It supports multiple versions, including Quick Charge 3.0 and 4.0, each offering improvements in efficiency and safety features to protect your battery. Quick Charge is commonly found in smartphones and tablets equipped with Qualcomm Snapdragon processors, ensuring rapid power delivery tailored to your device's needs.
What is USB Power Delivery (USB PD)?
USB Power Delivery (USB PD) is an advanced charging protocol that delivers higher power levels up to 100 watts, enabling faster and more efficient charging for a variety of devices including smartphones, laptops, and tablets. It supports dynamic power adjustment, allowing devices to negotiate and receive the optimal voltage and current for safe and rapid charging. USB PD uses the USB Type-C connector standard, promoting universal compatibility and simplifying cable use across multiple devices.
Key Differences: Quick Charge vs USB Power Delivery
Quick Charge utilizes variable voltage levels to rapidly increase charging speed, primarily supporting Qualcomm Snapdragon devices, while USB Power Delivery (USB PD) employs flexible voltage and current negotiation for broader device compatibility, including smartphones, laptops, and tablets. Quick Charge typically offers power outputs up to 36W, optimized for rapid charging of specific devices, whereas USB PD supports power delivery up to 100W or more, enabling fast charging of a wider range of electronics. USB PD's standardized protocol ensures universal interoperability across devices and chargers, whereas Quick Charge operates as a proprietary technology with limited compatibility.
Device Compatibility and Adoption
Quick Charge technology is widely adopted by Qualcomm-powered devices, particularly Android smartphones, offering fast charging speeds but limited compatibility with non-Qualcomm hardware. USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) boasts broader adoption across a diverse range of devices, including Apple products, laptops, tablets, and newer Android phones, due to its universal standard and ability to deliver higher power levels. Your choice between Quick Charge and USB-PD depends largely on your device ecosystem and the importance of cross-brand compatibility for seamless charging.
Charging Speed Comparison
Quick Charge technology offers fast charging speeds optimized for compatible devices, typically delivering up to 27W or higher in newer versions, while USB Power Delivery (USB PD) supports a broader voltage and current range, enabling charging speeds up to 100W for laptops and smartphones. USB PD's intelligent power negotiation provides efficient energy transfer, adapting to your device's power requirements for optimal charging speed. Comparing both, USB PD tends to outperform Quick Charge in versatility and maximum power output, especially for high-capacity devices.
Safety Features and Heat Management
Quick Charge technology incorporates advanced voltage regulation and thermal protection circuits to minimize overheating and ensure safe charging for compatible devices. USB Power Delivery (USB PD) offers dynamic power adjustment with built-in safeguards that monitor temperature and prevent excessive current flow, enhancing device safety and heat management. Your device benefits from efficient heat dissipation and reduced risk of damage when using chargers with robust safety protocols inherent in both Quick Charge and USB PD standards.
Cable and Adapter Requirements
Quick Charge requires compatible adapters and specific certified cables to achieve optimal charging speeds, typically utilizing thicker gauge wires to handle higher currents efficiently. USB Power Delivery demands USB-C cables with appropriate power capabilities and ID chips to safely negotiate voltage and current between devices, supporting up to 100W or more. Your charging setup's compatibility hinges on using matched cables and adapters designed explicitly for these fast-charging protocols to avoid reduced performance or potential safety risks.
Pros and Cons of Quick Charge and USB PD
Quick Charge offers faster charging speeds for compatible devices with optimized voltage and current, but it may cause heat generation and is limited to Qualcomm-supported gadgets. USB Power Delivery provides versatile power delivery up to 100W, enabling charging for a wide range of devices including laptops, but it may charge certain devices slower than Quick Charge due to standardized protocols. Your choice depends on device compatibility and charging needs, balancing speed with device safety and power flexibility.
Which Fast Charging Technology is Right for You?
Quick Charge offers rapid charging mainly for Qualcomm-powered devices, delivering voltage boosts in increments for faster power transfer, while USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) supports higher wattages and universal compatibility across smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Your choice depends on device compatibility and charging speed needs; USB-PD is ideal for multi-device users seeking a versatile solution, whereas Quick Charge excels with specific Qualcomm devices aiming for optimized quick top-ups. Prioritize USB-PD for future-proofing and broad device support, while Quick Charge suits those with compatible hardware focused on fast, efficient mobile charging.
Quick Charge vs USB Power Delivery Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com