HDMI and DisplayPort are both high-definition digital interfaces used to transmit audio and video signals, with HDMI being widely adopted for consumer electronics like TVs and gaming consoles, while DisplayPort is favored for computer monitors due to its higher bandwidth and support for multiple displays. Explore the detailed comparison to understand which connection best suits your setup and enhances your viewing experience.
Table of Comparison
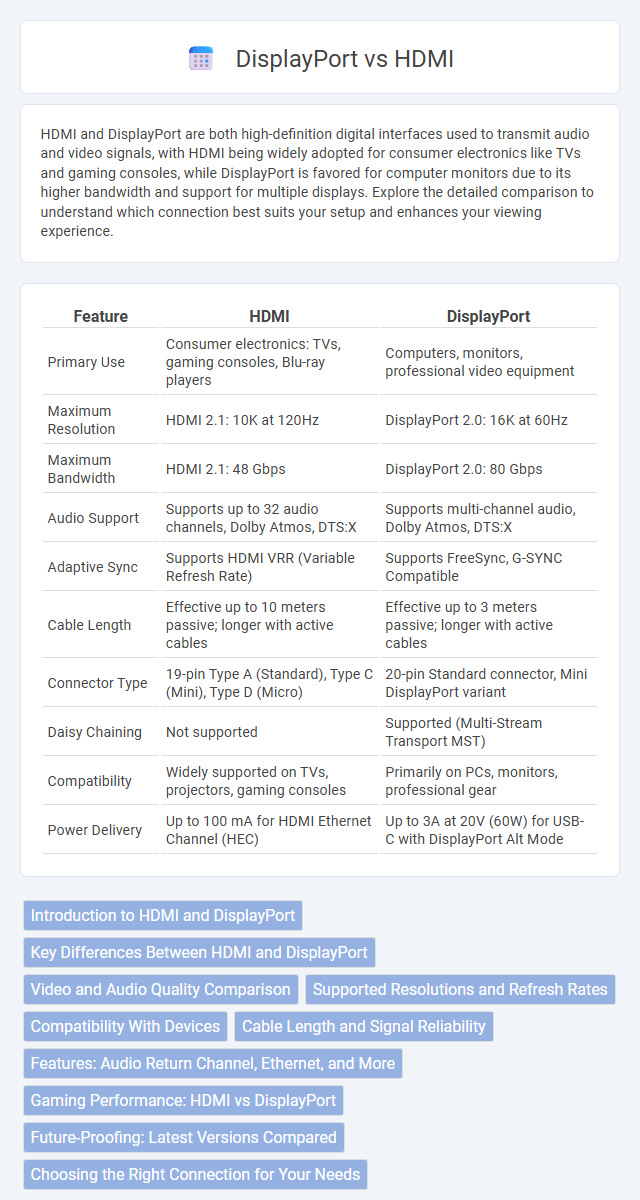
| Feature | HDMI | DisplayPort |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Consumer electronics: TVs, gaming consoles, Blu-ray players | Computers, monitors, professional video equipment |
| Maximum Resolution | HDMI 2.1: 10K at 120Hz | DisplayPort 2.0: 16K at 60Hz |
| Maximum Bandwidth | HDMI 2.1: 48 Gbps | DisplayPort 2.0: 80 Gbps |
| Audio Support | Supports up to 32 audio channels, Dolby Atmos, DTS:X | Supports multi-channel audio, Dolby Atmos, DTS:X |
| Adaptive Sync | Supports HDMI VRR (Variable Refresh Rate) | Supports FreeSync, G-SYNC Compatible |
| Cable Length | Effective up to 10 meters passive; longer with active cables | Effective up to 3 meters passive; longer with active cables |
| Connector Type | 19-pin Type A (Standard), Type C (Mini), Type D (Micro) | 20-pin Standard connector, Mini DisplayPort variant |
| Daisy Chaining | Not supported | Supported (Multi-Stream Transport MST) |
| Compatibility | Widely supported on TVs, projectors, gaming consoles | Primarily on PCs, monitors, professional gear |
| Power Delivery | Up to 100 mA for HDMI Ethernet Channel (HEC) | Up to 3A at 20V (60W) for USB-C with DisplayPort Alt Mode |
Introduction to HDMI and DisplayPort
HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is a widely used digital interface for transmitting high-definition video and audio between devices like TVs, gaming consoles, and Blu-ray players. DisplayPort is a digital display interface primarily used to connect video sources to computer monitors, offering higher resolutions and refresh rates tailored for PC gaming and professional applications. Both standards support audio and video transmission but differ in connector design, bandwidth capabilities, and target use cases.
Key Differences Between HDMI and DisplayPort
HDMI supports widespread consumer electronics with features like ARC (Audio Return Channel) and CEC (Consumer Electronics Control), making it ideal for home entertainment systems, while DisplayPort excels in high-performance PC setups due to higher bandwidth and support for daisy-chaining multiple monitors. HDMI versions 2.1 offer up to 48 Gbps bandwidth, suitable for 8K video at 60Hz, whereas DisplayPort 2.0 surpasses this with 80 Gbps, enabling 16K resolutions or multiple 4K displays at high refresh rates. Your choice depends on device compatibility and usage needs, with DisplayPort favored for gaming and professional displays, and HDMI preferred for TVs and consumer devices.
Video and Audio Quality Comparison
HDMI 2.1 supports uncompressed 8K video at 60Hz and 4K at 120Hz with dynamic HDR, delivering superior color depth and bandwidth up to 48 Gbps. DisplayPort 2.0 offers even higher bandwidth at 80 Gbps, supporting up to 16K resolution at 60Hz or multiple 4K displays simultaneously with HDR and 30-bit color depth. Both interfaces support multi-channel digital audio formats, but DisplayPort allows for higher audio sample rates and more flexible audio stream management, benefiting professional audio-visual setups.
Supported Resolutions and Refresh Rates
DisplayPort supports higher maximum resolutions and refresh rates compared to HDMI, with DisplayPort 2.0 capable of 10K resolution at 60Hz or 4K at 240Hz, while HDMI 2.1 supports up to 10K at 120Hz. HDMI 2.1 is widely compatible with TVs and consoles, offering 4K at 120Hz, whereas DisplayPort is preferred for high-performance PC monitors due to its superior bandwidth and multi-stream transport capabilities. Choosing the right interface depends on your device compatibility and whether you prioritize ultra-high resolutions or a smoother refresh rate for gaming and professional use.
Compatibility With Devices
HDMI offers broad compatibility with most consumer electronics including TVs, monitors, gaming consoles, and laptops, making it the preferred choice for general multimedia use. DisplayPort is commonly found on high-end PCs and professional-grade monitors, excelling in supporting multiple displays through daisy-chaining and higher refresh rates. Both interfaces support audio and video transmission, but HDMI's widespread adoption ensures greater compatibility across diverse device ecosystems.
Cable Length and Signal Reliability
DisplayPort supports longer cable lengths up to 15 meters while maintaining higher signal reliability compared to HDMI, which typically performs best under 10 meters. DisplayPort's advanced error correction and signal integrity features reduce data loss over extended distances, ensuring stable high-resolution video transmission. HDMI cables, though widely compatible, are more prone to signal degradation and interference beyond shorter lengths, affecting overall display quality.
Features: Audio Return Channel, Ethernet, and More
HDMI supports Audio Return Channel (ARC), allowing audio signals to travel both ways between devices, enhancing your home theater setup without extra cables. DisplayPort lacks ARC but offers higher bandwidth and supports multi-stream transport, enabling multiple monitors from a single port. HDMI includes an Ethernet channel for network connectivity, which DisplayPort does not, making HDMI more versatile for integrated systems.
Gaming Performance: HDMI vs DisplayPort
DisplayPort generally offers higher bandwidth than HDMI, enabling smoother gaming performance with higher refresh rates and resolutions, especially at 144Hz or above. HDMI 2.1 supports 4K at 120Hz and variable refresh rate technologies, making it suitable for gaming on consoles and some PCs. Your choice between HDMI and DisplayPort should depend on your monitor's specifications and the gaming hardware you use to maximize performance.
Future-Proofing: Latest Versions Compared
HDMI 2.1 supports resolutions up to 10K at 120Hz and features like eARC and Variable Refresh Rate (VRR), making it highly future-proof for entertainment systems and gaming consoles. DisplayPort 2.0 offers even greater bandwidth with up to 80 Gbps, enabling 16K resolution at 60Hz and enhanced multi-display setups, ideal for professional and high-end PC applications. Your choice depends on the devices you use and whether you prioritize ultra-high resolution displays or broad compatibility with consumer electronics.
Choosing the Right Connection for Your Needs
HDMI and DisplayPort each offer distinct advantages, with HDMI widely supported on TVs and consumer electronics, providing reliable audio and video transmission up to 8K resolution. DisplayPort excels in high-refresh-rate monitors and professional settings, supporting features like daisy-chaining multiple displays and adaptive sync technologies. Assess your device compatibility and performance requirements to select the connection that best suits your setup.
HDMI vs DisplayPort Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com