Lossless audio preserves the original sound quality by compressing files without any data loss, ensuring your music remains crisp and clear. Explore the differences between lossless and lossy audio formats to find out which option best suits your listening preferences.
Table of Comparison
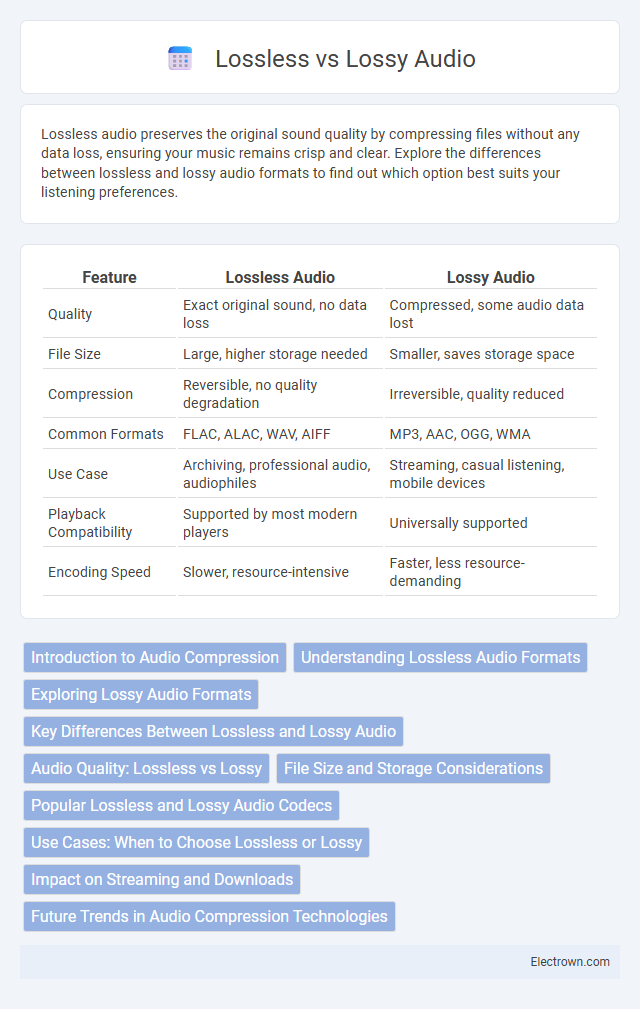
| Feature | Lossless Audio | Lossy Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | Exact original sound, no data loss | Compressed, some audio data lost |
| File Size | Large, higher storage needed | Smaller, saves storage space |
| Compression | Reversible, no quality degradation | Irreversible, quality reduced |
| Common Formats | FLAC, ALAC, WAV, AIFF | MP3, AAC, OGG, WMA |
| Use Case | Archiving, professional audio, audiophiles | Streaming, casual listening, mobile devices |
| Playback Compatibility | Supported by most modern players | Universally supported |
| Encoding Speed | Slower, resource-intensive | Faster, less resource-demanding |
Introduction to Audio Compression
Audio compression reduces file size by encoding sound data efficiently, with lossless formats like FLAC preserving original quality by perfectly reconstructing audio waveforms, while lossy formats like MP3 eliminate inaudible frequencies to achieve greater compression. Lossless compression maintains the full spectrum of audio details, making it ideal for audiophiles and archival purposes, whereas lossy compression balances sound quality and storage efficiency, widely used for streaming and portable devices. Understanding the trade-offs in bit rate, fidelity, and file size is essential when choosing between lossless and lossy audio formats.
Understanding Lossless Audio Formats
Lossless audio formats, such as FLAC, ALAC, and WAV, preserve the original sound quality by compressing audio data without any loss of information. These formats maintain every bit of the audio signal, ensuring playback identical to the source recording, making them ideal for audiophiles and professional applications. Unlike lossy formats, lossless files typically have larger file sizes but offer superior fidelity and accurate sound reproduction.
Exploring Lossy Audio Formats
Lossy audio formats such as MP3, AAC, and OGG compress audio data by permanently removing portions of sound deemed less audible, significantly reducing file size while maintaining acceptable sound quality for most listeners. These formats use perceptual coding techniques to eliminate redundant or less perceptible audio information, optimizing storage and streaming efficiency. Despite some quality degradation, lossy formats remain popular for music streaming services, portable devices, and online distribution due to their balance between compression rate and audio fidelity.
Key Differences Between Lossless and Lossy Audio
Lossless audio retains the original sound quality by preserving all audio data, providing bit-perfect reproduction ideal for audiophiles and professional use, whereas lossy audio compresses files by removing some audio information to reduce file size for easier storage and faster streaming, often resulting in lower fidelity. Lossless formats, such as FLAC, ALAC, and WAV, offer larger file sizes and higher bitrates compared to lossy formats like MP3, AAC, and OGG, which prioritize convenience and compatibility across devices. The key difference lies in fidelity versus file size, with lossless audio ensuring exact replication of the source, while lossy audio balances compression efficiency against sound quality loss.
Audio Quality: Lossless vs Lossy
Lossless audio formats, such as FLAC and ALAC, preserve 100% of the original sound data, delivering pristine audio quality identical to the source. Lossy formats like MP3 and AAC compress audio by removing some data, which may result in noticeable quality degradation, especially at lower bitrates. Your choice between lossless and lossy audio affects sound fidelity, with lossless ensuring crystal-clear playback and lossy prioritizing smaller file sizes and streaming efficiency.
File Size and Storage Considerations
Lossless audio files maintain original sound quality by preserving all data, resulting in significantly larger file sizes that demand more storage space on your devices. In contrast, lossy audio compresses files by removing some audio details, reducing file size and conserving storage but at the expense of audio fidelity. Choosing between lossless and lossy formats involves balancing your storage capacity with the desired sound quality for your listening experience.
Popular Lossless and Lossy Audio Codecs
Popular lossless audio codecs include FLAC, ALAC, and WAV, prized for preserving original sound quality without compression artifacts. Common lossy audio codecs such as MP3, AAC, and OGG achieve smaller file sizes by selectively removing audio data, which can slightly reduce sound fidelity. Audiophiles often prefer lossless formats for critical listening, while lossy codecs are favored for streaming and portable devices due to efficient bandwidth and storage usage.
Use Cases: When to Choose Lossless or Lossy
Lossless audio formats like FLAC or ALAC are ideal for audiophiles, professional musicians, and archivists who require the highest sound quality and detailed audio reproduction. Lossy formats such as MP3 or AAC are better suited for everyday listening, streaming, and portable devices where storage space and bandwidth are limited. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize audio fidelity or convenience and file size efficiency.
Impact on Streaming and Downloads
Lossless audio offers higher sound quality by preserving original data, resulting in larger file sizes that impact streaming bandwidth and download times. Lossy audio compresses files by removing some audio information, enabling faster streaming and lower storage use but with reduced fidelity. Your choice between lossless and lossy formats affects streaming performance, data consumption, and overall audio experience.
Future Trends in Audio Compression Technologies
Emerging audio compression technologies are advancing toward hybrid models that combine lossless and lossy algorithms to maximize sound quality while minimizing data size. Machine learning techniques are being integrated into codecs to dynamically adapt compression parameters based on audio content, ensuring efficient streaming without sacrificing fidelity. Your listening experience will benefit from these innovations as they enable ultra-high-definition audio across diverse platforms with reduced bandwidth requirements.
Lossless vs Lossy Audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com