A wired mouse offers consistent, lag-free performance ideal for tasks requiring precision, while a wireless mouse provides greater mobility and reduces cable clutter, enhancing your workspace flexibility. Explore the rest of the article to discover which mouse type best suits your needs and enhances your computing experience.
Table of Comparison
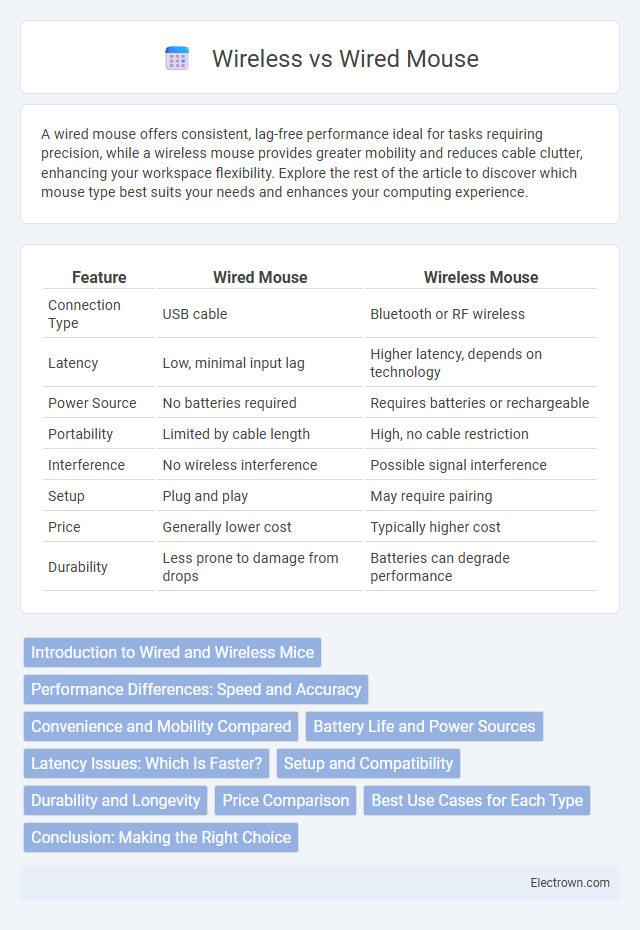
| Feature | Wired Mouse | Wireless Mouse |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | USB cable | Bluetooth or RF wireless |
| Latency | Low, minimal input lag | Higher latency, depends on technology |
| Power Source | No batteries required | Requires batteries or rechargeable |
| Portability | Limited by cable length | High, no cable restriction |
| Interference | No wireless interference | Possible signal interference |
| Setup | Plug and play | May require pairing |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
| Durability | Less prone to damage from drops | Batteries can degrade performance |
Introduction to Wired and Wireless Mice
Wired and wireless mice serve as essential computer peripherals, with wired mice connecting directly through USB ports to ensure consistent, lag-free performance ideal for precision tasks and gaming. Wireless mice use Bluetooth or RF technology, offering greater mobility and a clutter-free workspace, though they may require battery management and can occasionally face interference. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize stable connectivity and responsiveness or flexibility and ease of movement.
Performance Differences: Speed and Accuracy
Wired mice generally offer faster response times and greater accuracy due to their direct connection, minimizing input lag and signal interference. Wireless mice have improved significantly with technologies like Bluetooth 5.0 and proprietary RF, but may still experience slight latency or occasional delays depending on the environment. Your choice should prioritize performance needs, especially in gaming or precision tasks where every millisecond and pixel counts.
Convenience and Mobility Compared
A wireless mouse offers superior convenience and mobility by eliminating cable clutter and allowing you to use your device from a distance without being tethered. Wired mice provide consistent power without needing batteries but limit movement range and portability. For users prioritizing ease of use and mobility, a wireless mouse enhances flexibility in various work and travel environments.
Battery Life and Power Sources
Wired mice rely on a direct connection to the computer, eliminating the need for batteries and providing consistent power without interruptions. Wireless mice operate on rechargeable or replaceable batteries, with battery life varying from days to months depending on usage and device efficiency. Advanced models incorporate energy-saving technologies such as auto-sleep modes to extend battery life and reduce the frequency of recharging or battery replacement.
Latency Issues: Which Is Faster?
Wired mice generally exhibit lower latency compared to wireless mice due to direct USB connections minimizing input delay. High-end wireless mice use advanced Bluetooth or proprietary RF technologies to reduce lag, but wired options consistently outperform wireless in speed-critical gaming or professional tasks. Your choice should depend on whether ultra-low latency or freedom of movement is more important for your usage.
Setup and Compatibility
Wired mice offer straightforward setup by simply plugging into a USB port, ensuring immediate compatibility with most computers and operating systems without requiring additional software. Wireless mice provide greater flexibility and reduced desk clutter, often connecting via Bluetooth or a USB receiver, but may require battery management and driver installation depending on your device. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize hassle-free setup and universal compatibility or the convenience of cordless use.
Durability and Longevity
Wired mice generally offer greater durability and longevity due to their stable physical connection, which reduces the risk of signal interference and battery failure. The absence of internal batteries eliminates wear from charging cycles, contributing to a longer lifespan compared to wireless mice. High-quality wired models often feature reinforced cables and robust switches that withstand extensive use without degradation.
Price Comparison
Wired mice generally cost less than wireless models due to simpler technology and lower production expenses. Wireless mice often come at a premium price because of added components like batteries and Bluetooth or RF receivers. Your choice depends on budget priorities and the value you place on mobility and convenience.
Best Use Cases for Each Type
A wired mouse offers superior reliability and low latency, making it ideal for gaming, graphic design, and professional environments requiring precise control. Wireless mice provide greater mobility and convenience, perfect for casual users, travelers, and office workers seeking clutter-free desks. Choosing between wired and wireless depends on the balance of performance needs and mobility preferences.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Choosing between a wired and wireless mouse depends on specific user needs such as responsiveness, convenience, and portability. Wired mice offer consistent, lag-free performance ideal for gaming and precise work, while wireless mice provide freedom of movement and minimal desk clutter. Evaluating factors like battery life, latency, and usage environment ensures selecting the best mouse tailored to individual preferences and tasks.
Wired vs Wireless Mouse Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com