Level shifters enable communication between circuits operating at different voltage levels by safely translating signal voltages without altering power supply levels, while voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage regardless of input voltage fluctuations or load changes, ensuring stable power delivery. To understand how your electronics benefit from these components, explore the detailed differences that follow.
Table of Comparison
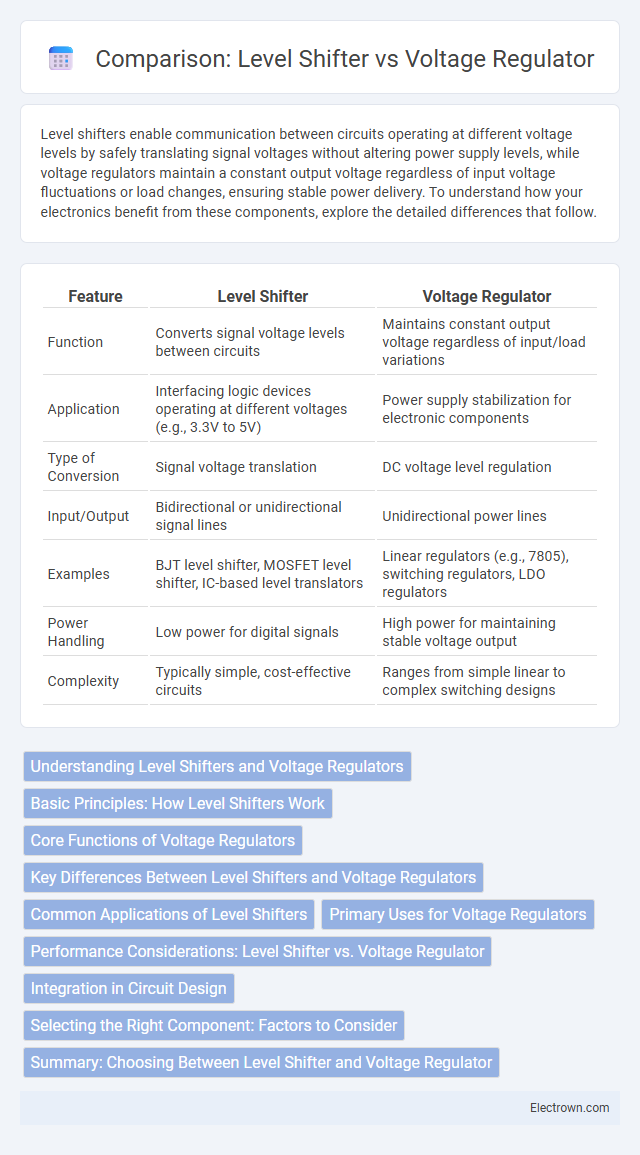
| Feature | Level Shifter | Voltage Regulator |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts signal voltage levels between circuits | Maintains constant output voltage regardless of input/load variations |
| Application | Interfacing logic devices operating at different voltages (e.g., 3.3V to 5V) | Power supply stabilization for electronic components |
| Type of Conversion | Signal voltage translation | DC voltage level regulation |
| Input/Output | Bidirectional or unidirectional signal lines | Unidirectional power lines |
| Examples | BJT level shifter, MOSFET level shifter, IC-based level translators | Linear regulators (e.g., 7805), switching regulators, LDO regulators |
| Power Handling | Low power for digital signals | High power for maintaining stable voltage output |
| Complexity | Typically simple, cost-effective circuits | Ranges from simple linear to complex switching designs |
Understanding Level Shifters and Voltage Regulators
Level shifters and voltage regulators both manage electrical signals, but they serve distinct functions; level shifters adjust signal voltages between different logic levels for communication between components, while voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage regardless of input fluctuations. Level shifters are crucial in interfacing devices operating at different voltage standards, such as translating 3.3V logic signals to 5V logic signals. Voltage regulators ensure stable power supply to sensitive electronics by converting variable input voltages to a fixed, reliable output voltage, preventing damage and ensuring optimal performance.
Basic Principles: How Level Shifters Work
Level shifters operate by translating signal voltages between different logic levels without altering the voltage supply, enabling communication between components with incompatible voltage requirements. They use devices such as MOSFETs or transistors to pass signals at the appropriate voltage level, ensuring data integrity across circuits running at different voltages. Understanding how level shifters work allows you to effectively manage interface compatibility in mixed-voltage systems without impacting power regulation.
Core Functions of Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage level despite variations in input voltage or load conditions, ensuring stable operation of electronic circuits. They protect sensitive components by preventing voltage spikes and fluctuations that can cause damage or malfunction. Unlike level shifters, which adjust signal voltage levels between different logic domains, voltage regulators primarily stabilize power supply voltages for reliable device performance.
Key Differences Between Level Shifters and Voltage Regulators
Level shifters and voltage regulators serve distinct roles in electronic circuits; level shifters translate signal voltages between different logic levels, while voltage regulators maintain a steady output voltage regardless of input fluctuations. Level shifters are crucial for interfacing components operating at different voltage domains, ensuring signal compatibility without altering power supply levels. Your choice depends on whether the goal is signal adaptation or power supply stability, as voltage regulators prioritize consistent voltage output and level shifters focus on signal integrity across varied voltage standards.
Common Applications of Level Shifters
Level shifters are primarily used in interfacing different voltage logic levels in digital circuits, such as connecting 3.3V microcontrollers with 5V sensors or communication modules. They are essential in I2C, SPI, and UART protocols for ensuring signal integrity across varying voltage domains. Unlike voltage regulators that provide a stable power supply voltage, level shifters maintain correct logic levels without altering the power rail voltage.
Primary Uses for Voltage Regulators
Voltage regulators primarily ensure a stable output voltage despite fluctuations in input voltage or load conditions, making them essential for protecting sensitive electronic components. They maintain consistent power supply levels in devices like computers, smartphones, and industrial equipment to prevent damage and ensure reliable operation. Your circuits rely on voltage regulators to deliver precise voltage for optimal performance and longevity.
Performance Considerations: Level Shifter vs. Voltage Regulator
Level shifters efficiently translate signal voltage levels between different digital components without regulating output voltage stability, making them ideal for communication between circuits operating at distinct logic levels. Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage regardless of input fluctuations or load changes, ensuring reliable power delivery but typically at the expense of conversion speed and signal integrity. Your choice depends on whether precise voltage regulation or fast, clean signal level translation is the priority in your electronic design.
Integration in Circuit Design
Level shifters enable seamless interfacing between components operating at different logic voltage levels, ensuring signal integrity without altering power supply lines. Voltage regulators maintain a stable output voltage regardless of input fluctuations, critical for powering sensitive circuit elements with consistent voltage. Integrating both components optimizes circuit reliability by managing voltage translation and power stability within mixed-voltage systems.
Selecting the Right Component: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right component between a level shifter and a voltage regulator depends on your circuit's voltage requirements and signal compatibility. Level shifters are ideal for translating logic signals between different voltage domains without altering power supply levels, whereas voltage regulators provide stable and consistent voltage output from a varying input source. Consider your device's power tolerance, signal integrity needs, and whether you require voltage conversion for logic signals or power stabilization when making your choice.
Summary: Choosing Between Level Shifter and Voltage Regulator
Choosing between a level shifter and a voltage regulator depends on your circuit's requirements for signal compatibility versus power supply stability. Level shifters are essential for translating signal voltages between devices operating at different logic levels, ensuring accurate communication without altering the power supply. Voltage regulators maintain a constant output voltage regardless of input fluctuations, protecting sensitive components and stabilizing power delivery in your electronic system.
Level shifter vs voltage regulator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com