An unclocked latch continuously changes its output based on input signals without waiting for a clock edge, leading to potential timing issues in synchronous circuits; a clocked flip-flop updates its state only at specific clock transitions, ensuring precise timing and synchronization. Explore the detailed differences to understand how each affects your digital design and timing control.
Table of Comparison
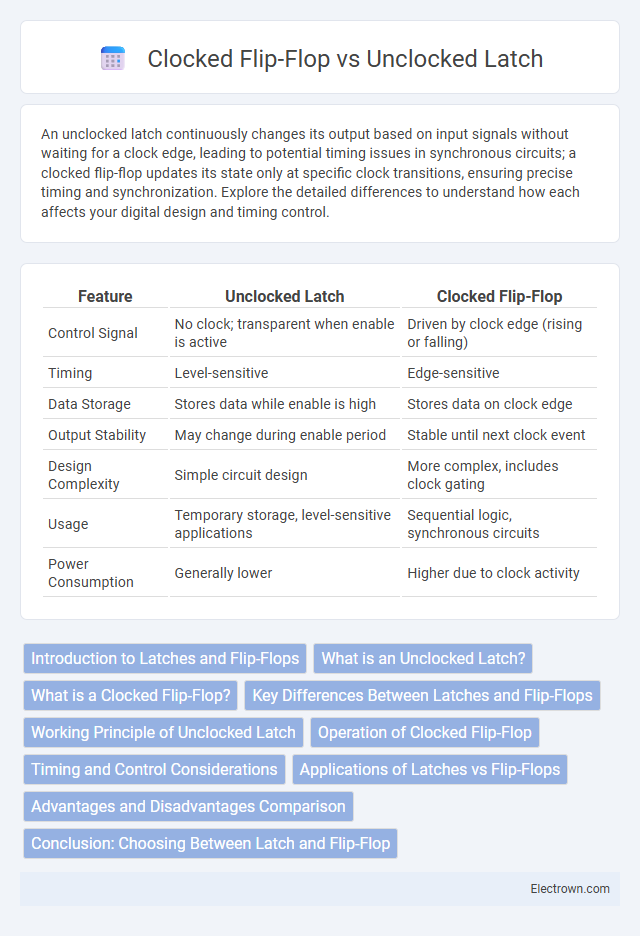
| Feature | Unclocked Latch | Clocked Flip-Flop |
|---|---|---|
| Control Signal | No clock; transparent when enable is active | Driven by clock edge (rising or falling) |
| Timing | Level-sensitive | Edge-sensitive |
| Data Storage | Stores data while enable is high | Stores data on clock edge |
| Output Stability | May change during enable period | Stable until next clock event |
| Design Complexity | Simple circuit design | More complex, includes clock gating |
| Usage | Temporary storage, level-sensitive applications | Sequential logic, synchronous circuits |
| Power Consumption | Generally lower | Higher due to clock activity |
Introduction to Latches and Flip-Flops
Latches and flip-flops are fundamental building blocks in digital electronics used for storing binary data. An unclocked latch operates as a level-sensitive device, continuously responding to input changes while the enable signal is active, making it suitable for asynchronous circuits. In contrast, a clocked flip-flop is edge-triggered, capturing data only at specific clock transitions, providing synchronous control essential for reliable sequential logic design.
What is an Unclocked Latch?
An unclocked latch is a basic memory device that continuously monitors its input signals and changes its output immediately when the inputs change, without waiting for a clock pulse. Unlike clocked flip-flops, which rely on a clock signal to control data storage timing, unclocked latches are level-sensitive and can lead to timing uncertainties in complex circuits. You should use unclocked latches in applications where simple, fast state storage is needed without strict timing constraints.
What is a Clocked Flip-Flop?
A clocked flip-flop is a digital memory circuit that stores binary data based on the timing signal from a clock input, ensuring data changes occur only at specific clock edges. It contrasts with unclocked latches, which are level-triggered and can change outputs anytime the enable signal is active. Clocked flip-flops provide synchronized and stable state changes essential for reliable sequential logic in processors and digital systems.
Key Differences Between Latches and Flip-Flops
Unclocked latches are level-sensitive devices that continuously respond to input changes when enabled, while clocked flip-flops are edge-triggered and update output only on specific clock transitions, ensuring precise timing control. Latches are simpler and faster but susceptible to glitches due to their transparency during the enable signal, whereas flip-flops provide better noise immunity and synchronization in sequential circuits. These fundamental differences impact their usage in digital design, with latches favoring asynchronous applications and flip-flops preferred in synchronous systems.
Working Principle of Unclocked Latch
An unclocked latch operates as a level-sensitive device that changes its output state based on the input signals as long as the enable signal is active. It continuously monitors the inputs, allowing data to pass through and update the output directly without waiting for a clock edge. This characteristic makes unclocked latches suitable for transparent data storage but prone to glitches in synchronous digital circuits.
Operation of Clocked Flip-Flop
Clocked flip-flops operate by capturing and storing data on the triggering edge of a clock signal, ensuring synchronization in digital circuits. Their edge-triggered mechanism allows them to change states only at specific clock intervals, providing precise timing control for sequential logic. This characteristic differentiates them from unclocked latches, which are level-sensitive and continuously transparent to input changes.
Timing and Control Considerations
Unclocked latches are transparent devices that change output immediately with input variations, making their timing highly sensitive to input signal glitches and requiring careful control to avoid race conditions. Clocked flip-flops capture input only on defined clock edges, providing precise timing control and synchronization in digital circuits, which reduces the risk of metastability and timing hazards. Your choice between the two depends on the desired timing accuracy and circuit complexity, with flip-flops favored for synchronous designs demanding strict timing constraints.
Applications of Latches vs Flip-Flops
Latches are commonly used in level-sensitive applications such as data storage in asynchronous circuits and temporary data holding within combinational logic, where simplicity and speed are crucial. Flip-flops, being edge-triggered devices, are preferred in synchronous systems including counters, shift registers, and memory elements, ensuring precise timing control and data synchronization at clock edges. Your choice between latches and flip-flops depends on whether the application demands level-sensitive operation or strict timing alignment with clock signals.
Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison
Unclocked latches offer simpler design and faster response times due to their level-sensitive operation, making them suitable for asynchronous circuits but suffer from transparency issues and unpredictable timing. Clocked flip-flops provide precise edge-triggered synchronization ideal for synchronous systems, reducing timing hazards at the cost of increased complexity and power consumption. Choosing between the two depends on the application's timing requirements, with flip-flops favored for clocked environments and latches for speed-critical or low-latency logic.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Latch and Flip-Flop
Choosing between unclocked latches and clocked flip-flops depends on timing requirements and design complexity within digital circuits. Unclocked latches offer transparency and simpler design, ideal for asynchronous operations but prone to timing issues such as glitches. Clocked flip-flops provide synchronized data storage with edge-triggered operation, making them preferable for synchronous systems requiring precise timing control and reduced race conditions.
Unclocked latch vs clocked flip-flop Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com