Odd parity ensures the total number of 1s in a binary sequence is odd, while even parity guarantees it is even, both used for error detection in data transmission. Explore the rest of this article to understand how your system can benefit from choosing the right parity type.
Table of Comparison
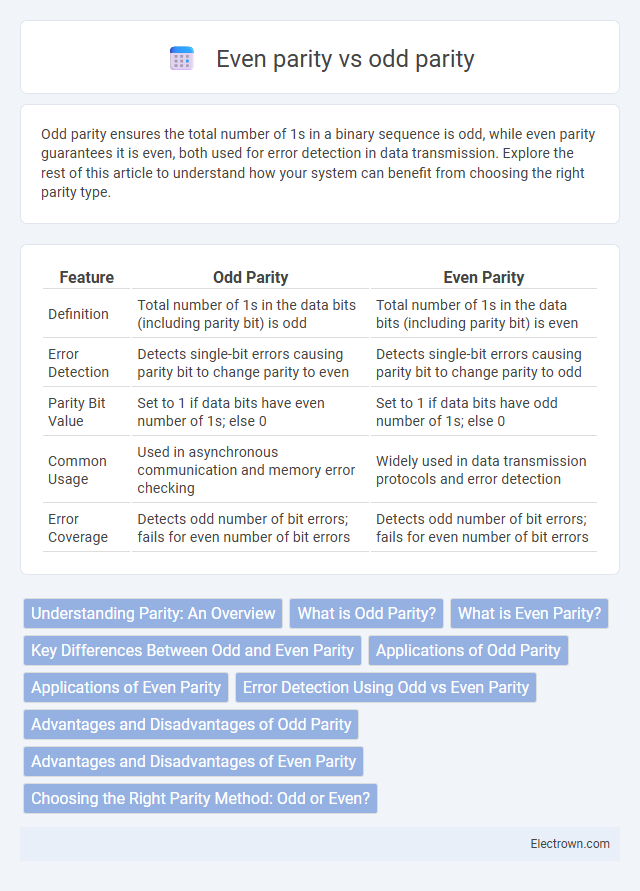
| Feature | Odd Parity | Even Parity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total number of 1s in the data bits (including parity bit) is odd | Total number of 1s in the data bits (including parity bit) is even |
| Error Detection | Detects single-bit errors causing parity bit to change parity to even | Detects single-bit errors causing parity bit to change parity to odd |
| Parity Bit Value | Set to 1 if data bits have even number of 1s; else 0 | Set to 1 if data bits have odd number of 1s; else 0 |
| Common Usage | Used in asynchronous communication and memory error checking | Widely used in data transmission protocols and error detection |
| Error Coverage | Detects odd number of bit errors; fails for even number of bit errors | Detects odd number of bit errors; fails for even number of bit errors |
Understanding Parity: An Overview
Parity is a fundamental error-detection technique used in data transmission, involving the addition of a parity bit to a set of binary data. Odd parity ensures the total number of 1s in the data, including the parity bit, is odd, while even parity guarantees an even number of 1s. This simple method helps detect single-bit errors by verifying parity consistency during data exchange.
What is Odd Parity?
Odd parity is a method of error detection in digital communication where the total number of 1s in a binary sequence is adjusted to be odd. This ensures that if a single bit error occurs during transmission, the parity check will detect the discrepancy. Using odd parity helps your system identify corrupted data by maintaining an odd count of bits with the value 1.
What is Even Parity?
Even parity is an error detection method in digital communication where the total number of 1s in a binary data set is made even by adding a parity bit. This parity bit ensures that data integrity is maintained during transmission, helping to identify single-bit errors. Your system uses even parity to verify that the received data matches the expected binary pattern with an even count of 1s.
Key Differences Between Odd and Even Parity
Odd parity ensures the total number of 1s in a binary sequence is odd by adding a parity bit, while even parity makes the total number of 1s even through its parity bit. Error detection relies on these parity bits, where odd parity flags an error if the count of 1s is even, and even parity flags an error if the count is odd. The choice between odd and even parity affects system compatibility and error detection mechanisms in communication protocols and memory storage.
Applications of Odd Parity
Odd parity finds crucial applications in error detection within digital communication systems, where a parity bit is added to ensure the total number of ones in a data unit is odd. This method is commonly employed in computer memory systems, such as ECC RAM, to identify single-bit errors and enhance data integrity. Your systems benefit from odd parity's simplicity and effectiveness in detecting transmission errors without adding significant overhead.
Applications of Even Parity
Even parity is widely utilized in error detection within digital communication systems, ensuring data integrity by making the total number of 1-bits even. It is commonly applied in computer memory storage, serial data transmission, and network communication protocols to identify single-bit errors efficiently. Your data's reliability is enhanced by implementing even parity checks, which provide a simple yet effective means to detect errors during data transfer.
Error Detection Using Odd vs Even Parity
Odd parity and even parity are fundamental methods for error detection in digital communication. Odd parity ensures that the total number of 1s in a data set is odd, while even parity guarantees an even count of 1s, allowing systems to identify single-bit errors efficiently. The choice between odd and even parity depends on system design, but both methods improve data integrity by enabling detection of single-bit transmission errors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Odd Parity
Odd parity offers the advantage of simple error detection by ensuring that the total number of 1s in the data plus parity bit is odd, making it easy to identify single-bit errors. Its drawback is limited error detection capability, as it cannot reliably detect errors involving an even number of flipped bits. When used in your system, odd parity provides a straightforward, low-overhead method for basic error checking but may require additional error-handling mechanisms for robustness.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Even Parity
Even parity offers the advantage of simple error detection by ensuring the total number of 1-bits in a data set is always even, making it easy to identify single-bit errors. Its disadvantage lies in its inability to detect errors when an even number of bits are corrupted, limiting error detection reliability in noisy communication channels. Despite this limitation, even parity is widely used in systems requiring minimal hardware complexity and moderate error checking.
Choosing the Right Parity Method: Odd or Even?
Choosing the right parity method depends on the error detection requirements of your communication system and the type of data being transmitted. Odd parity sets the parity bit to ensure the total number of 1s is odd, which can effectively detect single-bit errors by flipping the parity when necessary. Even parity, on the other hand, ensures the total number of 1s is even, offering a simple yet reliable way to maintain data integrity, so selecting between odd or even parity should be based on the expected error patterns and compatibility with your device protocols.
Odd parity vs even parity Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com