ARM Cortex-M processors deliver energy-efficient performance optimized for microcontroller applications in embedded systems, while ARM Cortex-A processors offer higher computing power tailored for complex operating systems and multimedia tasks. Explore the rest of the article to understand which ARM architecture best suits your project requirements.
Table of Comparison
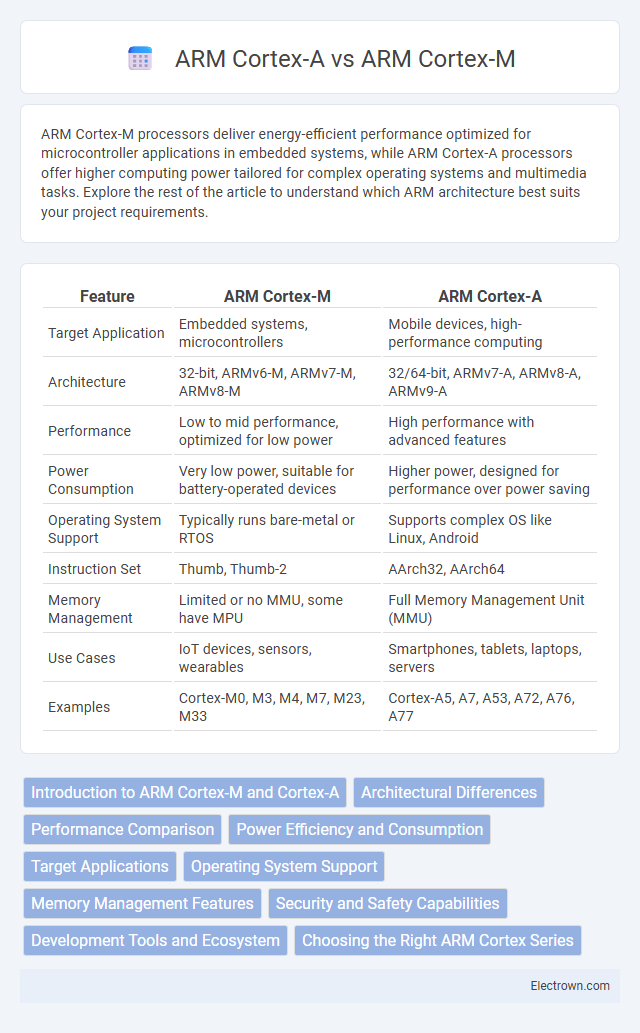
| Feature | ARM Cortex-M | ARM Cortex-A |
|---|---|---|
| Target Application | Embedded systems, microcontrollers | Mobile devices, high-performance computing |
| Architecture | 32-bit, ARMv6-M, ARMv7-M, ARMv8-M | 32/64-bit, ARMv7-A, ARMv8-A, ARMv9-A |
| Performance | Low to mid performance, optimized for low power | High performance with advanced features |
| Power Consumption | Very low power, suitable for battery-operated devices | Higher power, designed for performance over power saving |
| Operating System Support | Typically runs bare-metal or RTOS | Supports complex OS like Linux, Android |
| Instruction Set | Thumb, Thumb-2 | AArch32, AArch64 |
| Memory Management | Limited or no MMU, some have MPU | Full Memory Management Unit (MMU) |
| Use Cases | IoT devices, sensors, wearables | Smartphones, tablets, laptops, servers |
| Examples | Cortex-M0, M3, M4, M7, M23, M33 | Cortex-A5, A7, A53, A72, A76, A77 |
Introduction to ARM Cortex-M and Cortex-A
ARM Cortex-M processors are designed for low-power, real-time embedded applications, offering efficient performance in microcontrollers commonly used in IoT devices and automotive systems. ARM Cortex-A processors target high-performance applications such as smartphones, tablets, and advanced computing, featuring complex architectures optimized for running operating systems and multimedia processing. Both architectures leverage ARM's energy-efficient design principles but differ significantly in processing power, complexity, and typical use cases.
Architectural Differences
ARM Cortex-M processors feature a simpler, energy-efficient architecture designed for real-time embedded applications with a focus on deterministic interrupt handling and low latency. ARM Cortex-A processors incorporate a more complex, high-performance architecture with advanced features like out-of-order execution, caches, and Memory Management Unit (MMU) support for running rich operating systems and multitasking environments. Your choice depends on whether your application prioritizes real-time responsiveness and low power consumption (Cortex-M) or requires high computational power and sophisticated OS capabilities (Cortex-A).
Performance Comparison
ARM Cortex-M processors excel in low-power, real-time embedded applications with efficient interrupt handling and deterministic performance, typically running at lower clock speeds up to a few hundred MHz. ARM Cortex-A processors deliver higher performance with advanced features like out-of-order execution and higher clock speeds, often exceeding 2 GHz, targeting complex operating systems and multimedia processing. Your choice depends on the required balance between power efficiency and computational performance for specific embedded or application processor needs.
Power Efficiency and Consumption
ARM Cortex-M processors deliver superior power efficiency and low power consumption, making them ideal for energy-constrained applications like IoT devices, wearables, and embedded systems. In contrast, ARM Cortex-A cores prioritize higher performance with advanced processing capabilities, resulting in increased power consumption suited for smartphones, tablets, and consumer electronics. The Cortex-M series' architecture emphasizes minimal energy usage through simplified pipelines and clock gating, whereas Cortex-A employs out-of-order execution and higher clock speeds that demand greater power resources.
Target Applications
ARM Cortex-M processors are designed primarily for microcontroller and embedded system applications, excelling in low-power, real-time control environments such as IoT devices, automotive sensors, and industrial automation. In contrast, ARM Cortex-A processors target high-performance applications including smartphones, tablets, and consumer electronics that require advanced operating systems and multimedia capabilities. Your choice between Cortex-M and Cortex-A depends on whether your application demands energy-efficient, real-time processing or complex computing power and rich user interfaces.
Operating System Support
ARM Cortex-M processors are designed primarily for real-time embedded systems and typically run lightweight operating systems such as FreeRTOS or no OS at all, offering minimal support for complex OS features. ARM Cortex-A processors support full-featured operating systems like Linux, Android, and Windows, enabling advanced multitasking, user interfaces, and enhanced security. Your choice between Cortex-M and Cortex-A should consider the level of OS complexity and performance your application requires.
Memory Management Features
ARM Cortex-M processors utilize a simplified memory protection unit (MPU) for basic memory protection and partitioning, optimizing real-time embedded applications with limited memory resources. ARM Cortex-A processors incorporate advanced memory management units (MMUs) supporting full virtual memory, enabling complex operating systems and sophisticated memory virtualization. The Cortex-A's MMU facilitates efficient multitasking and memory isolation, essential for higher-level applications and security.
Security and Safety Capabilities
ARM Cortex-M processors offer built-in security features like TrustZone for Cortex-M, enabling hardware isolation of secure and non-secure code to protect sensitive data in embedded applications. Cortex-A processors provide more advanced security mechanisms, including ARM TrustZone technology with a richer execution environment, supporting complex operating systems and secure boot processes. Your choice between Cortex-M and Cortex-A depends on the required balance of safety-critical real-time capabilities versus robust security for high-performance applications.
Development Tools and Ecosystem
ARM Cortex-M processors benefit from a comprehensive ecosystem with development tools like Keil MDK, IAR Embedded Workbench, and CMSIS support, optimizing real-time embedded applications. ARM Cortex-A processors offer a robust ecosystem featuring professional tools such as ARM DS-5, LLVM, and extensive Linux support, catering to high-performance computing and multimedia applications. Your choice between these architectures depends on the development tools and ecosystem that best match your application's complexity and performance needs.
Choosing the Right ARM Cortex Series
Choosing the right ARM Cortex series depends on your application's requirements for performance and power efficiency. ARM Cortex-M processors are optimized for low-power, real-time embedded systems with deterministic interrupt handling, making them ideal for microcontroller-based applications. ARM Cortex-A processors deliver high-performance computing with rich operating system support, suitable for complex applications like smartphones and tablets where advanced multimedia processing is necessary.
ARM Cortex-M vs ARM Cortex-A Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com