Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume and better voltage stability, making them suitable for embedded systems requiring compact, reliable power supply filtering. Explore how your design choices can benefit from the specific characteristics of tantalum versus ceramic capacitors throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
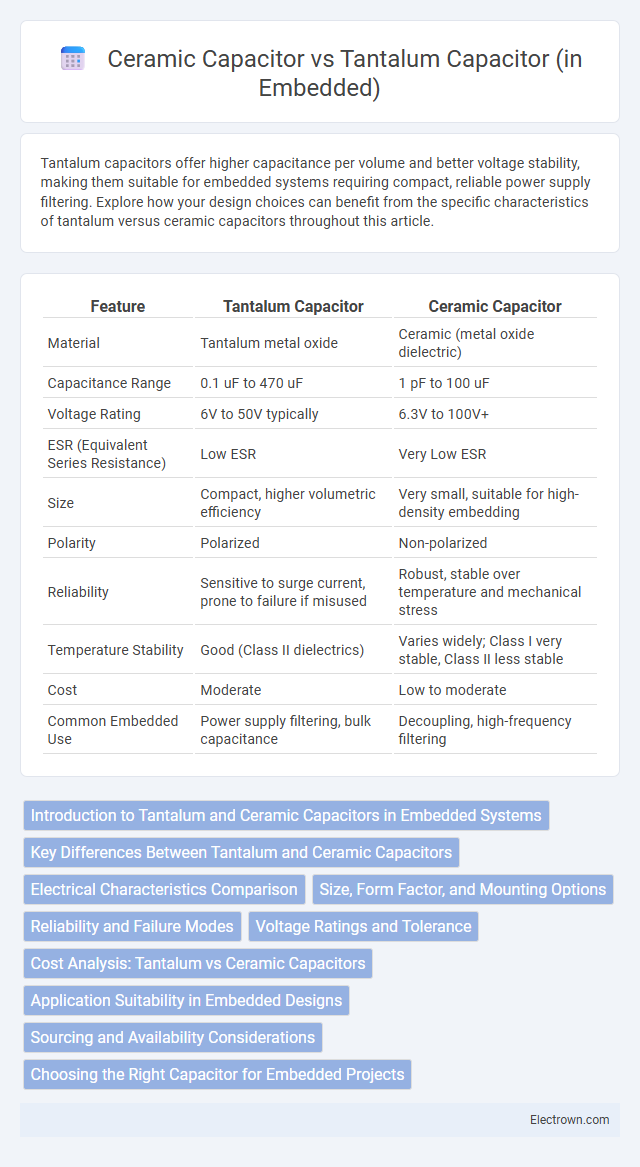
| Feature | Tantalum Capacitor | Ceramic Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Tantalum metal oxide | Ceramic (metal oxide dielectric) |
| Capacitance Range | 0.1 uF to 470 uF | 1 pF to 100 uF |
| Voltage Rating | 6V to 50V typically | 6.3V to 100V+ |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | Low ESR | Very Low ESR |
| Size | Compact, higher volumetric efficiency | Very small, suitable for high-density embedding |
| Polarity | Polarized | Non-polarized |
| Reliability | Sensitive to surge current, prone to failure if misused | Robust, stable over temperature and mechanical stress |
| Temperature Stability | Good (Class II dielectrics) | Varies widely; Class I very stable, Class II less stable |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Common Embedded Use | Power supply filtering, bulk capacitance | Decoupling, high-frequency filtering |
Introduction to Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors in Embedded Systems
Tantalum and ceramic capacitors serve crucial roles in embedded systems, each with distinct characteristics tailored to specific applications. Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and stable electrical performance, making them ideal for filtering and smoothing power supply lines in space-constrained environments. Ceramic capacitors provide low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and excellent high-frequency performance, benefiting decoupling and noise suppression tasks in embedded circuits.
Key Differences Between Tantalum and Ceramic Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance per volume and better stability at low frequencies compared to ceramic capacitors, making them ideal for power supply filtering in embedded systems. Ceramic capacitors provide lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and superior high-frequency characteristics, which enhance performance in high-speed signal decoupling and noise reduction. Your choice between tantalum and ceramic capacitors depends on the specific application's requirements for capacitance, frequency response, and reliability.
Electrical Characteristics Comparison
Tantalum capacitors exhibit higher capacitance per volume and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) compared to ceramic capacitors, making them suitable for stable voltage supply and filtering in embedded systems. Ceramic capacitors offer superior high-frequency performance and lower dielectric absorption, which enhances signal integrity in high-speed applications. Your choice depends on the specific electrical characteristics required, such as capacitance stability, ESR, and frequency response in your embedded design.
Size, Form Factor, and Mounting Options
Tantalum capacitors typically offer a smaller size and higher capacitance per volume compared to ceramic capacitors, making them ideal for embedded systems where space is limited. Ceramic capacitors come in a variety of form factors, including small, chip-scale sizes suitable for surface-mount technology (SMT), providing flexibility in layout design. Your choice depends on mounting options, with tantalum capacitors available in both through-hole and surface-mount packages, while ceramic capacitors predominantly support surface-mount mounting for compact, automated assembly.
Reliability and Failure Modes
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance values and better volumetric efficiency but are more susceptible to catastrophic failure due to dielectric breakdown and electrolyte degradation, especially under voltage spikes or surge conditions. Ceramic capacitors exhibit superior reliability with stable performance over a wide temperature range and minimal aging effects; however, they can suffer from microcracking and capacitance loss caused by mechanical stress or high voltage variation. Embedded system designers prioritize ceramic capacitors for long-term stability and robust failure tolerance, whereas tantalum capacitors require careful derating and protection circuits to mitigate failure risks.
Voltage Ratings and Tolerance
Tantalum capacitors typically offer higher capacitance per volume with voltage ratings commonly ranging from 4V to 50V, while ceramic capacitors can handle a broader spectrum from 6.3V up to 1kV or more, making them suitable for high-voltage applications in embedded systems. Tantalum capacitors generally have tighter tolerance levels, often around +-10%, providing stable performance in precision circuits, whereas ceramic capacitors exhibit wider tolerance variations, commonly between +-5% and +-20%, depending on their class (Class 1 or Class 2). Your choice between these two should consider voltage requirements and tolerance needs to ensure reliable operation in embedded design environments.
Cost Analysis: Tantalum vs Ceramic Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors typically have a higher cost per unit compared to ceramic capacitors due to their complex manufacturing process and superior volumetric efficiency. Ceramic capacitors offer a more cost-effective solution, especially in high-volume embedded applications, benefiting from widespread availability and simpler production. When evaluating cost analysis, ceramic capacitors provide lower overall expenditure, while tantalum capacitors may justify their premium price through enhanced performance in size-critical or high-reliability embedded systems.
Application Suitability in Embedded Designs
Tantalum capacitors provide stable capacitance and low equivalent series resistance (ESR), making them ideal for power supply filtering and decoupling in embedded designs where size and performance are critical. Ceramic capacitors excel in high-frequency applications due to their low loss and high reliability, often used for bypass and noise suppression on embedded circuit boards. Choosing between tantalum and ceramic capacitors depends on your embedded application's specific demands for capacitance value, voltage rating, and thermal stability.
Sourcing and Availability Considerations
Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance in compact sizes but face frequent supply chain constraints due to limited raw material sources and geopolitical risks associated with tantalum ore mining. Ceramic capacitors, benefiting from widespread raw materials like titanium and aluminum, generally provide greater availability and cost stability, making them easier to source for embedded systems manufacturing. Your component selection should factor in lead times and potential shortages to ensure reliable production schedules.
Choosing the Right Capacitor for Embedded Projects
Tantalum and ceramic capacitors each offer distinct advantages for embedded projects, with tantalum capacitors providing stable capacitance and high volumetric efficiency, ideal for applications requiring long-term reliability and low ESR. Ceramic capacitors excel in high-frequency performance and lower cost, making them suitable for decoupling and filtering in compact circuits. Understanding the electrical demands of your embedded system helps you choose the right capacitor to optimize performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Tantalum vs ceramic capacitor (in embedded) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com