Global interrupts affect the entire system, temporarily halting all processes to handle urgent tasks, while local interrupts target specific devices or processors without disturbing overall system operations. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these interrupt types impact your system's performance and responsiveness.
Table of Comparison
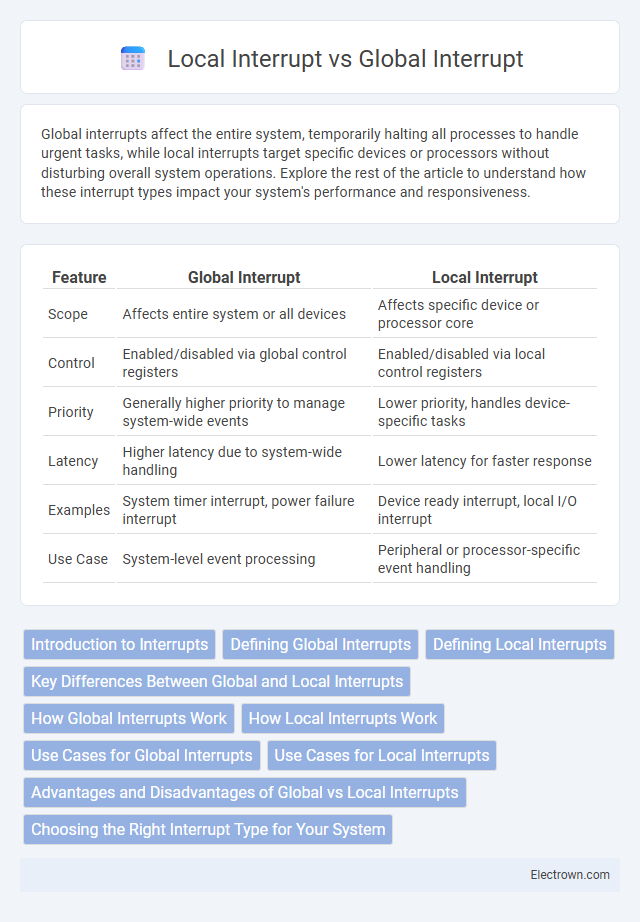
| Feature | Global Interrupt | Local Interrupt |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Affects entire system or all devices | Affects specific device or processor core |
| Control | Enabled/disabled via global control registers | Enabled/disabled via local control registers |
| Priority | Generally higher priority to manage system-wide events | Lower priority, handles device-specific tasks |
| Latency | Higher latency due to system-wide handling | Lower latency for faster response |
| Examples | System timer interrupt, power failure interrupt | Device ready interrupt, local I/O interrupt |
| Use Case | System-level event processing | Peripheral or processor-specific event handling |
Introduction to Interrupts
Interrupts are signals that temporarily halt the CPU's current operations to address urgent tasks, ensuring efficient multitasking. A global interrupt affects the entire system, pausing all processes, while a local interrupt targets specific components or peripherals. Understanding the difference helps you optimize system responsiveness and resource management in embedded systems or operating systems.
Defining Global Interrupts
Global interrupts are system-wide signals that temporarily halt the processor's current execution to address high-priority events, affecting all components of the system. They override local interrupts by disabling or preempting localized interrupt responses to ensure critical tasks receive immediate attention. These interrupts are crucial in embedded systems and operating system kernels for managing urgent hardware or software conditions across the entire platform.
Defining Local Interrupts
Local interrupts are specific to individual processors or device components, allowing them to handle events or signals independently from the system-wide operations. These interrupts enable targeted intervention within a single core or peripheral without affecting the entire system's interrupt handling. Understanding Local Interrupts helps you optimize hardware performance and responsiveness at a granular level.
Key Differences Between Global and Local Interrupts
Global interrupts affect the entire system by enabling or disabling all interrupt requests simultaneously, while local interrupts control specific interrupt lines or devices independently. Your system's responsiveness improves with local interrupts by allowing selective handling of critical tasks without impacting overall interrupt management. Global interrupts provide broad control, which simplifies interrupt handling but may increase latency for high-priority events managed by local interrupts.
How Global Interrupts Work
Global interrupts enable the CPU to temporarily halt its current execution to address high-priority signals from any peripheral device, ensuring efficient system responsiveness. When a global interrupt is triggered, the processor saves its current state and jumps to a predefined interrupt service routine, allowing you to manage critical tasks without delay. This mechanism overrides local interrupt masking, providing a universal control that ensures urgent events are always handled promptly.
How Local Interrupts Work
Local interrupts operate within a specific processor core or module, allowing immediate response to hardware or software events without involving the entire system. They enable low-latency handling by directly signaling the local interrupt controller, which prioritizes and manages interrupt requests for that particular core. This targeted mechanism reduces overhead and improves real-time performance in multicore processing environments.
Use Cases for Global Interrupts
Global interrupts are essential for handling critical system-wide events such as power failures, system resets, and emergency shutdowns, ensuring immediate processor attention regardless of the current task. They are commonly used in embedded systems and real-time operating environments where rapid response to overarching conditions is crucial to maintain system stability. Understanding your system's requirements helps determine when to prioritize global interrupts for effective event management.
Use Cases for Local Interrupts
Local interrupts are essential in real-time systems where immediate response to hardware events, such as input/output device signals or processor timers, is critical to performance and reliability. These interrupts are used to handle specific processor core functions, enabling quick context switching and efficient management of time-sensitive tasks like sensor data acquisition or communication protocol handling. Your system benefits from local interrupts by reducing latency and ensuring precise control over individual processor operations without affecting global system processes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Global vs Local Interrupts
Global interrupts enable efficient system-wide event handling by allowing a single interrupt signal to pause all processes, which simplifies control but can lead to higher latency for critical tasks. Local interrupts offer finer granularity by targeting specific components or processors, reducing unnecessary interrupt handling and improving response time, though they add complexity to system design and may require more overhead to manage. Balancing global and local interrupts is essential for optimizing performance, as global interrupts provide broad control while local interrupts enhance precision and efficiency in multitasking environments.
Choosing the Right Interrupt Type for Your System
Choosing the right interrupt type for your system depends on application requirements and hardware architecture. Global interrupts are ideal for handling critical, system-wide events that require immediate attention, while local interrupts optimize processor efficiency by managing tasks specific to individual cores or modules. Evaluating system complexity, latency sensitivity, and resource allocation ensures optimal interrupt management and improved overall performance.
Global Interrupt vs Local Interrupt Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com