A Memory Protection Unit (MPU) safeguards specific memory regions by enforcing access permissions to prevent unauthorized or accidental modifications, whereas a Memory Management Unit (MMU) provides advanced capabilities like virtual memory, address translation, and paging for efficient and flexible memory allocation. Discover how understanding the differences between MPU and MMU can help optimize your system's memory management by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
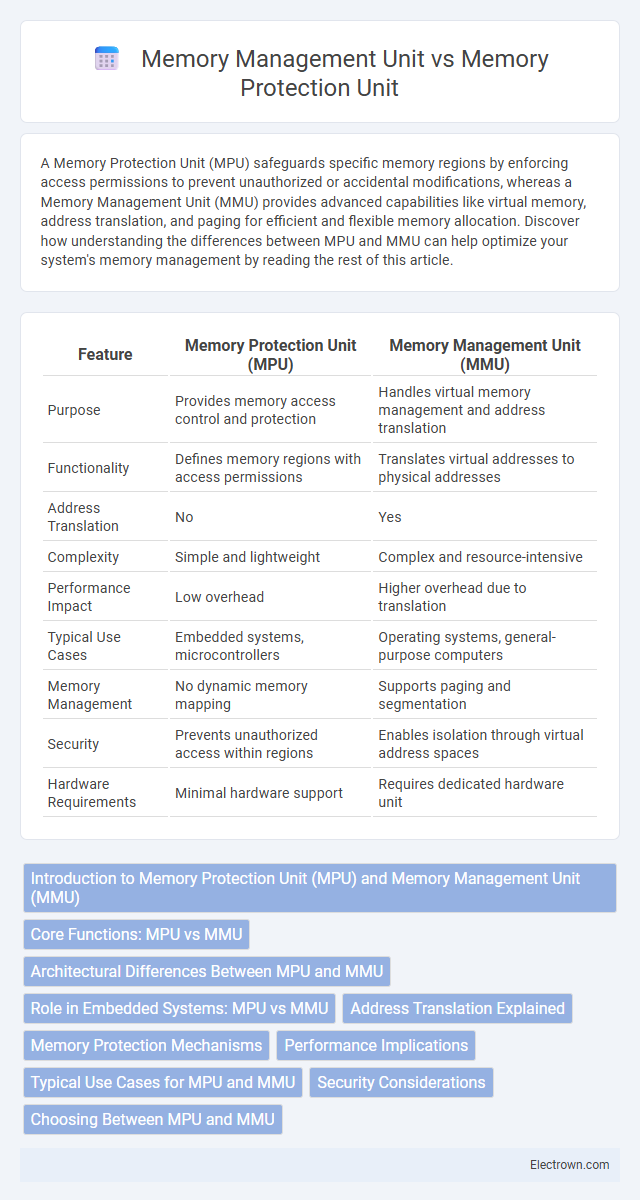
| Feature | Memory Protection Unit (MPU) | Memory Management Unit (MMU) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Provides memory access control and protection | Handles virtual memory management and address translation |
| Functionality | Defines memory regions with access permissions | Translates virtual addresses to physical addresses |
| Address Translation | No | Yes |
| Complexity | Simple and lightweight | Complex and resource-intensive |
| Performance Impact | Low overhead | Higher overhead due to translation |
| Typical Use Cases | Embedded systems, microcontrollers | Operating systems, general-purpose computers |
| Memory Management | No dynamic memory mapping | Supports paging and segmentation |
| Security | Prevents unauthorized access within regions | Enables isolation through virtual address spaces |
| Hardware Requirements | Minimal hardware support | Requires dedicated hardware unit |
Introduction to Memory Protection Unit (MPU) and Memory Management Unit (MMU)
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) is a hardware component that enforces access permissions and memory regions in embedded systems, ensuring real-time protection without complex address translation. The Memory Management Unit (MMU) handles virtual memory management, translating virtual addresses to physical ones and supporting features like paging and segmentation found in general-purpose operating systems. MPUs offer simpler, deterministic protection ideal for microcontrollers, while MMUs provide advanced memory virtualization essential for multitasking and isolation in modern computing environments.
Core Functions: MPU vs MMU
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) primarily enforces access permissions and protection for specific memory regions, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring system stability in real-time and embedded systems. The Memory Management Unit (MMU) provides advanced features like virtual memory management, address translation, and paging, allowing complex operating systems to efficiently allocate and protect process memory spaces. Understanding your system's core function needs is crucial when choosing between an MPU for lightweight protection or an MMU for sophisticated memory management.
Architectural Differences Between MPU and MMU
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) is designed for simple, real-time embedded systems, offering fixed regions with access control but lacking virtual memory support. The Memory Management Unit (MMU), found in complex operating systems, provides full address translation, enabling virtual memory, paging, and advanced protection mechanisms. Your choice depends on application complexity, with MPU providing lightweight protection and MMU supporting sophisticated memory management.
Role in Embedded Systems: MPU vs MMU
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) in embedded systems enforces access control and memory region permissions, ensuring real-time performance with low-latency protection ideal for resource-constrained environments. The Memory Management Unit (MMU) provides complex virtual memory capabilities such as paging and address translation, supporting advanced operating systems and multitasking in more powerful embedded processors. Choosing between MPU and MMU depends on your system's complexity, with MPU favored for safety-critical applications and MMU required for full-fledged OS tasks.
Address Translation Explained
A Memory Management Unit (MMU) performs comprehensive address translation by converting virtual addresses into physical addresses, enabling efficient use of memory and support for virtual memory systems. In contrast, a Memory Protection Unit (MPU) does not perform address translation but enforces access permissions on physical memory regions to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access. MMUs are critical for systems requiring complex memory handling and multitasking, while MPUs are used in simpler embedded systems where memory protection without translation suffices.
Memory Protection Mechanisms
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) provides memory protection mechanisms by defining access permissions and isolating memory regions at a fine granularity, preventing unauthorized access and enhancing system security. In contrast, the Memory Management Unit (MMU) offers more advanced memory protection by implementing virtual memory management with features such as address translation, page tables, and hardware-enforced access controls. Both MPUs and MMUs protect memory integrity, but MMUs enable sophisticated protection schemes including process isolation and demand paging, critical for modern multitasking operating systems.
Performance Implications
Memory Protection Units (MPUs) offer low-overhead, deterministic performance by restricting access permissions without complex address translation, making them ideal for real-time systems. Memory Management Units (MMUs) provide advanced features like virtual memory and paging but introduce latency due to address translation and page fault handling, impacting execution speed. Embedded applications favor MPUs for faster performance, while general-purpose systems rely on MMUs for flexibility despite higher overhead.
Typical Use Cases for MPU and MMU
Memory Protection Units (MPUs) are typically used in embedded systems for real-time applications where simple, deterministic memory access control is required without the overhead of virtual memory. Memory Management Units (MMUs) are common in general-purpose computing platforms, enabling complex features like virtual memory, process isolation, and address translation for multitasking operating systems. Your choice between MPU and MMU depends on whether you need efficient control in resource-constrained environments or advanced memory management for complex software ecosystems.
Security Considerations
The Memory Protection Unit (MPU) enforces access controls on specific memory regions, preventing unauthorized access and enhancing system security by isolating critical code and data. The Memory Management Unit (MMU) goes further by providing virtual memory support, enabling features like address translation and process isolation, which secure systems against attacks such as buffer overflows and privilege escalations. Understanding these security considerations helps you select the appropriate unit for protecting sensitive information and maintaining system integrity.
Choosing Between MPU and MMU
Choosing between a Memory Protection Unit (MPU) and a Memory Management Unit (MMU) depends on the complexity of your embedded system and the need for memory translation features. MPUs provide simple, hardware-based access control to protect memory regions, making them ideal for real-time or resource-constrained environments with fixed memory layouts. MMUs offer advanced virtual memory management, address translation, and support for multitasking operating systems, making them suitable for systems requiring dynamic memory allocation and complex process isolation.
Memory protection unit vs memory management unit Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com