The SSD1306 is a widely-used OLED driver chip known for its 128x64 pixel display resolution, making it ideal for small, monochrome screens with moderate graphics needs, while the SSD1322 offers a higher resolution of 256x64 pixels and supports grayscale rendering for more detailed and sophisticated visuals. Understanding the key differences between these chips can help you choose the best option for your OLED display project--read on to explore their features, performance, and applications in depth.
Table of Comparison
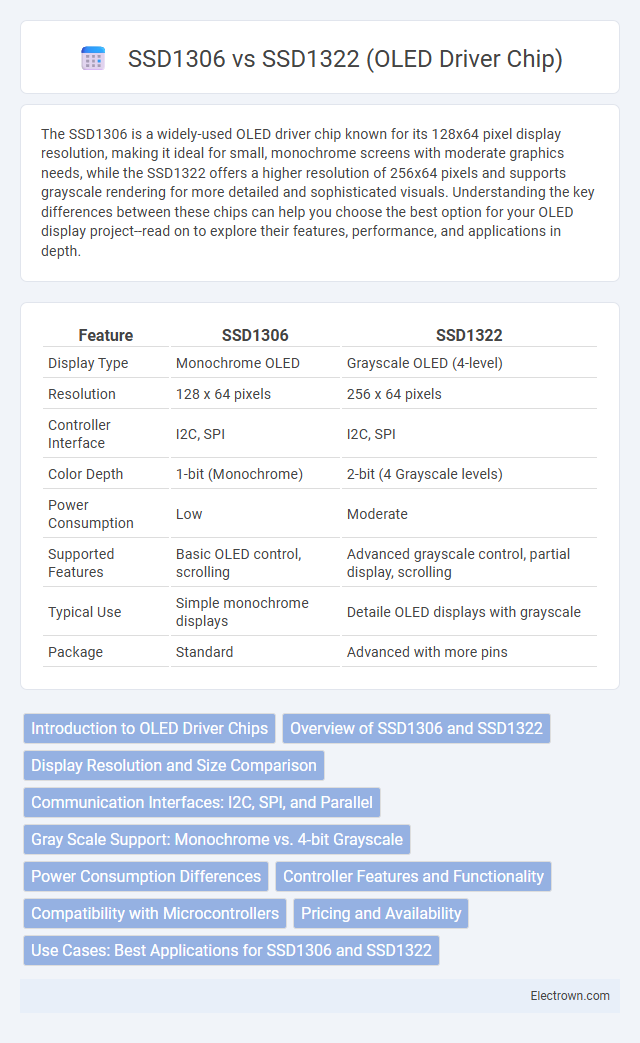
| Feature | SSD1306 | SSD1322 |
|---|---|---|
| Display Type | Monochrome OLED | Grayscale OLED (4-level) |
| Resolution | 128 x 64 pixels | 256 x 64 pixels |
| Controller Interface | I2C, SPI | I2C, SPI |
| Color Depth | 1-bit (Monochrome) | 2-bit (4 Grayscale levels) |
| Power Consumption | Low | Moderate |
| Supported Features | Basic OLED control, scrolling | Advanced grayscale control, partial display, scrolling |
| Typical Use | Simple monochrome displays | Detaile OLED displays with grayscale |
| Package | Standard | Advanced with more pins |
Introduction to OLED Driver Chips
OLED driver chips like the SSD1306 and SSD1322 control the communication and operation of OLED displays by managing pixel addressing, brightness, and refresh rates. The SSD1306 supports monochrome displays up to 128x64 pixels, making it suitable for simpler interface applications, while the SSD1322 drives larger grayscale OLEDs with resolutions up to 256x64 pixels, enabling more detailed and high-contrast visuals. Both chips integrate GDDRAM and feature I2C/SPI interfaces, but the SSD1322 offers enhanced grayscale levels and partial display capabilities tailored for advanced graphical content.
Overview of SSD1306 and SSD1322
The SSD1306 is a widely used OLED driver chip designed for monochrome displays, supporting resolutions up to 128x64 pixels with simple SPI or I2C interfaces, making it ideal for compact, low-power applications. In contrast, the SSD1322 supports higher resolutions up to 256x64 pixels, offers grayscale capabilities with 4-bit depth, and provides enhanced graphic rendering features suitable for more complex and dynamic visual output. Both chips are integral in driving OLED panels but cater to different requirements in display performance and graphics complexity.
Display Resolution and Size Comparison
The SSD1306 OLED driver supports a resolution of 128x64 pixels, typically used in 0.96-inch displays, while the SSD1322 offers a higher resolution of 256x64 pixels, suitable for larger 2.7-inch displays. The increased pixel count of the SSD1322 enables more detailed graphics and text rendering compared to the SSD1306's more compact display size. This difference makes the SSD1322 ideal for applications requiring wider screens and enhanced visual clarity.
Communication Interfaces: I2C, SPI, and Parallel
The SSD1306 OLED driver primarily supports I2C and SPI communication interfaces, making it ideal for simple, low-speed data transfers in compact displays. In contrast, the SSD1322 offers more versatile communication options including I2C, SPI, and an 8080 parallel interface, allowing for higher data throughput and faster refresh rates suitable for larger or more complex displays. Choosing between these chips depends on your application's speed requirements and interface compatibility, with SSD1322 providing enhanced flexibility for advanced display projects.
Gray Scale Support: Monochrome vs. 4-bit Grayscale
The SSD1306 OLED driver chip supports only monochrome displays, rendering images in strictly black and white without any gray scale differentiation, which is ideal for simple text and icon displays. In contrast, the SSD1322 enhances visual output by supporting 4-bit grayscale, allowing for 16 shades of gray that provide smoother gradients and more detailed graphics. If your project requires richer depth and nuanced images, the SSD1322 is a superior choice, while the SSD1306 serves well for basic, binary visual interfaces.
Power Consumption Differences
The SSD1306 OLED driver chip generally consumes less power compared to the SSD1322, as it supports lower resolution displays typically around 128x64 pixels, which require fewer active pixels and less voltage to operate. In contrast, the SSD1322 drives higher resolution OLEDs, such as 256x64 or 256x128 pixels, leading to increased power consumption due to more complex data processing and higher pixel count. Choosing between these chips impacts your device's battery life, with the SSD1306 offering more energy-efficient performance for lower resolution displays.
Controller Features and Functionality
The SSD1306 OLED driver chip supports monochrome displays with a resolution typically up to 128x64 pixels, featuring an 8-bit parallel interface and I2C/SPI communication, optimized for low-power applications. The SSD1322 enhances functionality by supporting grayscale OLED displays with up to 256x64 pixel resolution, incorporating a 4-level grayscale feature and a more advanced 18-bit RGB interface for richer image rendering. While the SSD1306 is suited for basic text and simple graphics, the SSD1322 excels in complex graphics applications requiring higher resolution and grayscale depth.
Compatibility with Microcontrollers
The SSD1306 and SSD1322 OLED driver chips differ significantly in compatibility with microcontrollers due to their interface capabilities. SSD1306 supports I2C and SPI interfaces, making it widely compatible with various microcontrollers, including Arduino, ESP32, and STM32. Your choice depends on the required resolution and display type, as SSD1322 often demands more advanced communication protocols and microcontroller resources for its higher resolution grayscale displays.
Pricing and Availability
The SSD1306 remains widely available and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for basic monochrome OLED displays in budget-conscious projects. In contrast, the SSD1322, featuring higher resolution and grayscale capabilities, typically commands a higher price due to its advanced functionality and lower production volume. You should evaluate your project requirements carefully to decide if the performance benefits of the SSD1322 justify the increased cost and potentially limited supply compared to the SSD1306.
Use Cases: Best Applications for SSD1306 and SSD1322
The SSD1306 OLED driver chip excels in compact displays for wearable devices, small gadgets, and simple user interfaces due to its efficient power consumption and ease of use with monochrome 128x64 pixel screens. The SSD1322 is better suited for high-resolution applications requiring grayscale support and larger displays, such as advanced smartwatches, automotive dashboards, and multimedia devices, offering enhanced contrast and richer visual details. Your choice depends on the display requirements, with SSD1306 ideal for basic, low-power projects and SSD1322 optimal for complex, feature-rich interfaces.
SSD1306 vs SSD1322 (OLED driver chip) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com