Standard UART operates with voltage levels compliant with RS-232 standards, typically ranging from +-3 to +-15 volts, which allows for longer transmission distances but requires level conversion for microcontroller compatibility. TTL UART uses Transistor-Transistor Logic voltage levels, generally 0 to 5V or 0 to 3.3V, making it suitable for direct microcontroller interfacing without additional hardware; explore the rest of this article to understand which UART type best fits your project needs.
Table of Comparison
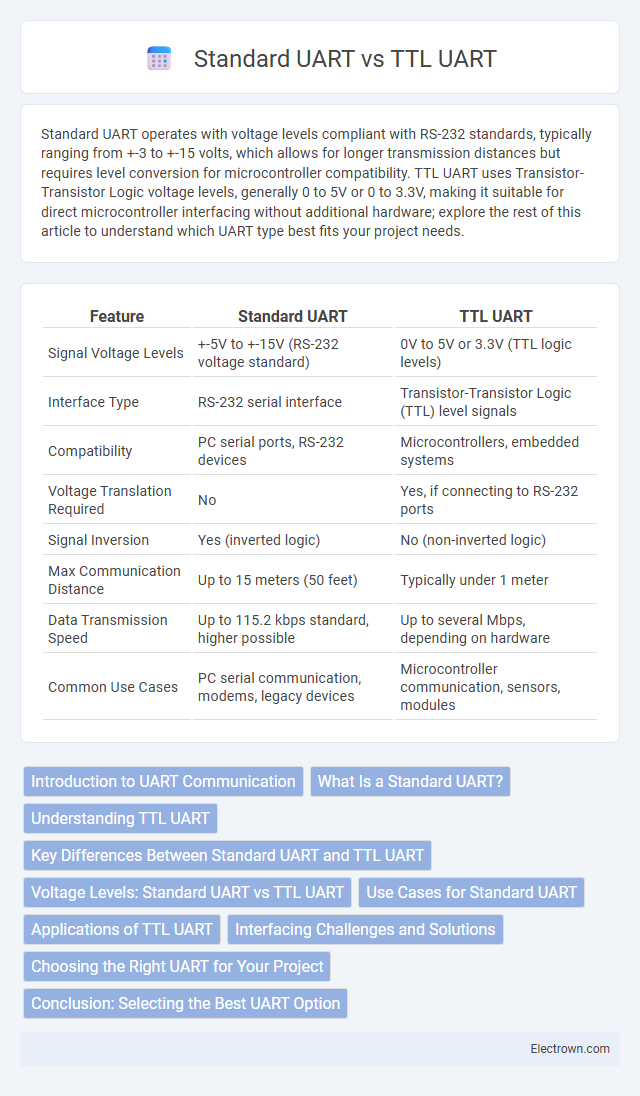
| Feature | Standard UART | TTL UART |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Voltage Levels | +-5V to +-15V (RS-232 voltage standard) | 0V to 5V or 3.3V (TTL logic levels) |
| Interface Type | RS-232 serial interface | Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) level signals |
| Compatibility | PC serial ports, RS-232 devices | Microcontrollers, embedded systems |
| Voltage Translation Required | No | Yes, if connecting to RS-232 ports |
| Signal Inversion | Yes (inverted logic) | No (non-inverted logic) |
| Max Communication Distance | Up to 15 meters (50 feet) | Typically under 1 meter |
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 115.2 kbps standard, higher possible | Up to several Mbps, depending on hardware |
| Common Use Cases | PC serial communication, modems, legacy devices | Microcontroller communication, sensors, modules |
Introduction to UART Communication
UART communication enables asynchronous serial data transmission between devices using two wires: TX (transmit) and RX (receive). Standard UART typically refers to voltage levels compatible with RS-232 protocols, operating around +-12V, while TTL UART uses lower voltage levels, typically 0V to 5V or 3.3V, suitable for direct microcontroller interfacing. Understanding the voltage and signal differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate UART type to ensure reliable data exchange and prevent hardware damage.
What Is a Standard UART?
A Standard UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) is a digital communication protocol used to transmit and receive serial data between devices. It operates with voltage levels compliant with RS-232 standards, typically ranging between +-3 to +-15 volts, ensuring reliable long-distance communication. Your device's compatibility with Standard UART depends on its voltage level requirements and communication interface specifications.
Understanding TTL UART
TTL UART operates at Transistor-Transistor Logic voltage levels, typically 0 to 5V, making it directly compatible with microcontrollers and digital circuits without requiring voltage level conversion. Standard UART signals, on the other hand, use RS-232 voltage levels, ranging from -12V to +12V, which are incompatible with TTL logic and need specialized level shifters such as MAX232. Understanding TTL UART enables you to interface microcontrollers with peripherals efficiently, minimizing complexity and enhancing signal integrity in embedded system designs.
Key Differences Between Standard UART and TTL UART
Standard UART operates at RS-232 voltage levels ranging from +-3 to +-15 volts, ensuring higher noise immunity for long-distance communication, whereas TTL UART functions at logic voltage levels of 0 to 5 volts or 3.3 volts, which is compatible with microcontrollers and low-voltage digital circuits. Standard UART signals are inverted compared to TTL UART, meaning a logical '1' is represented by a negative voltage in standard UART, while TTL UART uses positive voltages for logic high and low states. The distinct voltage ranges and signal polarity between standard UART and TTL UART dictate their respective applications and interfacing requirements in embedded systems and serial communication modules.
Voltage Levels: Standard UART vs TTL UART
Standard UART operates at RS-232 voltage levels, typically ranging from -12V to +12V, which ensures noise immunity over longer cable distances. TTL UART functions at transistor-transistor logic levels, usually 0V (low) and 5V or 3.3V (high), compatible with most microcontrollers and digital circuits. Understanding the voltage level differences helps you choose the right UART interface to prevent damage to your devices and ensure reliable communication.
Use Cases for Standard UART
Standard UART is commonly used for long-distance communication between microcontrollers and computers or external peripherals, benefiting from RS-232 voltage levels that support noise-resistant data transfer over cables exceeding 15 meters. This makes it ideal for industrial equipment, serial consoles, and legacy devices requiring robust connection standards. Standard UART interfaces enable reliable debugging and interface with modems or GPS modules in embedded systems.
Applications of TTL UART
TTL UART is commonly used in embedded systems and microcontroller communication due to its compatibility with low voltage logic levels, typically 3.3V or 5V. It facilitates direct interfacing with sensors, modules, and other hardware components in IoT devices, robotics, and development boards like Arduino and Raspberry Pi. These applications benefit from TTL UART's simplicity, low power consumption, and ease of integration without requiring level shifters.
Interfacing Challenges and Solutions
Standard UART operates with voltage levels of +-12V, making it compatible with RS-232 interfaces but unsuitable for direct connection to microcontrollers that use TTL levels of 0-5V or 0-3.3V, which characterizes TTL UART. Interfacing challenges include voltage mismatch that can damage microcontroller pins or cause communication failure, requiring level shifters or dedicated RS-232 transceiver ICs like MAX232 to translate voltage levels safely. Solutions involve using bi-directional voltage level converters or integrated driver chips to ensure signal integrity and protect hardware during UART communication between differing voltage standards.
Choosing the Right UART for Your Project
Standard UART interfaces operate at RS-232 voltage levels, typically +-12V, making them ideal for long-distance communication and compatibility with legacy serial ports, while TTL UART functions at 0-5V or 0-3.3V logic levels suited for direct microcontroller connections. Your project requires assessing voltage compatibility and communication distance; TTL UART simplifies integration with modern embedded systems, whereas Standard UART ensures robust signal integrity over extended cables. Selecting the correct UART type impacts signal reliability, device protection, and overall system performance.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best UART Option
Standard UART interfaces operate with RS-232 voltage levels typically ranging from +-3 to +-15 volts, ensuring longer cable lengths and noise immunity suitable for industrial or legacy systems. TTL UART uses 0-5V or 0-3.3V logic levels, offering direct compatibility with microcontrollers and low-power devices for shorter distance communication. Choosing the best UART option depends on your application requirements, such as voltage compatibility, signal integrity, and environment, where TTL UART fits embedded systems while standard UART suits robust, long-distance connections.
Standard UART vs TTL UART Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com