A Watchdog Timer is a specialized hardware timer designed to reset a system if the software becomes unresponsive, ensuring reliability and preventing system crashes. To understand how this differs from a regular Timer and its impact on your device's performance, read the full article.
Table of Comparison
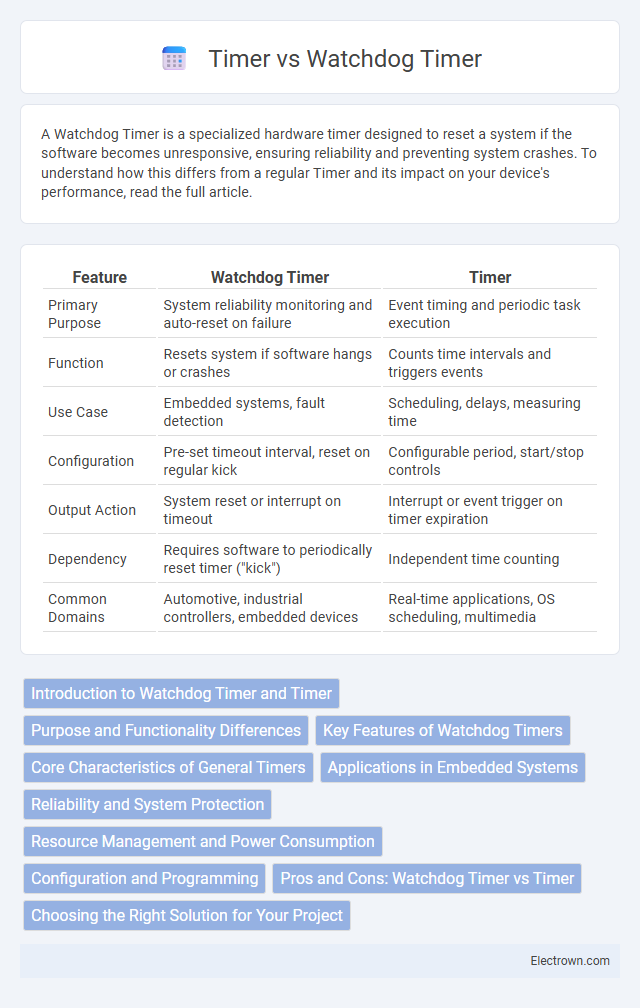
| Feature | Watchdog Timer | Timer |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | System reliability monitoring and auto-reset on failure | Event timing and periodic task execution |
| Function | Resets system if software hangs or crashes | Counts time intervals and triggers events |
| Use Case | Embedded systems, fault detection | Scheduling, delays, measuring time |
| Configuration | Pre-set timeout interval, reset on regular kick | Configurable period, start/stop controls |
| Output Action | System reset or interrupt on timeout | Interrupt or event trigger on timer expiration |
| Dependency | Requires software to periodically reset timer ("kick") | Independent time counting |
| Common Domains | Automotive, industrial controllers, embedded devices | Real-time applications, OS scheduling, multimedia |
Introduction to Watchdog Timer and Timer
A Watchdog Timer is a specialized hardware timer designed to automatically reset a system if software becomes unresponsive or enters an infinite loop, ensuring system reliability and fault tolerance in embedded applications. In contrast, a general Timer is a versatile hardware or software component used to measure time intervals, generate periodic interrupts, or schedule events in various computing environments. Both timers play critical roles in system timing management, but the Watchdog Timer specifically safeguards against software failures by triggering system recovery actions.
Purpose and Functionality Differences
A Watchdog Timer is designed to automatically reset a system if the software becomes unresponsive, ensuring reliability and preventing system hangs. In contrast, a standard Timer primarily measures or counts time intervals for tasks such as event scheduling, timing operations, or generating periodic interrupts. While the Watchdog Timer serves as a fail-safe mechanism for system stability, the Timer functions as a general-purpose timing tool within embedded systems and microcontrollers.
Key Features of Watchdog Timers
Watchdog timers provide a crucial safety mechanism by monitoring system operations and triggering a reset if the system becomes unresponsive, ensuring reliability in embedded systems. Key features include automatic system recovery, configurable timeout intervals, and low power consumption, making them essential for mission-critical applications. Your system's stability depends on these watchdog timers to prevent software freezes and maintain continuous operation.
Core Characteristics of General Timers
General timers measure elapsed time intervals by counting clock pulses and generate a signal upon reaching a set value, commonly used for event scheduling and delays in embedded systems. Watchdog timers differ as they reset the system if the software fails to respond within a predefined timeframe, ensuring system reliability. You can rely on general timers for precise timing control, while watchdog timers provide fault detection and recovery functionality.
Applications in Embedded Systems
Embedded systems utilize watchdog timers primarily to enhance reliability by automatically resetting the system during software malfunctions or unexpected freezes, ensuring continuous operation. Standard timers, however, are employed for precise timing operations such as event scheduling, pulse-width modulation, or timekeeping within microcontrollers. Your choice between a watchdog timer and a timer depends on whether system fault recovery or timing control is the critical requirement in your embedded application.
Reliability and System Protection
Watchdog timers enhance system reliability by automatically resetting the system during software malfunctions or hangs, preventing prolonged failures. Timers primarily manage task scheduling and time delays but do not inherently protect against system crashes or infinite loops. Incorporating a watchdog timer provides critical system protection by ensuring recovery from unexpected faults, which standard timers alone cannot guarantee.
Resource Management and Power Consumption
Watchdog timers specialize in monitoring system responsiveness by resetting hardware during malfunctions, consuming minimal power primarily in low-energy standby modes. In contrast, general-purpose timers manage periodic tasks and event scheduling, often requiring more active power due to continuous operation. Efficient resource management in embedded systems favors watchdog timers for fail-safe reliability with low power overhead, whereas timers prioritize precision in timing at the cost of higher energy use.
Configuration and Programming
Watchdog timers require specific configuration to reset the system upon detecting operational faults, often involving setting timeout intervals and enabling immediate system resets to ensure reliability. Timers, in contrast, are programmed for precise time measurement and event scheduling using counters, capture/compare registers, and interrupt generation to control task execution. Programming watchdog timers focuses on maintaining system stability, while timer configuration emphasizes creating accurate timing events for application logic.
Pros and Cons: Watchdog Timer vs Timer
Watchdog timers excel in system reliability by automatically resetting microcontrollers during software malfunctions, reducing downtime but adding complexity and potential false triggers. Timers offer precise time measurement and event scheduling with simplicity and low power consumption but lack built-in fault recovery capabilities. Choosing between them depends on the need for fault tolerance versus straightforward timing functions in embedded systems.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Project
Choosing the right solution between a watchdog timer and a standard timer depends on your project's reliability and timing requirements. A watchdog timer is essential for systems that need fault detection and automatic recovery by resetting the processor upon malfunction, while a standard timer primarily manages time-based events without fault detection capabilities. Your choice should prioritize system stability with a watchdog timer for critical applications, or precise event timing with a standard timer for simpler, time-sensitive tasks.
Watchdog Timer vs Timer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com