HSM (Hardware Security Module) and TPM (Trusted Platform Module) both provide embedded security by securely storing cryptographic keys and performing encryption tasks, but HSMs offer higher performance and scalability ideal for enterprise environments, while TPMs are integrated chips designed for individual device security. Discover which solution best fits Your security needs and how they impact overall system protection by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
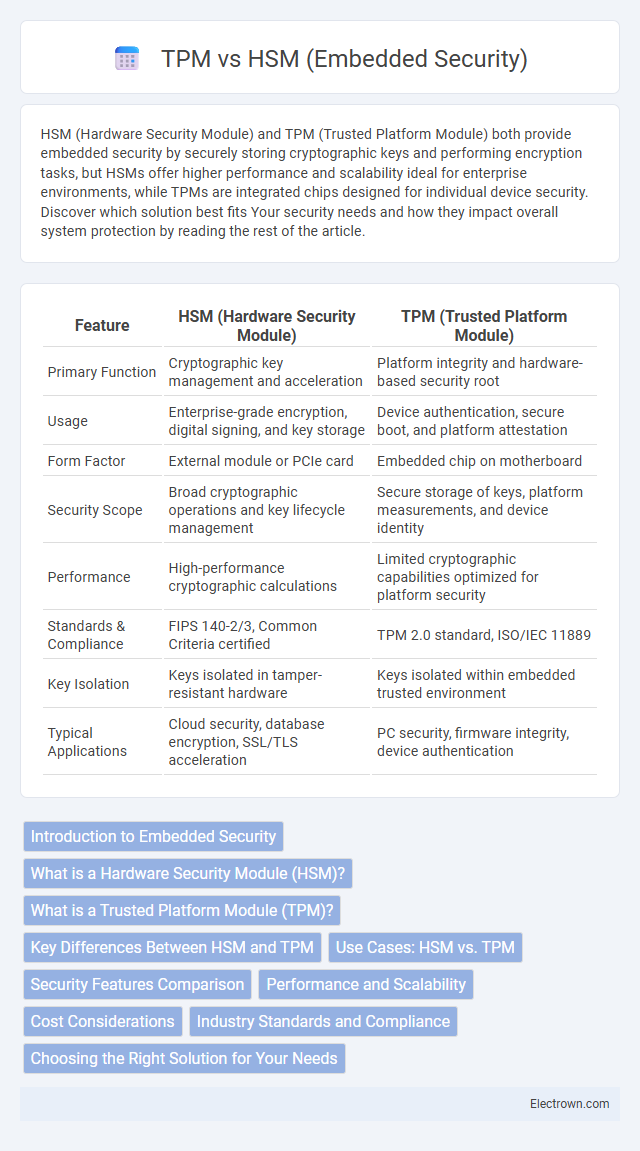
| Feature | HSM (Hardware Security Module) | TPM (Trusted Platform Module) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Cryptographic key management and acceleration | Platform integrity and hardware-based security root |
| Usage | Enterprise-grade encryption, digital signing, and key storage | Device authentication, secure boot, and platform attestation |
| Form Factor | External module or PCIe card | Embedded chip on motherboard |
| Security Scope | Broad cryptographic operations and key lifecycle management | Secure storage of keys, platform measurements, and device identity |
| Performance | High-performance cryptographic calculations | Limited cryptographic capabilities optimized for platform security |
| Standards & Compliance | FIPS 140-2/3, Common Criteria certified | TPM 2.0 standard, ISO/IEC 11889 |
| Key Isolation | Keys isolated in tamper-resistant hardware | Keys isolated within embedded trusted environment |
| Typical Applications | Cloud security, database encryption, SSL/TLS acceleration | PC security, firmware integrity, device authentication |
Introduction to Embedded Security
Embedded security integrates hardware modules like Hardware Security Modules (HSM) and Trusted Platform Modules (TPM) to protect sensitive data and cryptographic keys within devices. HSMs offer high-performance cryptographic processing tailored for enterprise-grade applications, while TPMs provide a cost-effective, embedded security solution for platform integrity and device authentication. Both technologies strengthen embedded systems by enabling secure boot, encryption, and trusted execution environments critical for IoT and industrial applications.
What is a Hardware Security Module (HSM)?
A Hardware Security Module (HSM) is a dedicated physical device designed to manage digital keys and perform cryptographic operations securely, offering high assurance for encryption, decryption, and authentication processes. It ensures robust key protection by generating and storing keys within a tamper-resistant environment, making it essential for safeguarding sensitive data and securing critical applications. Your organization can leverage an HSM to meet strict compliance requirements and enhance overall embedded security by isolating cryptographic functions from general-purpose hardware.
What is a Trusted Platform Module (TPM)?
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized hardware chip designed to provide secure cryptographic functions and safeguard sensitive data, such as encryption keys and platform integrity measurements. It ensures hardware-based security by generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys within a tamper-resistant environment, enabling trusted boot processes and secure authentication. TPMs are integrated into computing devices to enhance system security, protect against firmware attacks, and support secure credential storage compliant with industry standards like TPM 2.0.
Key Differences Between HSM and TPM
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) and Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) differ primarily in their scope and application; HSMs are dedicated cryptographic processors designed for high-volume key management and encryption tasks in enterprise environments, while TPMs are integrated chips aimed at securing platform integrity and device authentication. HSMs support a wide range of cryptographic algorithms and are used for managing large-scale cryptographic keys, digital signatures, and secure transactions, whereas TPMs specialize in generating and storing cryptographic keys tied to the hardware for system integrity checks and secure boot processes. The physical design also contrasts: HSMs are typically external devices or cards with tamper-resistant features, while TPMs are embedded chips within the motherboard, providing foundational security for individual devices.
Use Cases: HSM vs. TPM
HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) are designed for high-performance cryptographic operations in enterprise environments, securing cryptographic keys for applications such as digital signatures, encryption, and certificate authority management. TPMs (Trusted Platform Modules) are embedded in devices to provide secure hardware-based key storage, device authentication, and integrity measurement, primarily protecting end-user systems and IoT devices. Your choice depends on scalability needs and security requirements, with HSMs suited for centralized key management and TPMs ideal for embedded platform security.
Security Features Comparison
HSM (Hardware Security Module) offers robust cryptographic key management, secure key storage, and high-performance encryption designed for enterprise-level security, while TPM (Trusted Platform Module) provides hardware-based root of trust and platform integrity features primarily for individual device authentication and secure boot processes. HSMs typically support advanced features such as multi-tenancy, secure key backup, and tamper-resistance certifications (FIPS 140-2/3 Level 3+), whereas TPMs focus on secure generation and storage of cryptographic keys with emphasis on device security standards like TPM 2.0. Your choice depends on scalability needs and security requirements, with HSM favored for complex multi-user environments and TPM suited for embedded system integrity and platform protection.
Performance and Scalability
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) deliver superior cryptographic performance with dedicated processing power designed for high-throughput and low-latency operations, making them ideal for scalable enterprise environments requiring rapid encryption and key management. Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs), while offering foundational embedded security, provide more limited performance due to their integration in general-purpose hardware and are typically suited for device-specific authentication rather than large-scale cryptographic workloads. Scalability in HSMs is achieved through modular architectures and networked clusters, enabling seamless expansion across multiple nodes, whereas TPMs lack this capability as they are fixed components embedded within individual devices.
Cost Considerations
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) typically incur higher upfront costs due to specialized hardware and dedicated management resources, making them suitable for enterprises with stringent security requirements and larger budgets. Trusted Platform Modules (TPMs) offer a more cost-effective embedded security solution, integrated directly into devices, reducing deployment expenses while providing sufficient cryptographic functions for many applications. Organizations must balance budget constraints against required security levels, where TPMs serve well for mass deployments, and HSMs justify their cost for high-assurance environments.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Industry standards like FIPS 140-2 and Common Criteria define rigorous compliance requirements for both Hardware Security Modules (HSM) and Trusted Platform Modules (TPM), ensuring secure cryptographic key management and data protection. HSMs often meet higher assurance levels due to their dedicated hardware design and extensive certification processes, making them suitable for environments with stringent regulatory demands such as finance and healthcare. Your choice between HSM and TPM should consider specific compliance mandates relevant to your industry, as TPMs typically provide embedded security at a lower assurance level but are widely accepted for platform integrity and basic cryptographic functions.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
HSMs (Hardware Security Modules) provide robust cryptographic operations and key management with high performance, ideal for enterprises requiring dedicated, tamper-resistant hardware. TPMs (Trusted Platform Modules) offer embedded security at the device level, enabling secure boot and hardware-based authentication for endpoint protection. Choosing the right solution depends on your need for centralized, high-throughput cryptography versus integrated hardware security for individual devices.
HSM vs TPM (embedded security) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com