Passive matrix OLEDs feature simpler control and lower power consumption but suffer from slower refresh rates and less precise image quality compared to active matrix OLEDs, which use a thin-film transistor (TFT) array to deliver faster response times and higher resolution. Discover how these differences impact your viewing experience and which technology best suits your needs in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
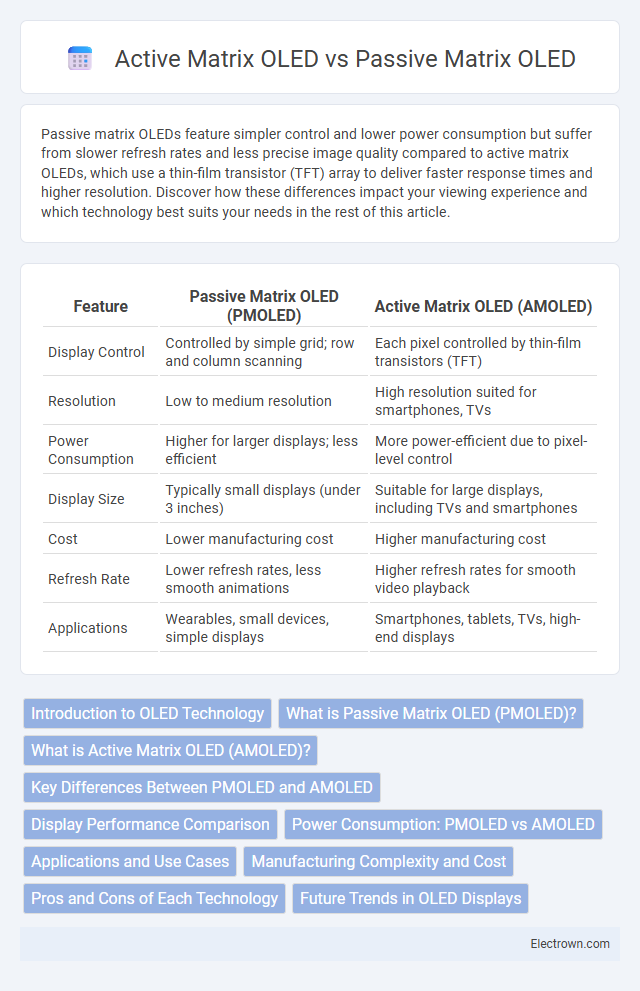
| Feature | Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) | Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) |
|---|---|---|
| Display Control | Controlled by simple grid; row and column scanning | Each pixel controlled by thin-film transistors (TFT) |
| Resolution | Low to medium resolution | High resolution suited for smartphones, TVs |
| Power Consumption | Higher for larger displays; less efficient | More power-efficient due to pixel-level control |
| Display Size | Typically small displays (under 3 inches) | Suitable for large displays, including TVs and smartphones |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher manufacturing cost |
| Refresh Rate | Lower refresh rates, less smooth animations | Higher refresh rates for smooth video playback |
| Applications | Wearables, small devices, simple displays | Smartphones, tablets, TVs, high-end displays |
Introduction to OLED Technology
Passive matrix OLED (PMOLED) and active matrix OLED (AMOLED) are two fundamental display technologies used in organic light-emitting diode panels. PMOLED controls each row and column sequentially, resulting in simpler circuitry but lower resolution and higher power consumption, making it suitable for smaller displays like wearable devices. AMOLED uses a thin-film transistor (TFT) array to control each pixel individually, enabling higher resolution, faster refresh rates, and better energy efficiency, which benefits your smartphone and television screens.
What is Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED)?
Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) is a display technology where the OLED pixels are controlled by applying voltage through a grid of orthogonal conductive lines without active switching components at each pixel. PMOLED screens use a simple addressing scheme that scans rows and columns sequentially, making them less complex and cost-effective for small displays. Due to their slower refresh rates and higher power consumption compared to Active Matrix OLEDs (AMOLED), PMOLEDs are typically used in small devices like wearables and basic display panels.
What is Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED)?
Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) is a display technology that uses a thin-film transistor (TFT) array to control each pixel individually, enabling faster response times and higher resolution compared to Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED). AMOLED screens offer superior color accuracy, brightness, and energy efficiency, making them ideal for smartphones, tablets, and high-end wearables. The active matrix system supports complex graphics and video playback with reduced motion blur and better overall image quality.
Key Differences Between PMOLED and AMOLED
Passive matrix OLED (PMOLED) uses a simple control scheme where each row and column is addressed sequentially, resulting in lower resolution and limited screen size compared to active matrix OLED (AMOLED), which employs thin-film transistor (TFT) backplanes to control each pixel individually with high precision. AMOLED displays offer faster refresh rates, higher brightness levels, and better power efficiency through selective pixel activation, making them ideal for smartphones, tablets, and high-performance wearables. In contrast, PMOLED technology remains suitable for smaller, low-cost applications such as basic screens on remote controls and simple digital devices.
Display Performance Comparison
Active matrix OLED (AMOLED) offers superior display performance compared to passive matrix OLED (PMOLED), providing faster refresh rates and higher resolutions ideal for dynamic content and complex graphics. AMOLED panels deliver better color accuracy, improved contrast ratios, and enhanced brightness control, resulting in vivid, sharp images that elevate your viewing experience. PMOLED, while simpler and more cost-effective, is generally limited to smaller displays with lower resolution and slower response times, making it less suitable for high-performance applications.
Power Consumption: PMOLED vs AMOLED
Passive matrix OLED (PMOLED) typically consumes more power than active matrix OLED (AMOLED) due to its simpler driving method, where current is applied row by row, causing higher energy use for larger displays. AMOLED technology uses a thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane that enables precise pixel control and lower power consumption, especially for displaying dynamic images or darker content. Your device's battery life can benefit significantly from AMOLED screens, as they deliver efficiency by activating only the necessary pixels.
Applications and Use Cases
Passive matrix OLED (PMOLED) is ideal for small screens and simple displays such as wearable devices, remote controls, and basic MP3 players due to its lower cost and simpler control scheme. Active matrix OLED (AMOLED) supports larger, high-resolution displays found in smartphones, tablets, and televisions, offering faster refresh rates and better image quality for multimedia applications. Your choice depends on whether you need affordability and simplicity (PMOLED) or advanced performance and vibrant visuals (AMOLED).
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Passive matrix OLED displays feature a simpler manufacturing process with fewer integrated components, resulting in lower production costs compared to active matrix OLEDs. Active matrix OLED technology involves complex backplane circuitry with thin-film transistors (TFTs), increasing fabrication difficulty and expenses. Your choice between the two should consider the trade-off between cost efficiency and display performance requirements.
Pros and Cons of Each Technology
Passive matrix OLED (PMOLED) offers simpler design and lower manufacturing costs, making it ideal for small-sized displays with low refresh rates but suffers from limited brightness, slower response times, and higher power consumption for larger screens. Active matrix OLED (AMOLED) provides superior image quality with higher brightness, faster refresh rates, and lower power consumption, enabling larger and more flexible displays; however, its complex circuitry and higher production costs pose challenges. Choosing between PMOLED and AMOLED depends on application requirements such as size, power efficiency, image performance, and budget constraints.
Future Trends in OLED Displays
Future trends in OLED displays emphasize the transition from Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) to Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) due to AMOLED's superior power efficiency, faster response time, and higher resolution capabilities. Innovations in AMOLED technology, such as flexible substrates and microLED integration, are driving advancements in foldable smartphones, wearables, and large-screen displays. Research into reducing manufacturing costs and enhancing lifespan continues to position AMOLED as the dominant choice for next-generation OLED devices.
Passive matrix OLED vs Active matrix OLED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com