A double stub tuner provides greater impedance matching flexibility and bandwidth control compared to a single stub tuner, making it ideal for complex transmission line adjustments. Explore the rest of the article to understand how you can optimize your RF system using these tuners.
Table of Comparison
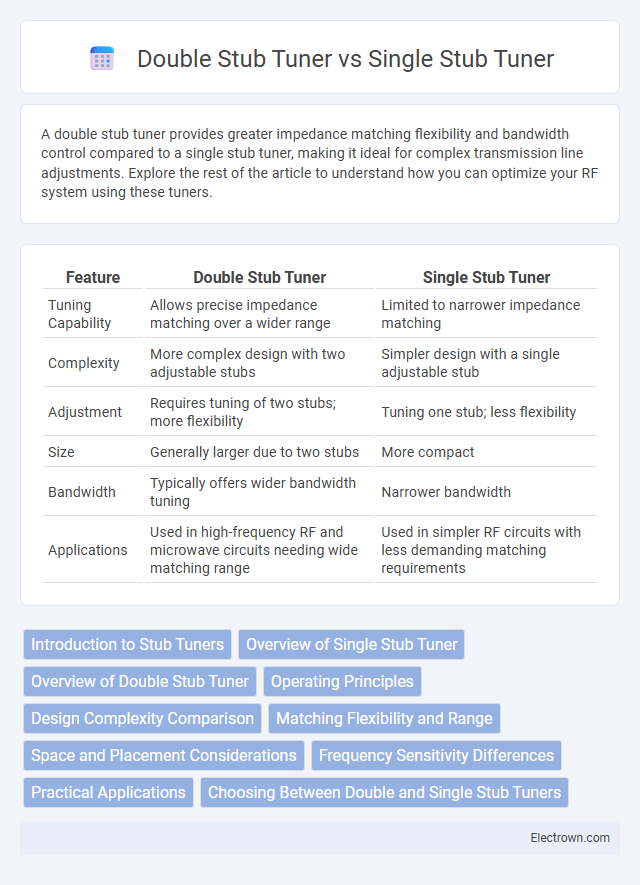
| Feature | Double Stub Tuner | Single Stub Tuner |
|---|---|---|
| Tuning Capability | Allows precise impedance matching over a wider range | Limited to narrower impedance matching |
| Complexity | More complex design with two adjustable stubs | Simpler design with a single adjustable stub |
| Adjustment | Requires tuning of two stubs; more flexibility | Tuning one stub; less flexibility |
| Size | Generally larger due to two stubs | More compact |
| Bandwidth | Typically offers wider bandwidth tuning | Narrower bandwidth |
| Applications | Used in high-frequency RF and microwave circuits needing wide matching range | Used in simpler RF circuits with less demanding matching requirements |
Introduction to Stub Tuners
Stub tuners are essential components in radio frequency (RF) circuits used to match impedances and minimize signal reflections. A single stub tuner employs one adjustable stub to achieve impedance matching at a specific frequency, offering simplicity and ease of use. In contrast, a double stub tuner uses two stubs spaced apart along the transmission line, providing greater flexibility and improved matching capabilities over a wider frequency range.
Overview of Single Stub Tuner
A single stub tuner is a compact impedance matching device used in RF circuits to minimize signal reflection and optimize power transfer. It consists of a transmission line section and a single adjustable stub placed either in parallel or series, allowing you to compensate for complex load impedances effectively. Compared to a double stub tuner, the single stub tuner simplifies design and tuning but may offer less flexibility in matching a wider range of impedance values.
Overview of Double Stub Tuner
Double stub tuners use two adjustable short-circuited stubs positioned along a transmission line to match impedance, providing greater flexibility and accuracy compared to single stub tuners. Your ability to independently adjust the length and position of each stub enables precise control over complex load impedances, minimizing reflection and maximizing power transfer in RF systems. This tuning method is especially effective for high-frequency applications where maintaining signal integrity is critical.
Operating Principles
A double stub tuner operates by placing two adjustable short-circuited stubs at specific distances along a transmission line to achieve impedance matching, allowing control over both the magnitude and phase of the reflection coefficient. In contrast, a single stub tuner uses one adjustable stub in combination with a fixed length of transmission line to cancel reactive components and match impedance at a particular frequency. Double stub tuners offer greater flexibility in tuning over a broader bandwidth, while single stub tuners provide a simpler, more compact design suitable for narrowband applications.
Design Complexity Comparison
Double stub tuners exhibit higher design complexity compared to single stub tuners due to the requirement of precise positioning and length adjustment of two stubs to achieve optimal impedance matching. Single stub tuners offer a simpler design with just one adjustable stub, making them easier to implement but less flexible in matching a wide range of impedances. Your choice between the two depends on the balance between design simplicity and the need for precise impedance matching in complex RF circuits.
Matching Flexibility and Range
Double stub tuners offer greater matching flexibility and a wider impedance matching range compared to single stub tuners, making them ideal for complex or rapidly changing load conditions. Your tuning precision improves as double stub tuners provide independent adjustable stubs that can fine-tune both reactance and susceptance separately. Single stub tuners tend to be simpler but are limited in matching range and may require multiple adjustments to achieve an optimal match.
Space and Placement Considerations
Double stub tuners offer greater flexibility in tuning across a wider frequency range without requiring precise placement along the transmission line, making them ideal for installations with limited or fixed space constraints. Single stub tuners require exact positioning to achieve impedance matching, often necessitating additional line length or adjustable sections, which can complicate layout and increase spatial requirements. The compact nature of double stub tuners allows for more versatile placement options, optimizing space utilization in complex RF systems.
Frequency Sensitivity Differences
Double stub tuners exhibit lower frequency sensitivity compared to single stub tuners due to their ability to independently adjust two stubs, enabling broader bandwidth matching and improved impedance control. Single stub tuners often require precise placement and are more susceptible to frequency shifts, causing narrow bandwidth and limited tuning flexibility. The dual adjustment mechanism of double stub tuners enhances stability across varying frequencies, making them preferable for applications demanding consistent impedance matching over wider frequency ranges.
Practical Applications
Double stub tuners offer greater flexibility and precision in practical applications such as antenna matching and RF circuit tuning by allowing adjustments at two points along a transmission line. Single stub tuners are simpler and more compact, making them ideal for quick impedance matching in systems with space constraints or less complex tuning needs. For your RF system, choosing between double and single stub tuners depends on the level of tuning accuracy required and available installation space.
Choosing Between Double and Single Stub Tuners
Choosing between double stub tuners and single stub tuners depends on your specific impedance matching requirements and available space. Double stub tuners offer greater flexibility and can match a wider range of impedances without adjusting the transmission line length, making them ideal for complex matching scenarios. Your selection should consider the trade-offs in tuner complexity, size, and ease of adjustment to optimize performance for your RF application.
Double stub tuner vs single stub tuner Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com