Slot antennas and patch antennas differ primarily in design; slot antennas feature a narrow slot cut into a metal surface that radiates energy, while patch antennas consist of a flat rectangular or circular metal patch on a grounded substrate. Understanding these differences can help you determine which antenna suits your specific communication needs--explore the rest of the article for a detailed comparison.
Table of Comparison
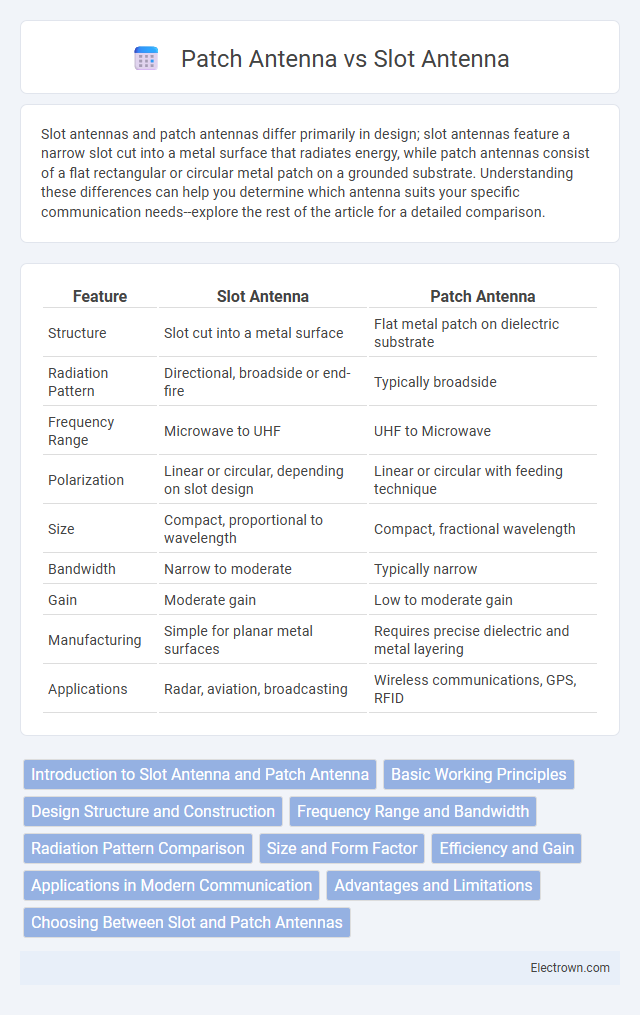
| Feature | Slot Antenna | Patch Antenna |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Slot cut into a metal surface | Flat metal patch on dielectric substrate |
| Radiation Pattern | Directional, broadside or end-fire | Typically broadside |
| Frequency Range | Microwave to UHF | UHF to Microwave |
| Polarization | Linear or circular, depending on slot design | Linear or circular with feeding technique |
| Size | Compact, proportional to wavelength | Compact, fractional wavelength |
| Bandwidth | Narrow to moderate | Typically narrow |
| Gain | Moderate gain | Low to moderate gain |
| Manufacturing | Simple for planar metal surfaces | Requires precise dielectric and metal layering |
| Applications | Radar, aviation, broadcasting | Wireless communications, GPS, RFID |
Introduction to Slot Antenna and Patch Antenna
Slot antennas feature a narrow slot cut into a metal surface and operate by radiating electromagnetic waves through the aperture, offering advantages such as a low profile and wide bandwidth. Patch antennas consist of a flat rectangular or circular metallic patch mounted on a dielectric substrate above a ground plane, known for their compact size, ease of fabrication, and integration in wireless devices. Both antennas are widely used in microwave and RF applications, with slot antennas suited for directional radiation and patch antennas favored for their versatility in various communication systems.
Basic Working Principles
Slot antennas operate by radiating electromagnetic waves through a narrow slot cut into a conductive surface, using the slot as a resonator that excites surface currents and generates radio frequency signals. Patch antennas consist of a flat rectangular or circular metallic patch suspended over a ground plane, where resonance is established through the patch's geometry, enabling efficient radiation via fringing fields at the patch edges. Both antennas rely on resonance principles, but slot antennas use the aperture coupling effect, while patch antennas depend on microstrip transmission line theory for signal propagation and radiation.
Design Structure and Construction
Slot antennas consist of a metal surface with a precisely cut slot that acts as the radiating element, typically fabricated on a ground plane with dimensions related to the operating wavelength. Patch antennas feature a flat rectangular or circular metal patch mounted above a ground plane separated by a dielectric substrate, creating a microstrip structure. The slot antenna's design leverages aperture coupling through the slot, while the patch antenna operates as a resonant cavity with the dimensions of the patch determining its resonant frequency and radiation pattern.
Frequency Range and Bandwidth
Slot antennas typically operate within the microwave frequency range, spanning from 1 GHz to 30 GHz, and offer moderate bandwidth suitable for radar and communication systems. Patch antennas generally function between 2 GHz and 18 GHz, providing narrower bandwidth but higher efficiency and ease of integration in compact devices. Frequency range and bandwidth optimization in slot antennas favors wideband applications, while patch antennas excel in narrowband and multi-band configurations.
Radiation Pattern Comparison
Slot antennas exhibit a bidirectional radiation pattern with nulls perpendicular to the slot axis, making them ideal for applications requiring broadside radiation. Patch antennas, in contrast, produce a highly directional radiation pattern focused normal to the patch surface, offering greater gain and directivity. Your choice depends on whether a broad or focused radiation pattern best suits your communication or sensing needs.
Size and Form Factor
Slot antennas typically offer a slimmer, more compact form factor compared to patch antennas, making them ideal for applications where space is limited. Patch antennas generally have a low profile but larger surface area due to their planar design, which can affect the overall device size. Your choice depends on the available installation space and design constraints, with slot antennas favored in sleek, embedded systems and patch antennas suited for flat, surface-mount scenarios.
Efficiency and Gain
Slot antennas typically exhibit higher efficiency due to their lower ohmic losses and simpler feeding mechanisms, resulting in minimal energy dissipation. Patch antennas often have moderate efficiency constrained by substrate dielectric losses but can achieve higher gain through array configurations and directional radiation patterns. In terms of gain, patch antennas generally outperform slot antennas owing to their ability to form focused beams, whereas slot antennas provide broader coverage with slightly reduced gain.
Applications in Modern Communication
Slot antennas are widely used in radar systems, satellite communications, and wireless networks due to their wide bandwidth and ease of integration into metal surfaces. Patch antennas, favored for their low profile, compact size, and ease of fabrication, find applications in mobile devices, GPS receivers, and IoT devices. Understanding your specific communication needs will help determine whether a slot or patch antenna is more suitable for optimized performance.
Advantages and Limitations
Slot antennas offer advantages like a compact structure and ease of integration into planar surfaces, making them ideal for applications requiring low profile designs and broadband performance. However, they have limitations such as lower gain compared to patch antennas and potential complexity in fabrication due to precise slot dimensions. Patch antennas provide higher gain, simple fabrication, and excellent directivity but suffer from narrow bandwidth and sensitivity to substrate material properties, impacting Your choice depending on the specific application requirements.
Choosing Between Slot and Patch Antennas
Selecting between slot and patch antennas depends on application requirements such as frequency range, bandwidth, and size constraints. Slot antennas offer excellent performance in terms of bandwidth and are typically embedded in metallic surfaces, making them suitable for rugged environments. Patch antennas feature compact size, ease of integration with printed circuit boards, and directional radiation patterns, favoring portable and wireless communication devices.
Slot Antenna vs Patch Antenna Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com