Wilkinson dividers offer excellent isolation and low insertion loss, making them ideal for power dividing and combining in RF and microwave circuits, while Gysel dividers provide superior power handling and enhanced port matching for balanced signal splitting. Explore the detailed comparison to understand which divider best suits your application needs and improve your circuit design effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
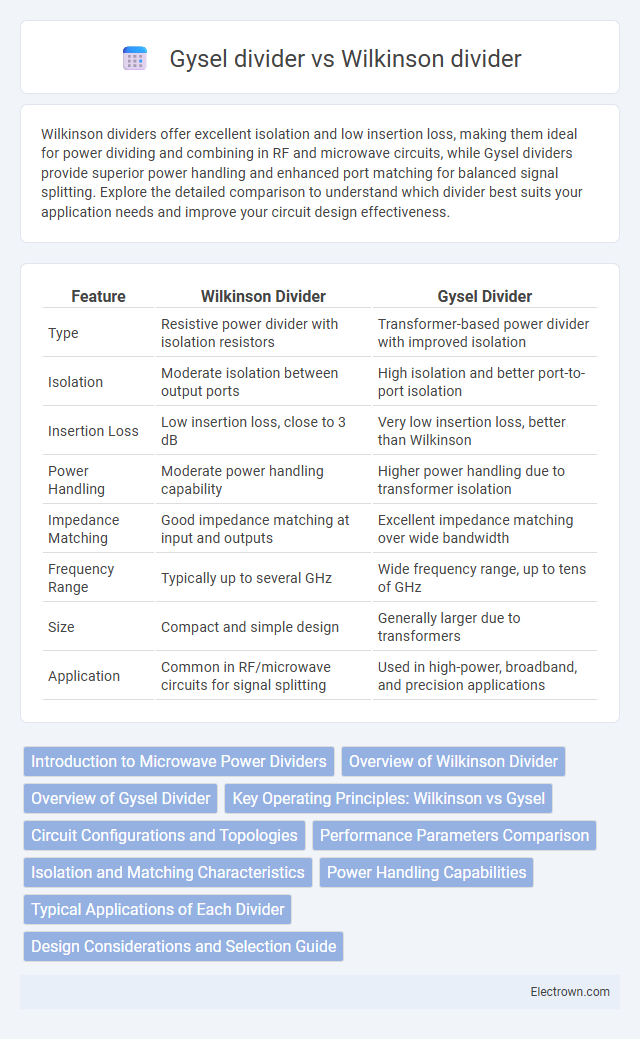
| Feature | Wilkinson Divider | Gysel Divider |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Resistive power divider with isolation resistors | Transformer-based power divider with improved isolation |
| Isolation | Moderate isolation between output ports | High isolation and better port-to-port isolation |
| Insertion Loss | Low insertion loss, close to 3 dB | Very low insertion loss, better than Wilkinson |
| Power Handling | Moderate power handling capability | Higher power handling due to transformer isolation |
| Impedance Matching | Good impedance matching at input and outputs | Excellent impedance matching over wide bandwidth |
| Frequency Range | Typically up to several GHz | Wide frequency range, up to tens of GHz |
| Size | Compact and simple design | Generally larger due to transformers |
| Application | Common in RF/microwave circuits for signal splitting | Used in high-power, broadband, and precision applications |
Introduction to Microwave Power Dividers
Microwave power dividers are essential components in RF and microwave circuits, splitting an input signal into multiple output paths with specific amplitude and phase characteristics. The Wilkinson divider provides excellent isolation and matched impedance through resistive elements, making it ideal for balanced signal applications. The Gysel divider, a variant of the Wilkinson, offers enhanced power handling and reduced insertion loss by using transmission line transformers and a grounded isolation resistor, suitable for high-power systems.
Overview of Wilkinson Divider
Wilkinson dividers are RF power splitters designed to equally divide input signals with minimal loss while providing excellent isolation between output ports. Characterized by their resistor-based isolation network, Wilkinson dividers ensure impedance matching and maintain signal integrity in communication systems. Your choice of a Wilkinson divider supports applications requiring high isolation and low insertion loss in microwave circuits.
Overview of Gysel Divider
The Gysel divider is a type of microwave power divider designed for broadband operation with improved isolation and power handling compared to the Wilkinson divider. It utilizes an internal transformer and matched resistive elements to achieve low insertion loss and enhanced performance at high frequencies. Commonly used in RF and microwave circuits, the Gysel divider offers superior amplitude and phase balance, making it ideal for phased array antenna systems and power combining applications.
Key Operating Principles: Wilkinson vs Gysel
Wilkinson dividers utilize quarter-wave transmission lines and resistive elements to achieve isolation between output ports while maintaining equal power split with minimal insertion loss. Gysel dividers employ coupled transmission lines and a unique resistive network to provide improved power handling and enhanced port isolation, especially at higher power levels. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize simplicity and isolation (Wilkinson) or higher power capacity and robustness (Gysel).
Circuit Configurations and Topologies
Wilkinson dividers utilize quarter-wave transformers and resistive elements arranged in a symmetric T-junction, providing isolation between output ports with minimal insertion loss. Gysel dividers employ transmission lines and grounded resistors in a parallel configuration, supporting high-power applications through improved power handling and thermal dissipation. Your choice between these topologies depends on the balance between isolation requirements and power capacity in the circuit design.
Performance Parameters Comparison
Wilkinson dividers provide excellent isolation typically above 20 dB and low insertion loss around 0.1 to 0.3 dB, making them ideal for signal splitting with minimal distortion. Gysel dividers offer improved power handling capabilities, often exceeding 100 W in compact designs, with isolation levels comparable to Wilkinson but enhanced VSWR stability under load mismatches. Both dividers maintain excellent phase and amplitude balance within +-1deg, but Gysel structures are preferred in high-power RF applications due to better thermal dissipation and fault tolerance.
Isolation and Matching Characteristics
Wilkinson dividers provide excellent isolation between output ports, typically exceeding 20 dB, due to their resistive element that absorbs reflected power, resulting in superior isolation characteristics vital for sensitive RF applications. Gysel dividers offer comparable isolation but achieve better power handling and can handle higher power levels without degradation, making them suitable for high-power RF systems. In terms of matching, Wilkinson dividers exhibit near-ideal input and output impedance matching (around 50 ohms), minimizing signal reflection, whereas Gysel dividers also maintain good matching but may show slightly increased mismatch at high power due to their coupled-line design.
Power Handling Capabilities
The Wilkinson divider typically offers moderate power handling capabilities suitable for many RF and microwave applications due to its resistive isolation elements that can dissipate power effectively. In contrast, the Gysel divider is designed to handle higher power levels by employing reactive isolation and heavy-duty transmission line structures that minimize power loss and heat generation. Engineers often prefer the Gysel divider for high-power scenarios exceeding several hundred watts, while Wilkinson dividers remain optimal for low to medium power distributions up to tens of watts.
Typical Applications of Each Divider
Wilkinson dividers are commonly used in RF and microwave circuits for power splitting and combining with excellent isolation and minimal signal loss, ideal for antenna feed networks and balanced mixers. Gysel dividers, offering improved power handling and isolation through their unique transformer and resistor design, are preferred in high-power applications like power amplifiers and transmitters. Your choice depends on system requirements, where Wilkinson suits low-to-moderate power and Gysel supports robust performance in demanding environments.
Design Considerations and Selection Guide
Wilkinson dividers feature equal power split with excellent isolation and low insertion loss, making them ideal for applications requiring impedance matching and minimal signal distortion. Gysel dividers are preferred in high-power RF and microwave circuits due to their superior power handling and robustness, despite slightly higher insertion loss compared to Wilkinson designs. Your selection depends on balancing power requirements, isolation needs, and physical design constraints to optimize performance in your specific application.
Wilkinson divider vs Gysel divider Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com