Interference and intermodulation both disrupt signal quality, but interference generally stems from external sources impacting your communication, while intermodulation arises from the mixing of multiple signals within a system creating undesired frequencies. Explore the article to understand how to identify and manage these issues effectively.
Table of Comparison
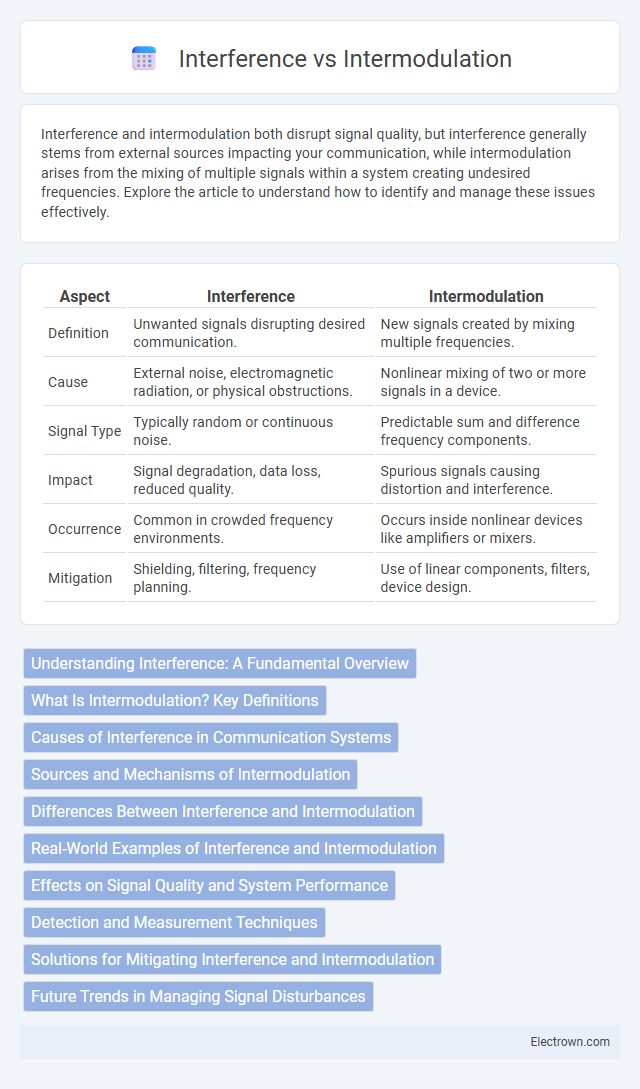
| Aspect | Interference | Intermodulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwanted signals disrupting desired communication. | New signals created by mixing multiple frequencies. |
| Cause | External noise, electromagnetic radiation, or physical obstructions. | Nonlinear mixing of two or more signals in a device. |
| Signal Type | Typically random or continuous noise. | Predictable sum and difference frequency components. |
| Impact | Signal degradation, data loss, reduced quality. | Spurious signals causing distortion and interference. |
| Occurrence | Common in crowded frequency environments. | Occurs inside nonlinear devices like amplifiers or mixers. |
| Mitigation | Shielding, filtering, frequency planning. | Use of linear components, filters, device design. |
Understanding Interference: A Fundamental Overview
Interference occurs when unwanted signals disrupt the desired communication or transmission, often caused by environmental noise, overlapping frequencies, or electromagnetic disturbances. Intermodulation is a specific type of interference resulting from the mixing of two or more signals, producing additional unwanted frequencies that can degrade signal quality. Understanding these concepts helps you identify and mitigate signal disruptions to maintain optimal system performance.
What Is Intermodulation? Key Definitions
Intermodulation occurs when two or more signals mix within a nonlinear system, creating additional frequencies that are combinations of the original signals. This phenomenon often leads to interference, as the new intermodulation products can overlap with desired signal frequencies, degrading communication quality. Understanding intermodulation is crucial for optimizing your system's performance by minimizing unwanted signal distortion and maintaining clear transmission.
Causes of Interference in Communication Systems
Interference in communication systems is primarily caused by external signals from other electronic devices, environmental noise, and electromagnetic radiation overlapping with desired communication frequencies. Intermodulation occurs when multiple signals mix within nonlinear components, creating unwanted frequencies that interfere with your signal clarity. Understanding these causes is essential to minimize disruptions and enhance overall system performance.
Sources and Mechanisms of Intermodulation
Intermodulation arises when two or more signals mix within non-linear components like amplifiers or mixers, creating spurious frequencies that interfere with the desired signal. Sources include active devices, passive components with non-linear characteristics, and external strong signals causing non-linear responses. Understanding these mechanisms helps you minimize signal distortion and optimize communication system performance.
Differences Between Interference and Intermodulation
Interference refers to unwanted signals that disrupt the normal operation of communication systems by overlapping frequency bands, while intermodulation is a specific type of interference caused by the mixing of two or more signals within non-linear devices, producing additional frequencies. Intermodulation products are predictable and occur at frequencies that are linear combinations of the original signals, whereas general interference can stem from various external sources and is often unpredictable. Your ability to troubleshoot signal issues improves by understanding that interference is broad and environmental, while intermodulation is inherently related to the internal nonlinearities of your equipment.
Real-World Examples of Interference and Intermodulation
Interference occurs when external signals disrupt the normal operation of electronic devices, such as radio broadcasts affected by nearby electrical equipment or Wi-Fi networks slowed down by microwave ovens. Intermodulation arises when two or more signals mix within a nonlinear system, producing new frequencies that can degrade communication systems, illustrated by cellular base stations experiencing dropped calls and distorted audio. Understanding these phenomena helps you optimize signal quality and minimize disruptions in real-world wireless and broadcast environments.
Effects on Signal Quality and System Performance
Interference degrades signal quality by introducing noise and unwanted signals, causing data loss and reduced clarity in communication systems. Intermodulation generates additional spurious frequencies from nonlinear mixing of multiple signals, leading to distortion and potential channel overlap that disrupts system performance. Managing interference and intermodulation is crucial for maintaining your system's reliability and ensuring high-quality signal transmission.
Detection and Measurement Techniques
Detection of interference primarily relies on spectrum analyzers and signal analyzers that measure undesired signals overlapping with the desired frequency band. Intermodulation is detected through two-tone testing, where signal generators produce distinct frequencies, and a spectrum analyzer identifies resulting intermodulation products at sum and difference frequencies. Advanced measurement techniques for both phenomena include vector signal analyzers and time-domain reflectometry to assess signal integrity and pinpoint interference sources accurately.
Solutions for Mitigating Interference and Intermodulation
Effective solutions for mitigating interference and intermodulation include the use of high-quality filters and isolators to reduce unwanted signals and prevent signal mixing. Implementing proper antenna spacing and orientation minimizes coupling effects, while deploying advanced signal processing techniques enhances detection and cancellation of interference. Regular maintenance and careful system design further ensure optimal performance by addressing potential sources of intermodulation distortion and signal interference.
Future Trends in Managing Signal Disturbances
Advancements in digital signal processing and AI-driven algorithms are transforming the approach to managing interference and intermodulation in communication systems. Future trends include adaptive filters and real-time spectrum analysis that enable precise identification and mitigation of signal disturbances, enhancing overall network performance. Your systems will increasingly rely on integrated solutions combining hardware and software for dynamic interference suppression and improved signal clarity.
Interference vs Intermodulation Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com