Baluns convert balanced signals to unbalanced ones, essential in radio and antenna systems, while ununs change impedance levels without altering signal balance, often improving antenna matching and reducing signal loss. Discover how choosing the right device can enhance Your setup by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
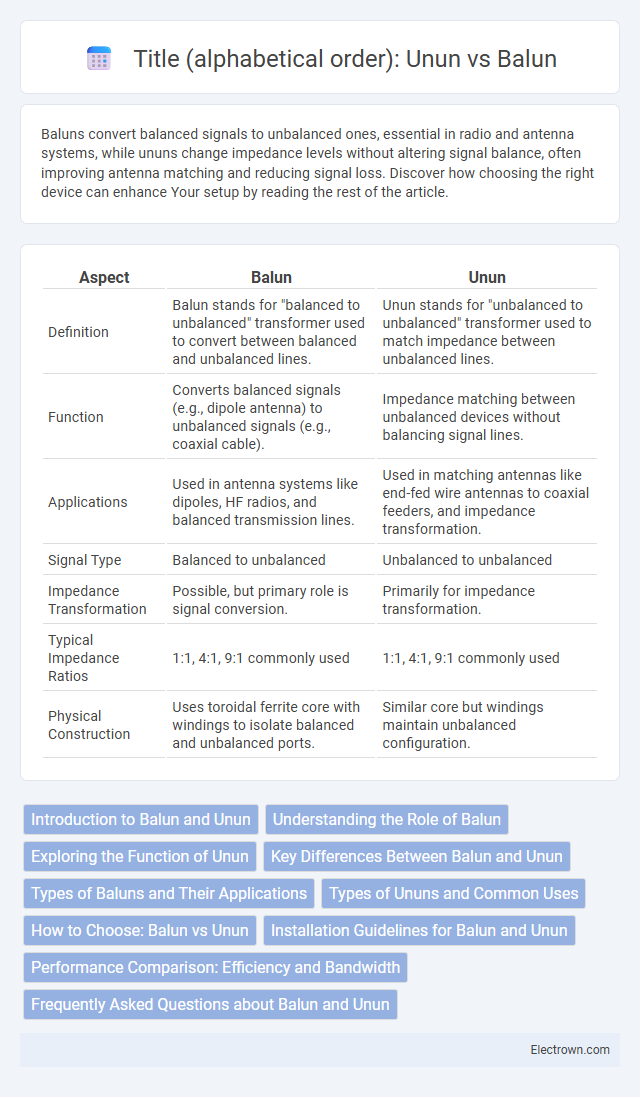
| Aspect | Balun | Unun |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Balun stands for "balanced to unbalanced" transformer used to convert between balanced and unbalanced lines. | Unun stands for "unbalanced to unbalanced" transformer used to match impedance between unbalanced lines. |
| Function | Converts balanced signals (e.g., dipole antenna) to unbalanced signals (e.g., coaxial cable). | Impedance matching between unbalanced devices without balancing signal lines. |
| Applications | Used in antenna systems like dipoles, HF radios, and balanced transmission lines. | Used in matching antennas like end-fed wire antennas to coaxial feeders, and impedance transformation. |
| Signal Type | Balanced to unbalanced | Unbalanced to unbalanced |
| Impedance Transformation | Possible, but primary role is signal conversion. | Primarily for impedance transformation. |
| Typical Impedance Ratios | 1:1, 4:1, 9:1 commonly used | 1:1, 4:1, 9:1 commonly used |
| Physical Construction | Uses toroidal ferrite core with windings to isolate balanced and unbalanced ports. | Similar core but windings maintain unbalanced configuration. |
Introduction to Balun and Unun
Balun, short for balanced to unbalanced transformer, is used to connect balanced transmission lines to unbalanced devices, ensuring proper impedance matching and signal transfer. Unun, meaning unbalanced to unbalanced transformer, transforms impedance between unbalanced lines, commonly applied in antenna systems and RF circuits. These components are essential for optimizing signal integrity and minimizing interference in radio frequency applications.
Understanding the Role of Balun
A balun (balanced to unbalanced transformer) is essential in RF and antenna systems to convert signals between balanced and unbalanced lines, reducing signal loss and minimizing interference. Unlike an unun that matches unbalanced lines, the balun maintains proper impedance and phase balance, improving system efficiency and signal integrity. Baluns are widely used in applications such as dipole antennas, coaxial cable feeds, and differential signal transmission to ensure optimal performance.
Exploring the Function of Unun
An unun (short for unbalanced to unbalanced transformer) is a type of RF transformer used to match impedance between an unbalanced source and an unbalanced load, commonly in antenna systems. It differs from a balun, which connects balanced and unbalanced devices, by specifically transforming impedances within unbalanced circuits. Understanding the function of an unun helps you optimize antenna performance and reduce signal loss in your RF applications.
Key Differences Between Balun and Unun
Balun and unun are both impedance transformers used in antenna and RF systems, but balun (balanced to unbalanced) converts signals between balanced and unbalanced lines, while unun (unbalanced to unbalanced) matches impedance between two unbalanced lines. Baluns typically have symmetrical windings and commonly transform 1:1, 4:1, or 9:1 impedance ratios, whereas ununs often handle a wider range of impedance transformations like 1:4 or 1:9 for unbalanced coaxial cables. Understanding these key differences helps optimize Your antenna system for efficient signal transmission and reduced interference.
Types of Baluns and Their Applications
Baluns, such as voltage baluns, current baluns, and transformer baluns, serve different purposes in RF and antenna systems by matching unbalanced coaxial feeds to balanced antennas. Voltage baluns provide balanced voltage outputs while current baluns ensure balanced current distribution for reduced noise and signal interference. Transformer baluns use ferrite cores to achieve impedance transformation and isolation, making them ideal for various amateur radio, broadcasting, and communication applications.
Types of Ununs and Common Uses
Ununs (unbalanced to unbalanced transformers) come in various types such as 1:1, 4:1, and 9:1 impedance ratios, designed to match different antenna systems and feedlines. Commonly used in HF and shortwave radio setups, ununs help improve signal strength and reduce noise by balancing impedance between unbalanced coaxial cables and unbalanced antennas. Your choice of unun depends on the desired impedance transformation and the specific antenna type to optimize transmission efficiency.
How to Choose: Balun vs Unun
Choosing between a balun and an unun depends primarily on the type of antenna and feed line used. A balun (balanced to unbalanced) matches balanced antennas, like dipoles, to unbalanced coaxial cables, reducing feed line radiation and interference. An unun (unbalanced to unbalanced) is ideal for unbalanced antennas, such as end-fed wires, ensuring impedance transformation and efficient power transfer from the transmitter to the antenna.
Installation Guidelines for Balun and Unun
Proper installation of a balun requires connecting the device between the balanced antenna and the unbalanced transmission line, ensuring secure grounding to minimize interference. For an unun, install it directly at the antenna feed point to match impedance between unbalanced loads, keeping feed lines short to reduce signal loss. Your setup benefits from following manufacturer guidelines on placement and secure connections to optimize performance for both balun and unun applications.
Performance Comparison: Efficiency and Bandwidth
Baluns generally offer higher efficiency and wider bandwidth compared to ununs, as they provide impedance transformation while maintaining balanced to unbalanced signal conversion. Ununs typically focus on impedance matching for unbalanced lines but may introduce more insertion loss and narrower bandwidth due to their simpler construction. Performance in specific applications varies, so choosing between balun and unun depends on the required impedance transformation ratio and frequency range.
Frequently Asked Questions about Balun and Unun
Balun and unun devices serve different purposes in antenna systems: baluns convert balanced signals to unbalanced, while ununs perform unbalanced-to-unbalanced impedance matching. You often wonder which to choose based on your antenna's feedline type and impedance requirements. Understanding their roles helps optimize signal transmission and reduce interference in your radio setup.
Balun vs unun Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com