Mixer spurs are unwanted frequency components generated by nonlinear mixing in radio frequency systems, causing interference that degrades signal clarity. Understanding the causes and effects of LO leakage helps you minimize these spurs and improve overall system performance; read on to explore effective mitigation techniques.
Table of Comparison
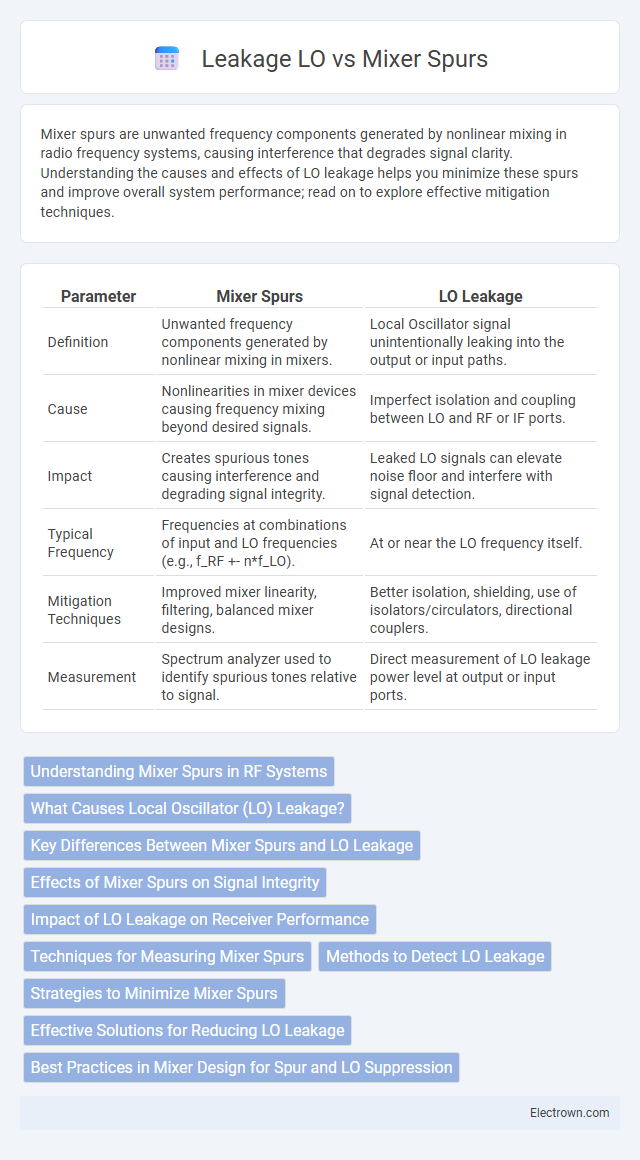
| Parameter | Mixer Spurs | LO Leakage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwanted frequency components generated by nonlinear mixing in mixers. | Local Oscillator signal unintentionally leaking into the output or input paths. |
| Cause | Nonlinearities in mixer devices causing frequency mixing beyond desired signals. | Imperfect isolation and coupling between LO and RF or IF ports. |
| Impact | Creates spurious tones causing interference and degrading signal integrity. | Leaked LO signals can elevate noise floor and interfere with signal detection. |
| Typical Frequency | Frequencies at combinations of input and LO frequencies (e.g., f_RF +- n*f_LO). | At or near the LO frequency itself. |
| Mitigation Techniques | Improved mixer linearity, filtering, balanced mixer designs. | Better isolation, shielding, use of isolators/circulators, directional couplers. |
| Measurement | Spectrum analyzer used to identify spurious tones relative to signal. | Direct measurement of LO leakage power level at output or input ports. |
Understanding Mixer Spurs in RF Systems
Mixer spurs in RF systems arise from nonlinear mixing of signals, creating unwanted spectral components at frequencies that are combinations of input signals and local oscillator (LO) leakage. These spurious signals degrade system performance by introducing interference and reducing signal-to-noise ratio, complicating signal integrity and demodulation. Understanding the mechanisms behind mixer spurs and their relationship with LO leakage enables engineers to design more effective filtering and isolation techniques in RF transceiver architectures.
What Causes Local Oscillator (LO) Leakage?
Local Oscillator (LO) leakage occurs when a portion of the LO signal unintentionally couples into the mixer output or input, causing unwanted interference. This leakage is primarily caused by imperfect isolation between the LO port and the RF or IF ports within the mixer, often due to component non-idealities or poor circuit design. Your system's performance can be compromised by LO leakage, leading to signal distortion and reduced dynamic range.
Key Differences Between Mixer Spurs and LO Leakage
Mixer spurs are unwanted frequency components that appear at the output of a mixer due to nonlinear mixing of the input signals, often manifesting as intermodulation products. LO leakage specifically refers to the unintended transmission of the local oscillator signal into the output or other parts of the system, causing signal contamination and interference. The key difference lies in their origin: mixer spurs arise from harmonic mixing processes, while LO leakage is a direct leakage of the local oscillator signal itself.
Effects of Mixer Spurs on Signal Integrity
Mixer spurs introduce unwanted spectral components that degrade signal integrity by causing distortion and interference in communication systems. These spurious signals increase noise floor and reduce the signal-to-noise ratio, leading to potential data loss or errors in your wireless transmission. Minimizing mixer spurs is essential for maintaining high-quality, reliable signal processing and overall system performance.
Impact of LO Leakage on Receiver Performance
LO leakage in mixers significantly affects receiver performance by introducing unwanted DC offsets and spurious signals, which degrade signal integrity and reduce sensitivity. Elevated LO leakage can cause mixer port voltage imbalances, increasing noise floor and distortion, thus impairing accurate signal demodulation. Mitigating LO leakage through careful mixer design and isolation techniques enhances overall receiver dynamic range and linearity.
Techniques for Measuring Mixer Spurs
Measuring mixer spurs involves using a spectrum analyzer to identify and quantify undesired spurious signals generated by nonlinear mixing in your RF system. Techniques such as two-tone testing and intermodulation distortion (IMD) analysis help isolate spurs by applying specific input frequencies and analyzing the output spectrum. Precise calibration of test equipment and careful selection of frequency offsets improve the accuracy of spur measurements in LO leakage scenarios.
Methods to Detect LO Leakage
LO leakage detection methods primarily include spectrum analysis using a high-frequency spectrum analyzer to identify spurious signals at the LO frequency. Time-domain reflectometry and vector network analysis can characterize the leakage path and quantify signal integrity. Employing harmonic balance simulations and near-field scanning further aids in pinpointing leakage sources within mixer circuits.
Strategies to Minimize Mixer Spurs
Minimizing mixer spurs involves implementing careful frequency planning to avoid overlapping harmonics and intermodulation products that generate unwanted signals. Using high-quality filters and ensuring proper impedance matching reduces spurious emissions by attenuating out-of-band frequencies effectively. Your system's performance can be optimized by selecting mixers with superior linearity and utilizing balanced mixer configurations to suppress even-order harmonic spurs.
Effective Solutions for Reducing LO Leakage
Effective solutions for reducing LO leakage in mixer spurs include implementing balanced mixer designs that cancel out undesired signals through symmetry. Utilizing isolation techniques such as shielding, use of buffer amplifiers, and proper layout optimization additionally minimize leakage paths. Your RF system performance improves significantly by integrating high-quality components and applying LO filtering to suppress spurious emissions effectively.
Best Practices in Mixer Design for Spur and LO Suppression
Effective mixer design for spur and LO leakage suppression involves implementing balanced or double-balanced topologies that inherently cancel unwanted signals, minimizing spurious emissions. Utilizing high-quality filters and isolators at both the RF and LO ports helps reduce leakage paths, improving overall signal purity. You can further enhance performance by carefully selecting mixers with superior port-to-port isolation and optimizing PCB layout to prevent parasitic coupling.
Mixer Spurs vs LO Leakage Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com