SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) offers a cost-effective, manual approach to measuring transmission lines' parameters, while VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) delivers precise, automated, and frequency-resolved characterization of complex RF components and networks. Discover how choosing the right instrument can enhance Your measurement accuracy and efficiency by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
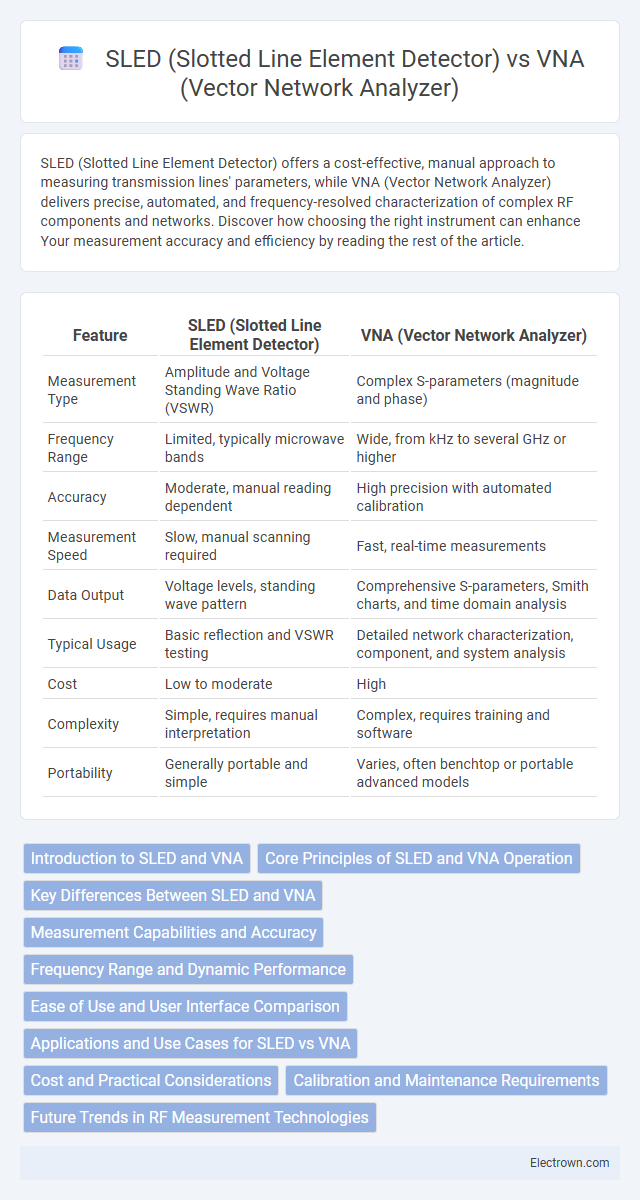
| Feature | SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) | VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Type | Amplitude and Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR) | Complex S-parameters (magnitude and phase) |
| Frequency Range | Limited, typically microwave bands | Wide, from kHz to several GHz or higher |
| Accuracy | Moderate, manual reading dependent | High precision with automated calibration |
| Measurement Speed | Slow, manual scanning required | Fast, real-time measurements |
| Data Output | Voltage levels, standing wave pattern | Comprehensive S-parameters, Smith charts, and time domain analysis |
| Typical Usage | Basic reflection and VSWR testing | Detailed network characterization, component, and system analysis |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High |
| Complexity | Simple, requires manual interpretation | Complex, requires training and software |
| Portability | Generally portable and simple | Varies, often benchtop or portable advanced models |
Introduction to SLED and VNA
SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) is a traditional microwave measurement device used to determine voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR), reflection coefficients, and impedance by manually detecting electric field variations along a transmission line. VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) is an advanced, automated instrument that measures complex scattering parameters (S-parameters) across a wide frequency range, providing comprehensive network characterization with high accuracy and speed. Your choice between SLED and VNA depends on the required measurement precision, frequency range, and the complexity of the network analysis.
Core Principles of SLED and VNA Operation
SLED operates by detecting standing wave patterns along a transmission line using a movable probe to measure voltage minima and maxima, enabling the calculation of reflection coefficients and impedance. VNA functions by generating and analyzing both the magnitude and phase of incident and reflected signals across a frequency spectrum, providing comprehensive scattering parameters (S-parameters) for detailed device characterization. The key distinction lies in SLED's reliance on physical measurements of waveform variations versus VNA's digital processing of complex signal data for precise, wideband network analysis.
Key Differences Between SLED and VNA
A SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) primarily measures reflection coefficients and voltage standing wave ratios (VSWR) using a mechanical probe along a transmission line, offering high accuracy in narrow frequency ranges. In contrast, a VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) provides comprehensive S-parameter measurements, including magnitude and phase across broad frequency spectrums, enabling detailed analysis of complex impedance and network behavior. Your choice between SLED and VNA depends on the required measurement scope, frequency range, and the level of detail needed for device characterization.
Measurement Capabilities and Accuracy
The Slotted Line Element Detector (SLED) provides accurate measurement of standing wave ratio (SWR) and reflection coefficients with high sensitivity in narrow frequency ranges, ideal for simple impedance characterization. In contrast, the Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) offers broad frequency sweep capabilities, enabling comprehensive S-parameter measurements, phase, and magnitude analysis with high precision and dynamic range across wide bandwidths. While SLED excels in basic reflection measurements with minimal setup, VNAs deliver superior accuracy and multi-port network analysis critical for advanced RF and microwave applications.
Frequency Range and Dynamic Performance
SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) typically operates in a narrower frequency range, often limited to microwave frequencies up to around 40 GHz, while VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) supports a much broader frequency range extending from low MHz through mmWave frequencies, beyond 110 GHz in advanced models. The dynamic performance of a VNA surpasses that of a SLED, offering higher measurement accuracy, superior sensitivity, faster sweep speeds, and enhanced dynamic range, which is critical for characterizing complex RF components and systems. Your choice between SLED and VNA should consider the specific frequency range required and the precision needed for your measurements.
Ease of Use and User Interface Comparison
SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) requires manual calibration and interpretation, making it less intuitive for beginners compared to a VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) that offers automated measurements with graphical user interfaces for real-time analysis and simplified operation. VNAs provide interactive touchscreens or software integrations that enhance user experience through visual feedback, while SLEDs rely on physical adjustments and external instruments, increasing complexity. Your testing efficiency improves significantly with a VNA, as it minimizes setup time and reduces human error through its advanced user interface.
Applications and Use Cases for SLED vs VNA
SLEDs (Slotted Line Element Detectors) are primarily used for simple, cost-effective measurements of standing wave ratios (SWR) and voltage distributions along transmission lines, making them ideal for basic antenna tuning and educational purposes. VNAs (Vector Network Analyzers), however, provide comprehensive S-parameter measurements, enabling precise analysis of complex RF components such as filters, amplifiers, and antennas, essential for advanced design and verification in professional labs. Your choice depends on the required measurement accuracy and application complexity, with SLED suited for straightforward diagnostics and VNA preferred for detailed, high-precision characterizations.
Cost and Practical Considerations
SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) is significantly more affordable than a VNA (Vector Network Analyzer), making it suitable for basic impedance and reflection measurements in budget-constrained settings. However, VNAs offer extensive functionality, including complex S-parameter measurements and automated calibration, which greatly improves accuracy and efficiency in professional environments. Your choice depends on balancing cost constraints against the need for detailed, high-precision network analysis.
Calibration and Maintenance Requirements
SLEDs (Slotted Line Element Detectors) require manual calibration using known standards, often demanding frequent adjustments to maintain accuracy due to sensitivity to environmental factors. VNAs (Vector Network Analyzers) feature automated calibration routines with built-in error correction, significantly reducing maintenance efforts and ensuring more consistent measurement reliability. For your testing needs, VNAs offer superior calibration convenience and lower maintenance, making them preferable for precision and efficiency.
Future Trends in RF Measurement Technologies
Future trends in RF measurement technologies emphasize enhanced accuracy and integration, with Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) advancing through improved digital signal processing, wider frequency ranges, and real-time data analysis. SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) devices continue to serve niche applications requiring simplicity and cost-effectiveness but face limitations in precision and automation compared to VNAs. Emerging developments in AI-driven diagnostics and miniaturized components are expected to further push VNAs as the preferred solution for complex RF characterization and automated testing environments.
SLED (Slotted Line Element Detector) vs VNA (Vector Network Analyzer) Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com