Oscillators generate raw sound waves by producing basic audio signals such as sine, square, or sawtooth waves, while synthesizers use these oscillators as building blocks to create complex, layered sounds through modulation, filtering, and effects. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your sound design skills can benefit from mastering both tools.
Table of Comparison
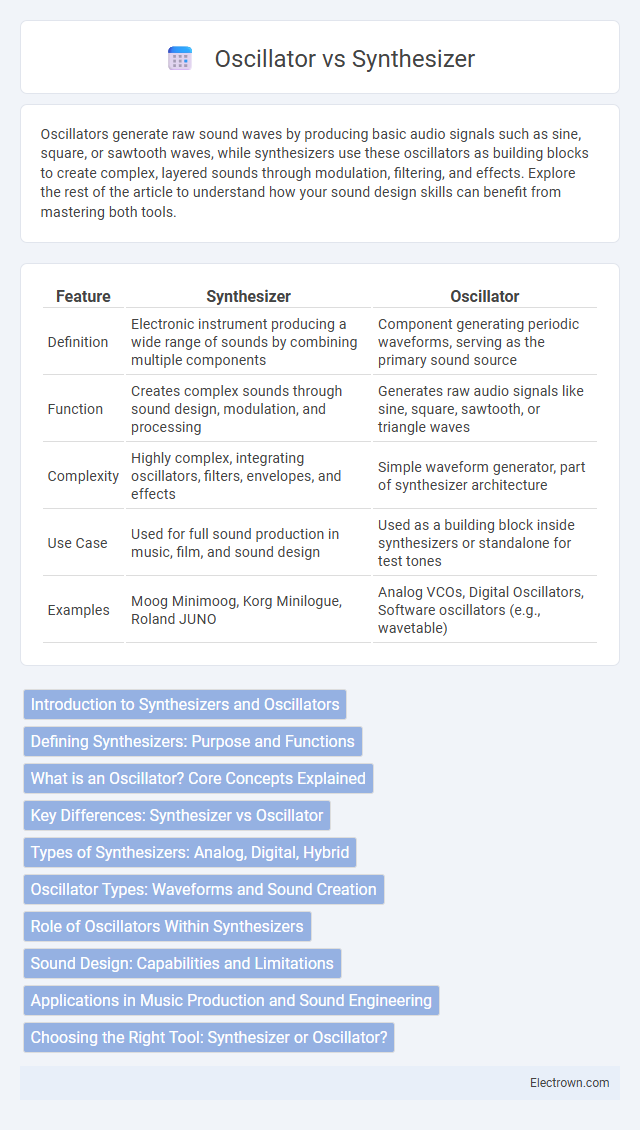
| Feature | Synthesizer | Oscillator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Electronic instrument producing a wide range of sounds by combining multiple components | Component generating periodic waveforms, serving as the primary sound source |
| Function | Creates complex sounds through sound design, modulation, and processing | Generates raw audio signals like sine, square, sawtooth, or triangle waves |
| Complexity | Highly complex, integrating oscillators, filters, envelopes, and effects | Simple waveform generator, part of synthesizer architecture |
| Use Case | Used for full sound production in music, film, and sound design | Used as a building block inside synthesizers or standalone for test tones |
| Examples | Moog Minimoog, Korg Minilogue, Roland JUNO | Analog VCOs, Digital Oscillators, Software oscillators (e.g., wavetable) |
Introduction to Synthesizers and Oscillators
Synthesizers generate audio signals using various components, with oscillators serving as the core sound source by producing basic waveforms like sine, square, and sawtooth waves. Oscillators create raw tones that synthesizers shape and modulate through filters, envelopes, and effects to form complex sounds. Understanding the relationship between oscillators and synthesizers enhances your ability to design and manipulate electronic music effectively.
Defining Synthesizers: Purpose and Functions
Synthesizers are electronic instruments designed to generate and shape complex sounds by combining various audio signals and modulating parameters such as amplitude, frequency, and timbre. Unlike oscillators, which produce simple waveforms like sine, square, or sawtooth waves, synthesizers integrate multiple oscillators, filters, envelopes, and effects to create rich, dynamic tones tailored for music production and sound design. Your ability to manipulate these components enables the creation of unique auditory textures suited for diverse genres and applications.
What is an Oscillator? Core Concepts Explained
An oscillator is a fundamental electronic component in sound synthesis that generates repetitive waveforms such as sine, square, triangle, or sawtooth waves, forming the raw sound source in synthesizers. It operates by converting direct current into alternating current at specific frequencies, allowing control over pitch and timbre in music production. Understanding oscillators is essential for manipulating waveform shapes and modulation to create diverse sonic textures within synthesizers.
Key Differences: Synthesizer vs Oscillator
A synthesizer is a complex electronic instrument that generates and combines multiple sound waves, including oscillators, filters, and modulators, to create rich audio textures. An oscillator is a fundamental component within a synthesizer, producing a basic waveform such as sine, square, or sawtooth, which serves as the raw sound source. The key difference lies in functionality: oscillators generate simple tones, while synthesizers manipulate and shape those tones into diverse and dynamic sounds.
Types of Synthesizers: Analog, Digital, Hybrid
Analog synthesizers generate sound using voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs) and filters, producing warm, rich tones favored in classic music production. Digital synthesizers utilize digital signal processing techniques and oscillators to create a wide variety of sounds, offering precise control and versatility. Hybrid synthesizers combine analog oscillators with digital components, blending the warmth of analog sound with modern digital flexibility.
Oscillator Types: Waveforms and Sound Creation
Oscillators generate raw sound waves fundamental to synthesizer tones, with common waveform types including sine, square, sawtooth, and triangle, each producing distinct timbres and harmonic content. Sine waves offer pure tones ideal for bass and sub-bass sounds, while sawtooth waves provide rich harmonics suited for brass and string emulations. Your choice of oscillator waveform directly shapes your sound creation, influencing the texture and character of synthesized audio.
Role of Oscillators Within Synthesizers
Oscillators serve as the foundational sound generators within synthesizers, producing raw audio waveforms such as sine, square, sawtooth, and triangle waves that define the basic tonal character. Synthesizers rely on multiple oscillators to create complex timbres through layering, detuning, and modulation, enabling rich and dynamic sound design. The interaction and modulation of oscillators within filters, envelopes, and LFOs shape the final audio output, making oscillators essential components in synthesizer architecture.
Sound Design: Capabilities and Limitations
Synthesizers offer a comprehensive sound design platform by integrating multiple oscillators, filters, and modulators, enabling complex timbral creation and dynamic modulation. Oscillators serve as the fundamental sound sources, generating basic waveforms like sine, square, and sawtooth, but lack standalone sound-shaping features found in synthesizers. This difference highlights synthesizers' superior flexibility in crafting evolving textures compared to the static tones produced by individual oscillators.
Applications in Music Production and Sound Engineering
Synthesizers and oscillators play distinct roles in music production and sound engineering, with synthesizers serving as comprehensive instruments that generate and shape complex sounds through multiple oscillators, filters, and modulators. Oscillators function as the core sound source within synthesizers, producing basic waveforms like sine, square, and sawtooth that form the foundation of tonal textures. Understanding how your synthesizer's oscillators interact enhances sound design possibilities and allows for tailored audio creation in studio production and live performance settings.
Choosing the Right Tool: Synthesizer or Oscillator?
Choosing between a synthesizer and an oscillator depends on your music production goals and the complexity of sounds you wish to create. A synthesizer offers an all-in-one solution with built-in modulation, filters, and effects to shape your sound, ideal for crafting complete tracks or intricate textures. An oscillator, by contrast, is the fundamental sound source that you can integrate into modular setups or hardware synths, giving you granular control over basic waveforms to build customized tones from the ground up.
Synthesizer vs Oscillator Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com