Enhancement mode transistors remain off at zero gate voltage and require a positive voltage to conduct, while depletion mode transistors are normally on and need a negative gate voltage to switch off. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right transistor for your circuit design, so explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
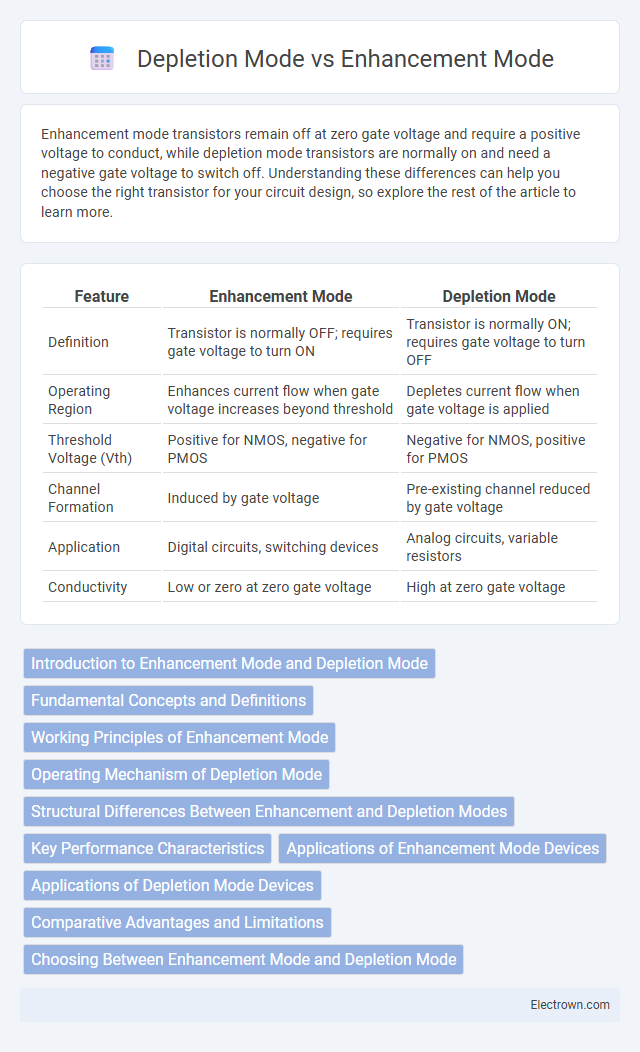
| Feature | Enhancement Mode | Depletion Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Transistor is normally OFF; requires gate voltage to turn ON | Transistor is normally ON; requires gate voltage to turn OFF |
| Operating Region | Enhances current flow when gate voltage increases beyond threshold | Depletes current flow when gate voltage is applied |
| Threshold Voltage (Vth) | Positive for NMOS, negative for PMOS | Negative for NMOS, positive for PMOS |
| Channel Formation | Induced by gate voltage | Pre-existing channel reduced by gate voltage |
| Application | Digital circuits, switching devices | Analog circuits, variable resistors |
| Conductivity | Low or zero at zero gate voltage | High at zero gate voltage |
Introduction to Enhancement Mode and Depletion Mode
Enhancement mode and depletion mode refer to two types of MOSFET operation characterized by the behavior of the channel under zero gate-to-source voltage. In enhancement mode MOSFETs, the transistor is normally off, requiring a positive gate voltage to induce a conductive channel. In depletion mode MOSFETs, the device is normally on, with a conductive channel formed at zero gate bias, and a negative gate voltage depletes carriers to switch it off.
Fundamental Concepts and Definitions
Enhancement mode transistors require a positive gate voltage to induce a conductive channel, operating normally in an off state without gate bias, while depletion mode transistors have a conductive channel at zero gate voltage that can be turned off by applying a negative gate voltage. Enhancement mode MOSFETs function as normally-off devices, utilizing gate voltage to enhance channel conductivity, whereas depletion mode MOSFETs are normally-on devices, relying on gate voltage polarity to deplete carriers and reduce current flow. Understanding these fundamental operational differences is crucial for selecting appropriate transistor types in digital and analog circuit designs.
Working Principles of Enhancement Mode
Enhancement mode MOSFETs operate by applying a positive gate-to-source voltage to induce a conductive channel in an initially non-conductive semiconductor substrate. This voltage attracts electrons (N-channel) or holes (P-channel), increasing channel conductivity and allowing current flow between drain and source terminals. The device remains off at zero gate bias and turns on only when the gate voltage exceeds a specific threshold voltage.
Operating Mechanism of Depletion Mode
Depletion mode transistors operate by default with a conducting channel that allows current to flow even without any gate voltage applied. Applying a gate voltage of opposite polarity depletes the channel of charge carriers, thereby reducing or completely stopping current flow through the device. Your understanding of this operating mechanism is crucial for selecting the right transistor type in analog switching and amplification circuits.
Structural Differences Between Enhancement and Depletion Modes
Enhancement mode transistors feature a normally off channel that requires a positive gate voltage to induce conduction, while depletion mode transistors have a normally on channel that can be turned off by applying a negative gate voltage. The key structural difference lies in the channel doping: enhancement mode devices have an undoped or lightly doped channel region, whereas depletion mode devices possess a heavily doped channel to maintain conductivity without gate bias. Your choice between these modes depends on the application's switching requirements and power efficiency considerations.
Key Performance Characteristics
Enhancement mode devices require a positive gate-to-source voltage to conduct, offering high input impedance and low leakage current, making them ideal for switching applications. Depletion mode devices conduct at zero gate bias and require a negative gate voltage to turn off, providing normally-on operation and fast response times suitable for analog circuits. Understanding these key performance characteristics allows you to select the right MOSFET type for your specific power and signal control needs.
Applications of Enhancement Mode Devices
Enhancement mode devices, such as MOSFETs, are widely used in digital circuits, power amplifiers, and switching power supplies due to their ability to remain off when the gate-to-source voltage is zero, enabling efficient low-power operation. These devices are preferred in microprocessors and memory chips for fast switching speeds and high input impedance characteristics. Enhancement mode transistors dominate in applications requiring precise control of current flow and minimal leakage currents, enhancing overall circuit performance and energy efficiency.
Applications of Depletion Mode Devices
Depletion mode devices are widely used in analog circuits such as voltage regulators, current limiters, and load switches due to their normally-on characteristic, which allows conduction without gate voltage. Their capability to operate as resistive elements in linear regions makes them ideal for use in programmable resistors and analog signal processing. You can find depletion mode transistors in power control applications where fail-safe operation is essential, ensuring devices remain active unless explicitly turned off.
Comparative Advantages and Limitations
Enhancement mode transistors offer low power consumption and are typically easier to control because they require a positive gate voltage to conduct, making them ideal for switching applications in digital circuits. Depletion mode devices conduct at zero gate voltage and allow for normally-on operation, which can be advantageous for fail-safe designs but may lead to higher static power dissipation. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy efficiency and ease of control with enhancement mode or the inherent conduction capabilities and reliability of depletion mode transistors.
Choosing Between Enhancement Mode and Depletion Mode
Selecting between enhancement mode and depletion mode transistors depends on the required switching characteristics and circuit design. Enhancement mode devices remain off at zero gate voltage and activate when a positive voltage is applied, making them ideal for low-power and digital switching applications. Depletion mode transistors conduct at zero gate voltage and turn off with a gate bias, providing fail-safe operation and analog signal control in specific circuits.
Enhancement mode vs depletion mode Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com