Active filters use external power sources like batteries or amplifiers to enhance signal strength and provide precise frequency control, while passive filters rely solely on passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors without amplification. Discover how understanding the differences between these filters can improve Your electronic circuit designs by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
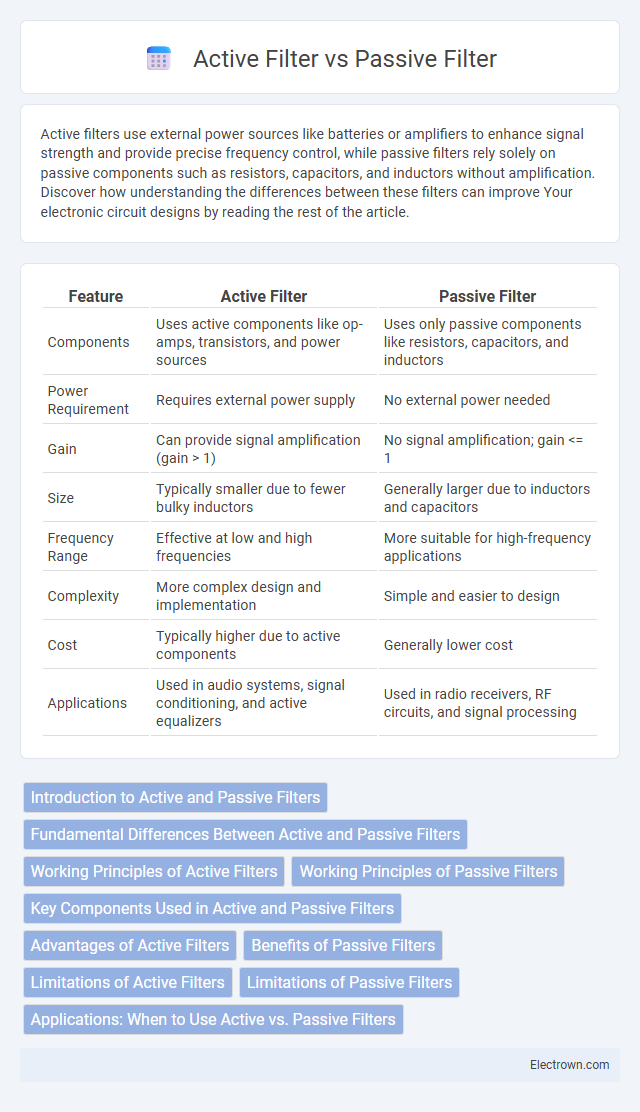
| Feature | Active Filter | Passive Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Components | Uses active components like op-amps, transistors, and power sources | Uses only passive components like resistors, capacitors, and inductors |
| Power Requirement | Requires external power supply | No external power needed |
| Gain | Can provide signal amplification (gain > 1) | No signal amplification; gain <= 1 |
| Size | Typically smaller due to fewer bulky inductors | Generally larger due to inductors and capacitors |
| Frequency Range | Effective at low and high frequencies | More suitable for high-frequency applications |
| Complexity | More complex design and implementation | Simple and easier to design |
| Cost | Typically higher due to active components | Generally lower cost |
| Applications | Used in audio systems, signal conditioning, and active equalizers | Used in radio receivers, RF circuits, and signal processing |
Introduction to Active and Passive Filters
Active filters utilize operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors to amplify and filter signals without requiring inductors, enabling precise control over frequency response. Passive filters rely solely on resistors, capacitors, and inductors, operating without external power sources but often experiencing signal attenuation and limited gain. The choice between active and passive filters depends on factors such as desired frequency range, power consumption, signal integrity, and component size.
Fundamental Differences Between Active and Passive Filters
Active filters use powered components like operational amplifiers, transistors, or integrated circuits to amplify and manipulate signals, while passive filters rely solely on resistors, capacitors, and inductors without external power. Active filters can provide gain and better control over frequency response, making them suitable for low-frequency applications, whereas passive filters are limited to signal attenuation and are preferred for high-power or high-frequency situations. Your choice between active and passive filters depends on requirements such as signal amplification, power consumption, and frequency characteristics.
Working Principles of Active Filters
Active filters use operational amplifiers, capacitors, and resistors to amplify and shape signals without requiring inductors, enabling precise control over frequency response. These filters leverage powered components to provide gain, improving signal strength and allowing for better filtering performance compared to passive filters. Your audio or signal processing system benefits from active filters' ability to deliver stable, tunable frequency characteristics with minimal signal loss.
Working Principles of Passive Filters
Passive filters operate using only passive components such as resistors, inductors, and capacitors to attenuate or pass specific frequency ranges without requiring an external power source. Their working principle involves shaping signal frequencies based on the inherent impedance and reactance of these components, creating selective paths for certain frequencies to be blocked or allowed. You should consider passive filters for simple frequency filtering tasks where power consumption and component cost need to remain low.
Key Components Used in Active and Passive Filters
Active filters use operational amplifiers, resistors, and capacitors as their key components, enabling signal amplification without external power sources. Passive filters rely solely on resistors, capacitors, and inductors, which do not provide gain and depend on the input signal's power. Your choice between active and passive filters depends on the desired signal processing capabilities and component complexity.
Advantages of Active Filters
Active filters offer superior gain control and signal amplification without the need for inductors, making them more compact and easier to integrate into electronic circuits. They provide higher input impedance and lower output impedance, ensuring minimal signal loss and better interfacing with other components. Compared to passive filters, active filters enable precise frequency response tuning and improved stability across a wide range of frequencies.
Benefits of Passive Filters
Passive filters offer benefits such as simple design, low cost, and high reliability due to the absence of active components like transistors or op-amps. They function without external power sources, making them energy-efficient and suitable for harsh environments. Their durability and ease of maintenance make passive filters ideal for applications requiring robust and stable frequency selection.
Limitations of Active Filters
Active filters face limitations such as restricted power handling capabilities and potential distortion at high frequencies, which can affect signal integrity in demanding applications. They rely on external power sources, introducing noise and requiring careful power management, unlike passive filters that operate without power. Your choice between active and passive filters should consider these constraints alongside factors like frequency range and signal amplitude.
Limitations of Passive Filters
Passive filters, composed solely of resistors, capacitors, and inductors, face limitations such as signal attenuation and lack of amplification, which can reduce overall system performance. They are unable to provide gain, making them less effective in applications requiring signal boosting or impedance matching. Your circuit design might require active filters to overcome these constraints by incorporating operational amplifiers for enhanced control and signal integrity.
Applications: When to Use Active vs. Passive Filters
Active filters are preferred in applications requiring signal amplification, precise frequency selection, and low-frequency filtering, such as audio processing, instrumentation, and communication systems. Passive filters are ideal for simple, high-frequency applications where power consumption is critical, like RF circuits and antenna tuning, due to their no-power requirement and inherent reliability. Choosing between active and passive filters depends on performance needs, signal levels, frequency ranges, and power availability in the specific application.
active filter vs passive filter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com