Analog synths generate warm, rich sounds through continuous electrical signals, offering a tactile experience favored by many musicians for its organic tone and subtle imperfections. Digital synths use advanced algorithms and sampling to produce a wide range of sounds with precision and versatility, giving You more options for complex sound design; explore the rest of the article to discover which synth suits Your creative needs.
Table of Comparison
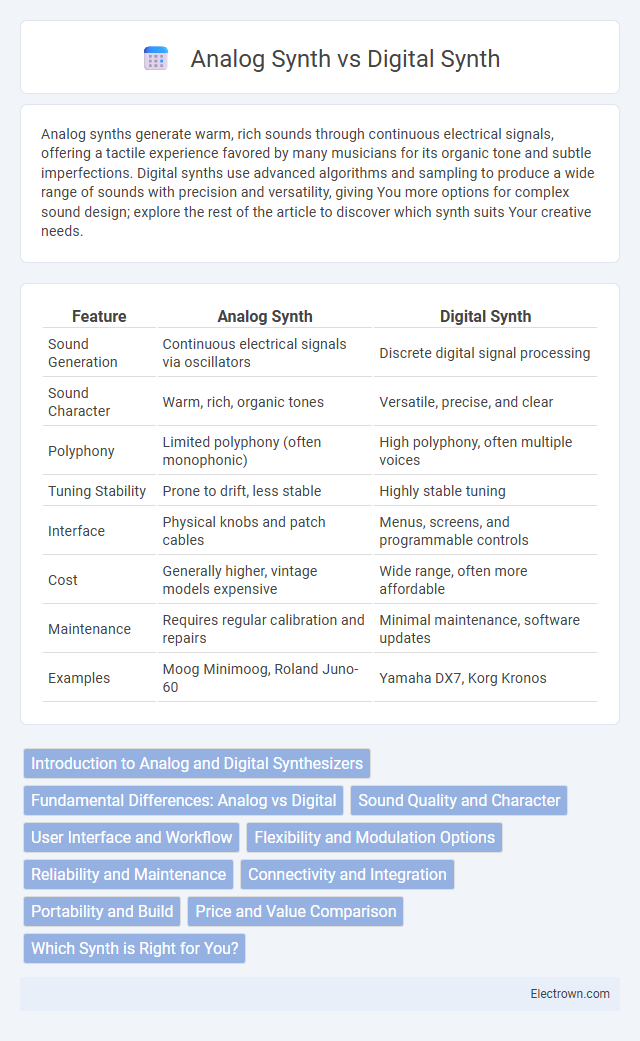
| Feature | Analog Synth | Digital Synth |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Generation | Continuous electrical signals via oscillators | Discrete digital signal processing |
| Sound Character | Warm, rich, organic tones | Versatile, precise, and clear |
| Polyphony | Limited polyphony (often monophonic) | High polyphony, often multiple voices |
| Tuning Stability | Prone to drift, less stable | Highly stable tuning |
| Interface | Physical knobs and patch cables | Menus, screens, and programmable controls |
| Cost | Generally higher, vintage models expensive | Wide range, often more affordable |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and repairs | Minimal maintenance, software updates |
| Examples | Moog Minimoog, Roland Juno-60 | Yamaha DX7, Korg Kronos |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Synthesizers
Analog synthesizers generate sound using continuous electrical signals through oscillators, filters, and amplifiers, providing warm, rich tones preferred by many musicians for their organic character. Digital synthesizers use digital signal processing (DSP) to create and manipulate sounds via algorithms, offering greater versatility, presets, and the ability to emulate various instruments. Your choice between analog and digital synths depends on whether you prioritize authentic analog warmth or the expansive sound design options that digital technology offers.
Fundamental Differences: Analog vs Digital
Analog synthesizers generate sound through continuous electrical signals processed by voltage-controlled oscillators, filters, and amplifiers, producing warm, rich tones with natural variations. Digital synthesizers create sound using digital signal processing algorithms and samples, offering precise control, extensive modulation options, and the ability to replicate a wide range of sounds with consistent accuracy. The fundamental difference lies in analog synths using hardware-driven electrical waveforms while digital synths rely on computer-based numerical computations for sound creation.
Sound Quality and Character
Analog synths produce rich, warm tones with natural variations due to their continuous voltage-based circuits, offering a distinctive, organic sound character favored by musicians seeking authenticity. Digital synths rely on precise numerical algorithms and sampling, delivering a broader range of sounds with clarity and stability, but sometimes lacking the subtle imperfections that define analog warmth. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the authentic, textured sound of analog or the versatile, consistent output of digital synthesis.
User Interface and Workflow
Analog synths provide tactile control with physical knobs, sliders, and patch cables, fostering intuitive sound design through hands-on manipulation. Digital synths often feature menu-driven interfaces and presets, enabling deep parameter editing and complex modulation options but may slow workflow due to less immediate access. Users prioritizing quick, expressive adjustments may prefer analog, while those seeking versatility and detailed sound sculpting benefit from digital interfaces.
Flexibility and Modulation Options
Analog synths excel in producing warm, rich tones with their voltage-controlled oscillators and filters but often have limited modulation routings compared to digital synths. Digital synths offer extensive flexibility and complex modulation options through multiple LFOs, envelopes, and matrix routing, allowing for intricate sound design and evolving textures. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize hands-on, organic control or vast modulation possibilities for diverse sonic exploration.
Reliability and Maintenance
Analog synths require regular maintenance due to their reliance on physical components like capacitors and oscillators, which may drift or degrade over time, affecting tuning and sound stability. Digital synths offer enhanced reliability with stable performance and minimal upkeep, as their sound generation depends on software algorithms and solid-state electronics less prone to wear. Musicians seeking consistent performance often prefer digital synths for touring, while analog synths appeal to those valuing vintage sound characteristics despite higher maintenance demands.
Connectivity and Integration
Analog synths offer straightforward connectivity through traditional CV/Gate and MIDI interfaces, enabling seamless integration with modular setups and vintage gear. Digital synths provide enhanced connectivity options, including USB, MIDI over USB, and Ethernet, allowing easy integration with modern DAWs, software instruments, and networked audio systems. Hybrid synthesizers combine analog sound generation with digital control and connectivity, maximizing flexibility in diverse studio and live environments.
Portability and Build
Analog synths typically feature robust, often bulky hardware with tactile knobs and patch cables, making them heavier and less portable compared to digital synths. Digital synths leverage compact, lightweight designs and often integrate software components that enhance portability, allowing musicians to easily transport and set up their gear. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the hands-on control and classic sound of analog build or the convenience and versatility offered by digital synth portability.
Price and Value Comparison
Analog synthesizers often carry a higher price tag due to costly vintage components and handcrafted circuitry, appealing to musicians seeking warm, rich sound textures. Digital synthesizers provide better value for budget-conscious buyers, offering versatile sound libraries, advanced features, and easier maintenance at a lower cost. The choice depends on prioritizing authentic analog tonal quality or affordable, multifunctional digital sound production.
Which Synth is Right for You?
Choosing between analog and digital synths depends on your sound preference and workflow: analog synths offer warm, rich tones with hands-on control, ideal for those who value classic, tactile experience. Digital synths provide versatile soundscapes, precise modulation, and extensive presets, perfect for users seeking innovation and flexibility in music production. Your decision should consider whether you prioritize authentic analog warmth or the expansive possibilities of digital synthesis.
analog synth vs digital synth Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com