Darlington pairs offer high current gain by cascading two transistors, making them ideal for applications requiring significant amplification with a simple configuration. Your understanding of these transistor configurations will deepen as you explore the detailed comparison of their performance, advantages, and practical uses in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
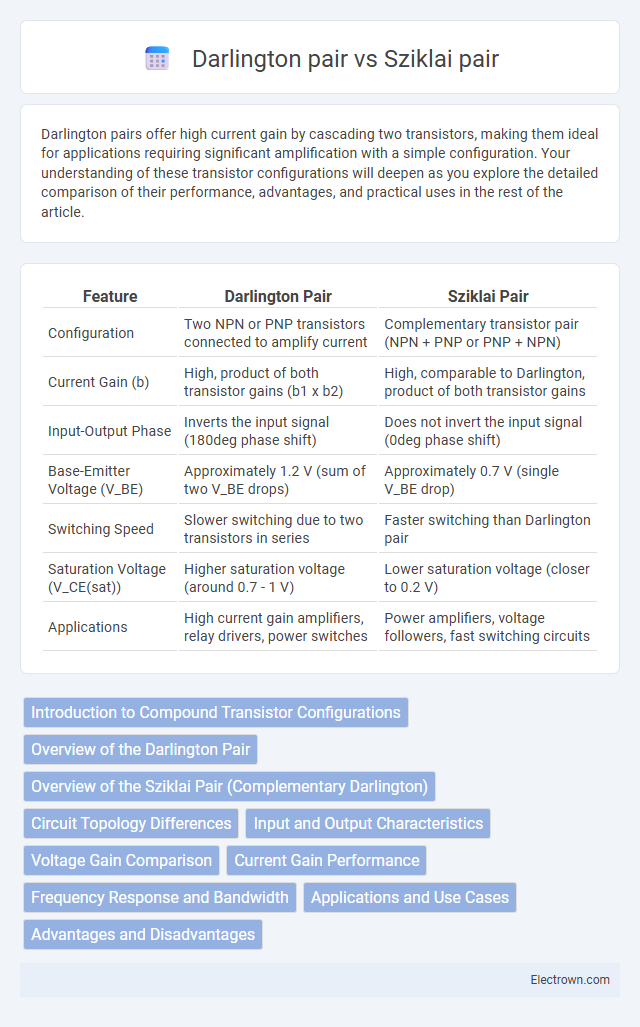
| Feature | Darlington Pair | Sziklai Pair |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | Two NPN or PNP transistors connected to amplify current | Complementary transistor pair (NPN + PNP or PNP + NPN) |
| Current Gain (b) | High, product of both transistor gains (b1 x b2) | High, comparable to Darlington, product of both transistor gains |
| Input-Output Phase | Inverts the input signal (180deg phase shift) | Does not invert the input signal (0deg phase shift) |
| Base-Emitter Voltage (V_BE) | Approximately 1.2 V (sum of two V_BE drops) | Approximately 0.7 V (single V_BE drop) |
| Switching Speed | Slower switching due to two transistors in series | Faster switching than Darlington pair |
| Saturation Voltage (V_CE(sat)) | Higher saturation voltage (around 0.7 - 1 V) | Lower saturation voltage (closer to 0.2 V) |
| Applications | High current gain amplifiers, relay drivers, power switches | Power amplifiers, voltage followers, fast switching circuits |
Introduction to Compound Transistor Configurations
Compound transistor configurations enhance amplifier performance by combining two bipolar junction transistors to achieve higher current gain and improved input/output characteristics. The Darlington pair features two NPN or PNP transistors connected so the current amplified by the first is further amplified by the second, resulting in a high overall current gain but with increased voltage drop. The Sziklai pair, also known as the complementary feedback pair, uses transistors of opposite types (NPN and PNP) to provide similar current gain with lower saturation voltage and improved switching performance.
Overview of the Darlington Pair
The Darlington pair consists of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected to provide high current gain by combining their current amplification factors. This configuration allows a small base current to control a much larger collector current, making it ideal for applications requiring high input impedance and power amplification. Your choice between a Darlington pair and a Sziklai pair depends on factors such as voltage drop, switching speed, and complexity in your circuit design.
Overview of the Sziklai Pair (Complementary Darlington)
The Sziklai pair, also known as the complementary Darlington, combines two transistors of opposite types (NPN and PNP) to achieve high current gain with improved bandwidth and lower saturation voltage compared to a traditional Darlington pair. This configuration offers better switching speed and efficiency, making it suitable for applications where minimizing power loss and distortion is crucial. Understanding the Sziklai pair can enhance your circuit design by leveraging its complementary transistor arrangement for optimized performance.
Circuit Topology Differences
The Darlington pair consists of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected in a way that the current amplified by the first transistor is further amplified by the second, resulting in a high current gain with both transistor emitters tied together. The Sziklai pair, also known as the complementary feedback pair, combines an NPN and a PNP transistor, enabling a similar high current gain but with improved input voltage characteristics and simpler biasing. Understanding these circuit topology differences helps optimize your amplifier design for stability and efficiency in various electronic applications.
Input and Output Characteristics
The Darlington pair exhibits high input impedance and a significant current gain due to its two-transistor configuration, making it ideal for amplifying weak signals. The Sziklai pair, also known as the complementary feedback pair, offers similar current gain but provides better linearity and a lower base-emitter voltage drop, improving efficiency in switching applications. Both configurations deliver high output current capability, but the Sziklai pair often results in reduced saturation voltage, enhancing performance in power amplifier circuits.
Voltage Gain Comparison
The Darlington pair typically offers a higher voltage gain than the Sziklai pair due to its cascading transistor configuration, which multiplies the current gain of both transistors. However, the Sziklai pair can achieve similar voltage gain with fewer saturation voltage drops, improving efficiency in low-voltage applications. Your choice between these pairs depends on whether maximum gain or energy efficiency is the priority in the circuit design.
Current Gain Performance
Darlington pairs typically offer higher current gain by combining two transistors in a cascading configuration, resulting in a gain equal to the product of the individual transistor gains. Sziklai pairs, also known as complementary feedback pairs, provide a comparable current gain but with fewer saturation voltage drops, enhancing efficiency in certain applications. Your choice between these pairs depends on whether maximum current gain or improved voltage performance is more critical for your circuit design.
Frequency Response and Bandwidth
Darlington pairs typically exhibit lower frequency response and reduced bandwidth compared to Sziklai pairs due to the increased base-collector junction capacitance from two transistors in series. Sziklai pairs offer improved high-frequency performance as their configuration minimizes input capacitance and overall gain bandwidth product limitations. Consequently, Sziklai pairs are preferred in applications requiring wider bandwidth and better frequency response in amplification stages.
Applications and Use Cases
Darlington pairs excel in applications requiring high current gain and straightforward amplification, such as in audio amplifiers, relay drivers, and power regulation circuits. Sziklai pairs are favored in situations demanding improved frequency response and lower saturation voltage, making them ideal for precise analog circuits and audio output stages. Both configurations enhance transistor performance but are chosen based on specific requirements like efficiency, switching speed, and linearity in diverse electronic devices.
Advantages and Disadvantages
A Darlington pair offers high current gain and simple design ideal for low-frequency amplification but suffers from increased voltage drop and slower switching speeds. The Sziklai pair provides similar current gain with lower saturation voltage and faster switching performance, yet its complexity and sensitivity to component variations can complicate design and stability. Choosing between these configurations depends on application requirements such as efficiency, switching speed, and circuit simplicity.
Darlington pair vs Sziklai pair Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com