Collector feedback bias occurs when the data collector's expectations or actions influence the information gathered, while base bias refers to errors arising from inaccurate or unrepresentative baseline data used for comparison. Understanding these distinctions can help you recognize potential pitfalls in data analysis and improve the reliability of your conclusions; explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
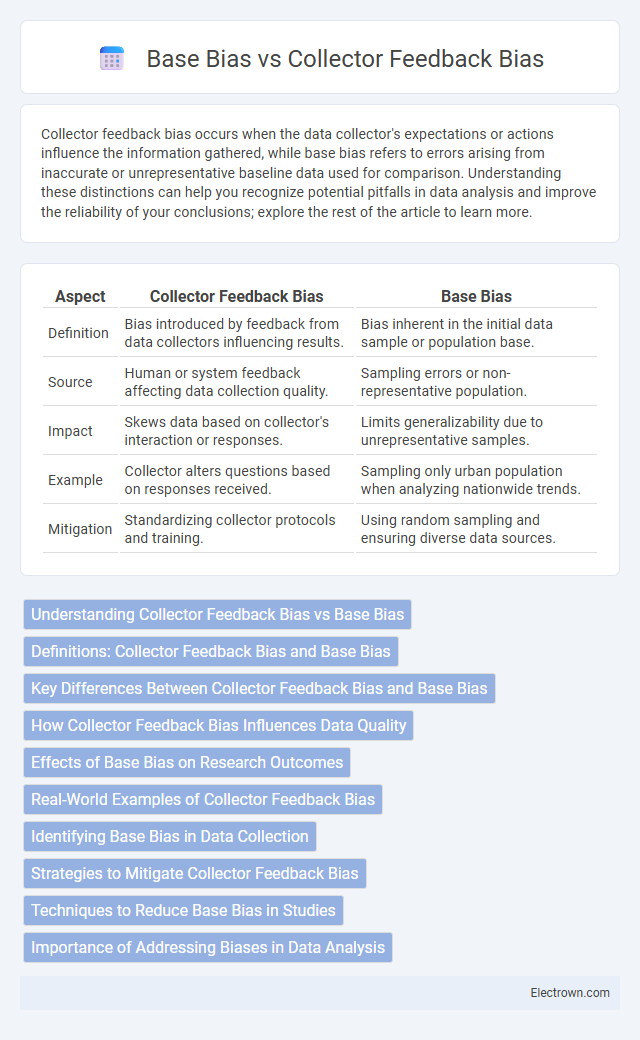
| Aspect | Collector Feedback Bias | Base Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Bias introduced by feedback from data collectors influencing results. | Bias inherent in the initial data sample or population base. |
| Source | Human or system feedback affecting data collection quality. | Sampling errors or non-representative population. |
| Impact | Skews data based on collector's interaction or responses. | Limits generalizability due to unrepresentative samples. |
| Example | Collector alters questions based on responses received. | Sampling only urban population when analyzing nationwide trends. |
| Mitigation | Standardizing collector protocols and training. | Using random sampling and ensuring diverse data sources. |
Understanding Collector Feedback Bias vs Base Bias
Collector feedback bias occurs when data is skewed due to the feedback loop created by the collector's actions influencing future data collection, leading to overrepresentation of certain outcomes. Base bias refers to the distortion arising from an unrepresentative sample that does not accurately reflect the true population distribution. Understanding the distinction helps in designing unbiased data collection processes and improving the reliability of analytical models.
Definitions: Collector Feedback Bias and Base Bias
Collector Feedback Bias occurs when the information gathered by a collector influences their subsequent data collection, skewing results due to prior feedback or expectations. Base Bias refers to the distortion arising from the initial sample or dataset foundation, which may not accurately represent the entire population or target group. Understanding these biases helps you design more reliable studies by recognizing how both feedback loops and foundational data choices impact the validity of findings.
Key Differences Between Collector Feedback Bias and Base Bias
Collector feedback bias occurs when data collection is influenced by feedback loops, causing overrepresentation of certain outcomes based on prior results, while base bias arises from sampling errors where the initial dataset is not representative of the overall population. Collector feedback bias typically distorts real-time data aggregation, leading to skewed trends, whereas base bias affects foundational data quality, impacting long-term analytics accuracy. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for designing robust data collection methods and improving predictive model reliability.
How Collector Feedback Bias Influences Data Quality
Collector feedback bias affects data quality by skewing responses based on the collector's reactions or expectations, potentially leading to inaccurate or unrepresentative data sets. This bias introduces systematic errors during data collection, as the collector's influence may alter participant behavior or responses, compromising the validity of the results. Understanding and mitigating collector feedback bias is crucial to ensure that your data accurately reflects the target population and supports reliable analysis.
Effects of Base Bias on Research Outcomes
Base bias skews research outcomes by distorting the foundational sample or dataset, leading to inaccurate generalizations and compromised validity. This bias alters the representativeness of data, resulting in misleading conclusions that affect the reliability of findings. Understanding how base bias impacts your research ensures more accurate data interpretation and enhances the credibility of study results.
Real-World Examples of Collector Feedback Bias
Collector feedback bias occurs when the data collector's expectations or prior knowledge influence the data collection process, leading to skewed results. For instance, in customer satisfaction surveys, if a salesperson collects feedback from their own clients, positive responses may be overrepresented, demonstrating collector feedback bias. In contrast to base bias, which stems from improper sampling frames, collector feedback bias specifically arises from subjective data collection practices in real-world scenarios such as medical trials or market research studies.
Identifying Base Bias in Data Collection
Identifying base bias in data collection involves examining whether the sample accurately represents the entire population or if certain groups are systematically excluded, leading to skewed results. This form of bias occurs when data collection methods inherently limit the scope, such as relying on a specific demographic or geographic region. Addressing base bias requires careful sampling design and validation against population parameters to ensure data integrity and generalizability.
Strategies to Mitigate Collector Feedback Bias
To mitigate collector feedback bias, implement anonymous data collection methods and standardize feedback questions to reduce subjective influence. Training collectors on unbiased data recording and regularly auditing feedback consistency can further minimize errors. Your organization should also use automated data validation tools to detect and correct inconsistencies caused by human bias.
Techniques to Reduce Base Bias in Studies
Techniques to reduce base bias in studies include careful selection of representative samples and stratified sampling to ensure all subgroups are proportionately included. Employing weighting adjustments and sensitivity analyses can correct distortions from sampling errors or nonresponse bias. Your research reliability increases by implementing these practices to minimize base bias and enhance the accuracy of study conclusions.
Importance of Addressing Biases in Data Analysis
Addressing collector feedback bias and base bias is essential for ensuring accurate data analysis and reliable insights. Collector feedback bias occurs when data collector's expectations influence data recording, while base bias arises from an unrepresentative sample skewing results. Correcting these biases improves the validity of your conclusions and supports data-driven decision-making.
collector feedback bias vs base bias Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com