Synchronous demodulation provides accurate and noise-resistant signal recovery by mixing the incoming signal with a reference carrier, while envelope detection offers a simpler, cost-effective method suitable for amplitude-modulated signals but is more susceptible to noise. Explore the detailed comparison to understand which demodulation technique best suits your communication system needs.
Table of Comparison
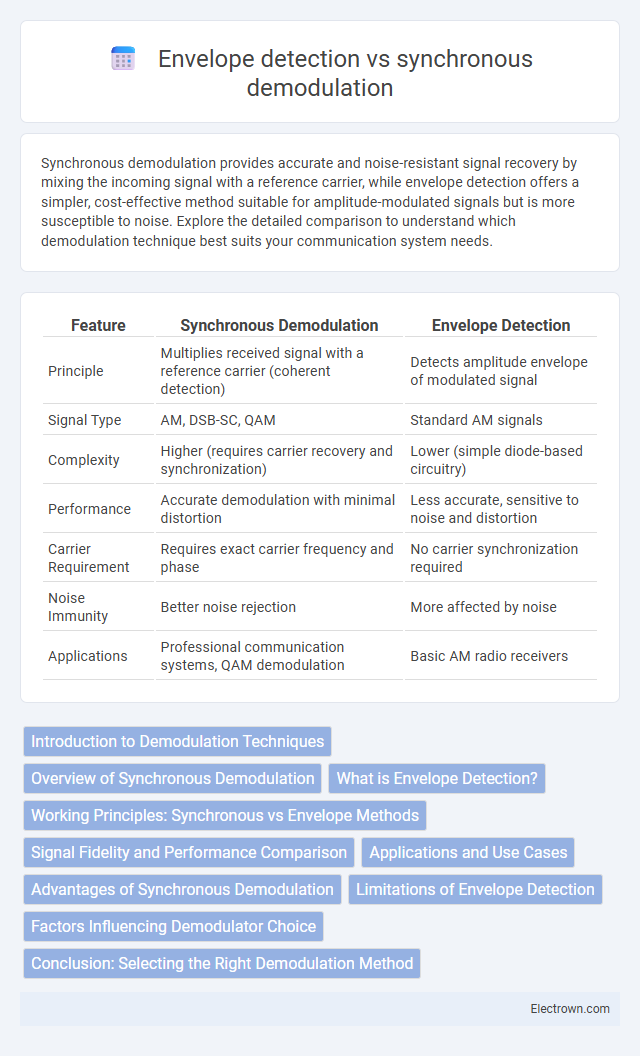
| Feature | Synchronous Demodulation | Envelope Detection |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Multiplies received signal with a reference carrier (coherent detection) | Detects amplitude envelope of modulated signal |
| Signal Type | AM, DSB-SC, QAM | Standard AM signals |
| Complexity | Higher (requires carrier recovery and synchronization) | Lower (simple diode-based circuitry) |
| Performance | Accurate demodulation with minimal distortion | Less accurate, sensitive to noise and distortion |
| Carrier Requirement | Requires exact carrier frequency and phase | No carrier synchronization required |
| Noise Immunity | Better noise rejection | More affected by noise |
| Applications | Professional communication systems, QAM demodulation | Basic AM radio receivers |
Introduction to Demodulation Techniques
Demodulation techniques extract original information from modulated carrier signals, with synchronous demodulation utilizing a reference carrier synchronized in frequency and phase to enhance accuracy, particularly in noisy environments. Envelope detection, a simpler and cost-effective method, retrieves the amplitude envelope of the modulated signal, commonly used in amplitude modulation (AM) systems but less effective under low signal-to-noise conditions. Your choice between synchronous demodulation and envelope detection impacts signal fidelity and complexity based on application requirements.
Overview of Synchronous Demodulation
Synchronous demodulation is a coherent detection technique that multiplies the received modulated signal with a locally generated carrier signal synchronized in frequency and phase. This method effectively recovers the original baseband message by eliminating noise and distortion, making it highly suitable for weak or noisy signals. Your communication system benefits from improved signal-to-noise ratio and reduced distortion when employing synchronous demodulation compared to simple envelope detection.
What is Envelope Detection?
Envelope detection is a method used in signal processing to extract the amplitude variations of a modulated carrier wave, typically in amplitude modulation (AM) systems. It involves rectifying the input signal followed by low-pass filtering to retrieve the envelope, which represents the original information signal. This technique is simple and cost-effective but less effective in noisy environments compared to synchronous demodulation.
Working Principles: Synchronous vs Envelope Methods
Synchronous demodulation operates by mixing the received signal with a locally generated carrier that is phase-locked to the original signal, allowing precise extraction of the modulating signal through coherent detection. Envelope detection, on the other hand, relies on rectifying the incoming amplitude-modulated wave and filtering out the high-frequency carrier to recover the envelope representing the modulated information. The synchronous method offers superior noise rejection and fidelity in demodulating signals compared to the simpler but less precise envelope detection technique.
Signal Fidelity and Performance Comparison
Synchronous demodulation offers superior signal fidelity compared to envelope detection by accurately tracking both amplitude and phase of the carrier signal, resulting in reduced distortion and better noise immunity. Envelope detection is simpler and effective for strong signal conditions but suffers from performance degradation in low signal-to-noise ratio environments due to its inability to reject noise and phase variations. Overall, synchronous demodulation is preferred in high-performance applications requiring precise signal recovery and minimal error rates.
Applications and Use Cases
Synchronous demodulation excels in applications requiring high accuracy and noise immunity, such as digital communication systems, phase-sensitive detection in lock-in amplifiers, and radar signal processing. Envelope detection is simpler and widely used in AM radio receivers, audio signal processing, and low-cost amplitude modulation systems where signal distortion and noise are less critical. Your choice between these techniques should depend on the precision requirements and complexity of the communication or signal processing system.
Advantages of Synchronous Demodulation
Synchronous demodulation offers superior noise immunity and accuracy compared to envelope detection, making it ideal for recovering signals in low signal-to-noise ratio environments. It effectively eliminates distortion caused by amplitude variations, ensuring precise amplitude and phase information retrieval. Your communication system benefits from enhanced signal fidelity and improved performance under challenging conditions.
Limitations of Envelope Detection
Envelope detection faces limitations such as susceptibility to noise and distortion, which can degrade signal quality and accuracy in demodulation. This method struggles with amplitude variations caused by multipath fading or interference, leading to erroneous signal interpretation. Your communication system may require synchronous demodulation for improved sensitivity and robustness in low signal-to-noise ratio environments.
Factors Influencing Demodulator Choice
Synchronous demodulation offers superior noise immunity and accuracy compared to envelope detection, making it ideal for complex or low-SNR signals. Envelope detection is simpler and cost-effective but less effective in the presence of distortion or carrier frequency shifts. Your choice depends on signal quality, hardware complexity, and system requirements for precision and robustness.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Demodulation Method
Synchronous demodulation offers superior performance in noisy environments and for signals with low amplitude, providing accurate phase and amplitude recovery essential for modern communication systems. Envelope detection remains a simple, cost-effective choice for AM signals with strong carrier components and low noise conditions. The selection depends on application requirements, where high fidelity and robustness favor synchronous demodulation, while simplicity and low power consumption favor envelope detection.
Synchronous demodulation vs envelope detection Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com