An active preamplifier uses powered electronic components to boost audio signals with added control over tone and gain, while a passive preamplifier relies solely on passive components like resistors and capacitors, offering minimal signal alteration but no amplification. Understanding the differences between active and passive preamplifiers can help you choose the best setup for your audio system--read on to explore their unique features and benefits.
Table of Comparison
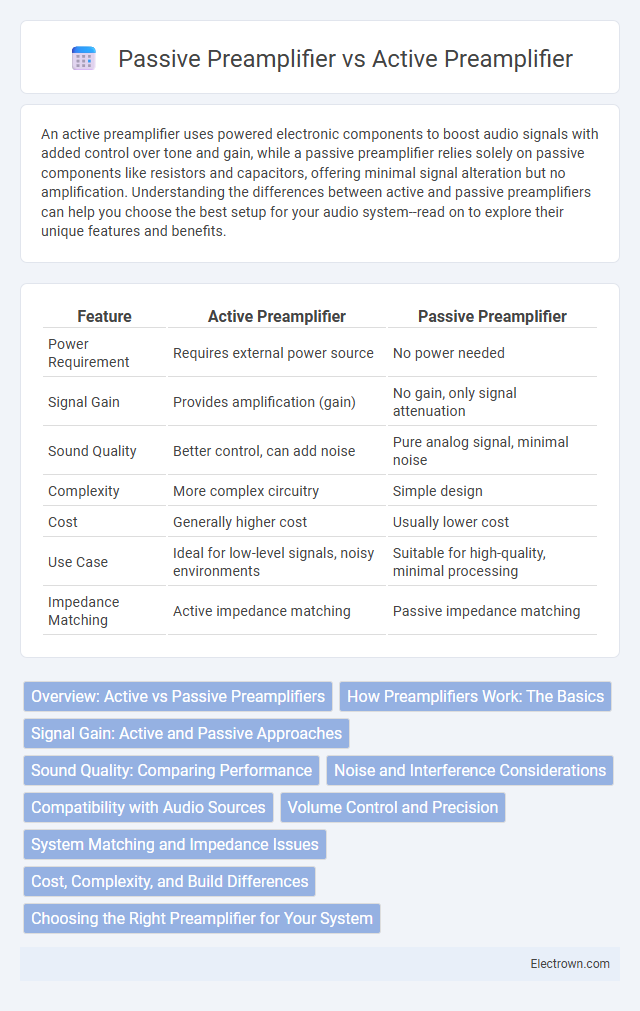
| Feature | Active Preamplifier | Passive Preamplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Power Requirement | Requires external power source | No power needed |
| Signal Gain | Provides amplification (gain) | No gain, only signal attenuation |
| Sound Quality | Better control, can add noise | Pure analog signal, minimal noise |
| Complexity | More complex circuitry | Simple design |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Usually lower cost |
| Use Case | Ideal for low-level signals, noisy environments | Suitable for high-quality, minimal processing |
| Impedance Matching | Active impedance matching | Passive impedance matching |
Overview: Active vs Passive Preamplifiers
Active preamplifiers use powered electronic components, such as transistors or operational amplifiers, to boost audio signals with added gain and control over frequency response. Passive preamplifiers rely on passive components like resistors, capacitors, and transformers, offering signal attenuation without amplification, preserving the source's purity but lacking gain. Active designs provide higher output levels and adjustable tonal shaping, whereas passive preamps emphasize minimal signal coloration and simplicity in design.
How Preamplifiers Work: The Basics
Active preamplifiers use powered electronic components like transistors or op-amps to amplify weak audio signals, providing gain and better signal-to-noise ratio. Passive preamplifiers rely on passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and transformers, simply controlling signal levels without adding gain or noise. Understanding how your preamplifier works helps optimize audio quality by matching the right type to your system's needs.
Signal Gain: Active and Passive Approaches
Active preamplifiers provide significant signal gain through powered components like transistors or op-amps, boosting weak signals effectively for further processing. Passive preamplifiers rely on passive components such as resistors, capacitors, or transformers and do not offer intrinsic gain, instead preserving the signal's integrity without amplification. The choice between active and passive preamplifiers directly impacts signal strength, noise levels, and overall audio fidelity in sound systems.
Sound Quality: Comparing Performance
Active preamplifiers use powered components to amplify audio signals, resulting in higher gain, lower noise, and improved dynamic range compared to passive preamplifiers that rely solely on passive components like resistors and capacitors. Sound quality in active preamplifiers is often characterized by clearer, more detailed audio reproduction with enhanced signal fidelity, while passive preamplifiers tend to preserve the original signal without adding coloration but may suffer from signal loss and lower output levels. Audiophiles generally prefer active preamplifiers for their ability to drive subsequent amplification stages effectively and maintain audio integrity in complex sound systems.
Noise and Interference Considerations
Active preamplifiers use powered electronic components to amplify weak signals, significantly reducing noise and interference by improving the signal-to-noise ratio. Passive preamplifiers rely on passive components like transformers or resistors, which may introduce higher noise levels and are more susceptible to external electromagnetic interference. For applications demanding high fidelity and minimal noise, active preamplifiers provide superior performance compared to passive designs.
Compatibility with Audio Sources
Active preamplifiers offer superior compatibility with a wide range of audio sources due to their built-in amplification and impedance matching, ensuring optimal signal strength and clarity. Passive preamplifiers rely solely on volume attenuation without power, making them best suited for sources with strong output signals but less adaptable to low-level or high-impedance sources. Choosing the right preamplifier depends on Your audio sources' output characteristics and the level of signal control required for your setup.
Volume Control and Precision
Active preamplifiers offer precise volume control through built-in amplification circuits that maintain signal integrity even at low levels, ensuring minimal noise and distortion. Passive preamplifiers rely on attenuating the signal without amplification, which can lead to signal degradation and less accurate volume adjustments. Your choice impacts the clarity and accuracy of audio volume adjustments, with active preamps generally providing superior precision and control.
System Matching and Impedance Issues
Active preamplifiers provide improved system matching by using powered circuits to maintain consistent impedance levels, enhancing signal transfer and minimizing distortion in audio setups. Passive preamplifiers rely on passive components, which can introduce impedance mismatches and signal loss due to the absence of amplification and buffering capabilities. Optimal impedance matching in active preamplifiers results in better noise performance and preserves audio fidelity, making them preferable for high-performance audio systems.
Cost, Complexity, and Build Differences
Active preamplifiers typically cost more due to the inclusion of powered components like transistors or op-amps, whereas passive preamplifiers are generally less expensive, relying solely on resistors and capacitors. The complexity of active preamplifiers is higher because they require power supplies and careful circuit design to minimize noise and distortion, while passive preamplifiers have simpler builds with fewer parts but may suffer from signal loss and lack of gain control. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize precise amplification with added circuitry or a straightforward, cost-effective solution with minimal complexity.
Choosing the Right Preamplifier for Your System
Choosing the right preamplifier for your system depends on factors such as sound quality, signal control, and power handling. Active preamplifiers offer built-in amplification and superior tone shaping through electronic components, ideal for improving weak signals and reducing noise in complex audio setups. Passive preamplifiers rely on simple passive components like resistors and capacitors, providing a more transparent sound with minimal coloration, best suited for users valuing purity and simplicity with high-quality source material.
active preamplifier vs passive preamplifier Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com