Ladder DACs provide higher precision through a series of weighted resistors forming a voltage ladder, while R-2R DACs use a repetitive resistor network offering easier scalability and manufacturing simplicity. Explore the rest of the article to understand which DAC suits Your application needs best.
Table of Comparison
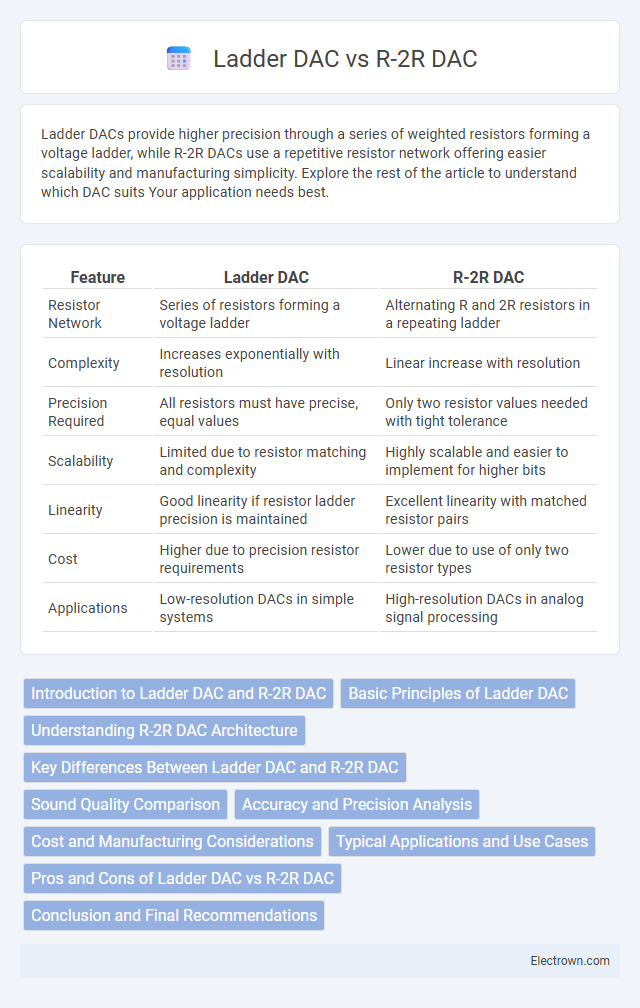
| Feature | Ladder DAC | R-2R DAC |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor Network | Series of resistors forming a voltage ladder | Alternating R and 2R resistors in a repeating ladder |
| Complexity | Increases exponentially with resolution | Linear increase with resolution |
| Precision Required | All resistors must have precise, equal values | Only two resistor values needed with tight tolerance |
| Scalability | Limited due to resistor matching and complexity | Highly scalable and easier to implement for higher bits |
| Linearity | Good linearity if resistor ladder precision is maintained | Excellent linearity with matched resistor pairs |
| Cost | Higher due to precision resistor requirements | Lower due to use of only two resistor types |
| Applications | Low-resolution DACs in simple systems | High-resolution DACs in analog signal processing |
Introduction to Ladder DAC and R-2R DAC
Ladder DACs employ a network of precision resistors arranged in a ladder-like structure to convert digital signals into accurate analog voltages, making them ideal for high-accuracy applications. R-2R DACs use a repeating pattern of resistors with values R and 2R, providing a simpler, more scalable design that maintains consistent impedance and reduces complexity. Your choice between Ladder and R-2R DAC architectures depends on factors like resolution, linearity, and manufacturing considerations.
Basic Principles of Ladder DAC
Ladder DACs operate on the principle of using a network of precisely matched resistors arranged in a ladder-like configuration to convert digital signals into analog voltages. Each rung of the ladder corresponds to a binary weight, allowing the DAC to output a voltage proportional to the digital input code. Your choice of Ladder DAC ensures highly accurate and stable conversion by leveraging uniform resistor values and binary-weighted voltage division.
Understanding R-2R DAC Architecture
R-2R DAC architecture consists of a repetitive ladder network made up of precisely matched resistors with values of R and 2R, enabling efficient binary-weighted voltage division. This design simplifies manufacturing compared to the Ladder DAC by using only two resistor values, improving accuracy and scalability for high-resolution digital-to-analog conversion. Your choice of an R-2R DAC can enhance performance in applications requiring precise and stable analog output signals.
Key Differences Between Ladder DAC and R-2R DAC
Ladder DACs utilize a binary-weighted resistor network that offers high-speed digital-to-analog conversion with straightforward implementation but can suffer from mismatched resistor tolerances affecting accuracy. R-2R DACs employ a repetitive resistor structure consisting of only two resistor values, which simplifies manufacturing and improves linearity and scalability for higher resolution. The key differences lie in resistor configuration, scalability, and accuracy, where Ladder DACs excel in speed, and R-2R DACs provide enhanced precision and ease of design for large bit-depth applications.
Sound Quality Comparison
Ladder DACs typically deliver superior sound quality due to their simple architecture and precise current summation, resulting in lower distortion and noise compared to R-2R DACs. R-2R DACs often exhibit higher linearity errors and mismatched resistor tolerances, which can slightly degrade audio fidelity. Audiophiles generally prefer Ladder DACs for their cleaner, more natural sound reproduction in high-end audio applications.
Accuracy and Precision Analysis
Ladder DACs offer high linearity and accuracy due to their binary-weighted resistor structure, minimizing errors in voltage division and providing precise output steps. R-2R DACs maintain consistent precision with their repetitive resistor network, reducing the impact of manufacturing tolerances on linearity and ensuring stable and accurate digital-to-analog conversion. Both DAC architectures are capable of high resolution, but Ladder DACs typically achieve superior accuracy in high-bit applications, while R-2R DACs excel in ease of production and matching precision.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Ladder DACs typically offer lower manufacturing costs due to simpler resistor networks, making them more suitable for high-volume production. R-2R DACs require precise resistor matching, increasing complexity and cost, especially for high-resolution designs. The straightforward design of Ladder DACs enables easier automation and consistent yields, whereas R-2R DACs may demand tighter process controls, impacting scalability and overall expenses.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Ladder DACs, known for their simplicity and fast conversion speeds, are typically used in audio applications and embedded systems where cost-efficiency and moderate resolution are sufficient. R-2R DACs offer higher linearity and precision, making them ideal for instrumentation, measurement equipment, and high-fidelity audio where accuracy is crucial. Both DAC types are employed in signal generation, control systems, and digital synthesizers, but R-2R DACs dominate applications requiring fine resolution and minimal distortion.
Pros and Cons of Ladder DAC vs R-2R DAC
Ladder DACs offer high linearity and fast conversion speeds, making them ideal for high-precision applications, but they can become complex and costly as resolution increases. R-2R DACs provide simplicity and scalability with consistent resistor values, which reduces manufacturing errors, yet they may suffer from lower accuracy due to resistor matching issues at higher resolutions. Your choice between Ladder DAC and R-2R DAC should balance performance needs against cost and complexity constraints.
Conclusion and Final Recommendations
Ladder DACs offer superior linearity and speed, making them ideal for high-precision and high-frequency applications. R-2R DACs provide simpler design and scalability, suitable for cost-sensitive and medium-resolution uses. Choose Ladder DACs for accuracy-critical tasks, while R-2R DACs are recommended for flexible, lower-complexity projects.
Ladder DAC vs R-2R DAC Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com