Linear power supplies provide stable, low-noise voltage with simpler designs but tend to be less efficient and bulkier compared to switching power supplies, which offer higher efficiency and lighter weight by rapidly switching on and off. Understanding the differences between these power supply types will help you choose the best option for your specific electronic needs, so explore the rest of this article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
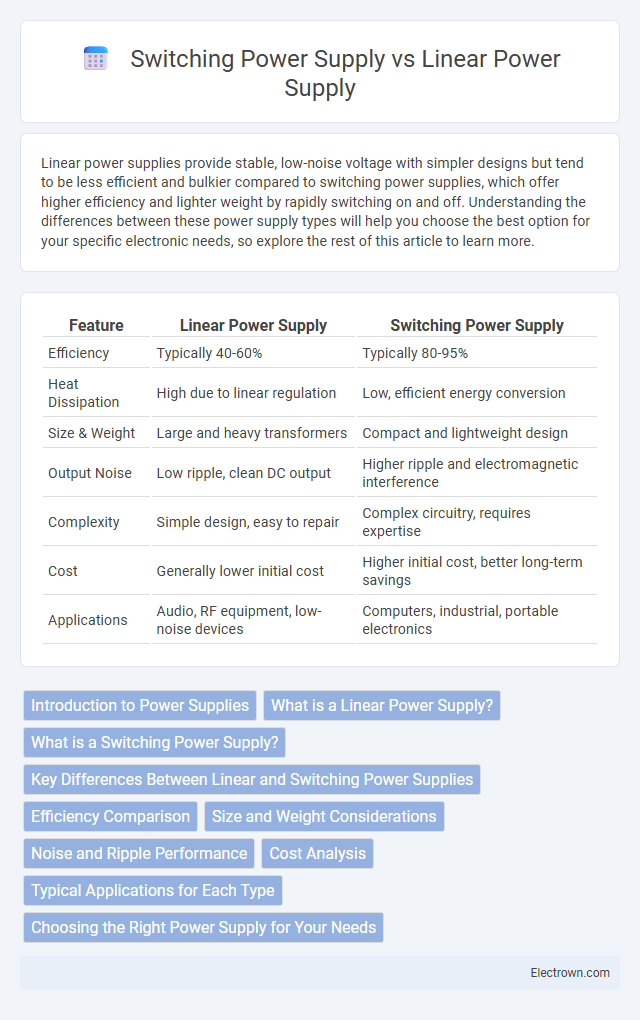
| Feature | Linear Power Supply | Switching Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Typically 40-60% | Typically 80-95% |
| Heat Dissipation | High due to linear regulation | Low, efficient energy conversion |
| Size & Weight | Large and heavy transformers | Compact and lightweight design |
| Output Noise | Low ripple, clean DC output | Higher ripple and electromagnetic interference |
| Complexity | Simple design, easy to repair | Complex circuitry, requires expertise |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost, better long-term savings |
| Applications | Audio, RF equipment, low-noise devices | Computers, industrial, portable electronics |
Introduction to Power Supplies
Linear power supplies deliver stable and low-noise DC voltage by using a transformer, rectifier, and linear regulator, making them ideal for sensitive analog circuits. Switching power supplies convert power through high-frequency switching and energy storage components, offering higher efficiency, smaller size, and lighter weight compared to linear designs. Your choice between these power supplies depends on factors like efficiency needs, output noise sensitivity, and form factor constraints.
What is a Linear Power Supply?
A linear power supply converts AC voltage to a lower DC voltage using a transformer, rectifier, and linear regulator, providing a stable and low-noise output ideal for sensitive electronics. It operates by dissipating excess voltage as heat, resulting in less efficiency compared to switching power supplies. Despite lower efficiency, linear power supplies offer superior electromagnetic compatibility and minimal ripple, making them preferred in audio and precision measurement applications.
What is a Switching Power Supply?
A switching power supply converts electrical power efficiently by rapidly switching on and off electronic components, regulating voltage through high-frequency pulses. It offers higher efficiency and lighter weight compared to linear power supplies, making it ideal for compact devices and applications requiring precise voltage control. Commonly found in computers, LED drivers, and telecommunications, switching power supplies minimize energy loss and heat generation.
Key Differences Between Linear and Switching Power Supplies
Linear power supplies regulate voltage using a linear regulator, resulting in low noise, simple design, and better performance in sensitive analog applications, but they are less efficient and generate more heat. Switching power supplies use high-frequency switching components to convert voltage, offering higher efficiency, smaller size, and lighter weight, but they produce more electrical noise and require complex filtering. Key differences include efficiency rates (linear typically 30-60% vs. switching up to 85-95%), thermal management needs, and noise levels affecting suitability for various electronic devices.
Efficiency Comparison
Linear power supplies typically have lower efficiency, often around 30-60%, due to continuous voltage regulation and heat dissipation through a series transistor. Switching power supplies achieve higher efficiency, ranging from 75% to over 90%, by rapidly switching components on and off, minimizing power loss. Choosing a switching power supply enhances Your system's energy efficiency and reduces wasted power, making it ideal for applications where conserving energy is crucial.
Size and Weight Considerations
Linear power supplies are significantly larger and heavier due to bulky transformers and heat sinks required for voltage regulation, making them less suitable for compact or portable applications. Switching power supplies utilize high-frequency oscillators, allowing for smaller transformers and components, resulting in a compact and lightweight design ideal for space-constrained environments. Your choice between the two should consider the size and weight constraints of your project, with switching supplies offering superior efficiency in these aspects.
Noise and Ripple Performance
Linear power supplies produce significantly lower noise and ripple compared to switching power supplies, making them ideal for sensitive audio, RF, and precision measurement applications. The absence of high-frequency switching in linear supplies results in a clean and stable output voltage with minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI). Your choice should prioritize a linear power supply when noise reduction is critical for optimal device performance.
Cost Analysis
Linear power supplies generally have higher costs due to larger bulky components and inefficient heat dissipation, leading to greater energy loss and higher operating expenses. Switching power supplies use advanced technology with smaller transformers and better energy efficiency, resulting in lower production and operational costs over time. If you prioritize long-term savings, a switching power supply offers a more cost-effective solution despite a potentially higher initial investment.
Typical Applications for Each Type
Linear power supplies are commonly used in audio equipment, laboratory instruments, and precision measurement devices due to their low noise and stable output voltage. Switching power supplies find typical applications in computers, telecommunications, and industrial machinery where higher efficiency and compact size are essential. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize clean power output or energy efficiency in demanding environments.
Choosing the Right Power Supply for Your Needs
Linear power supplies provide clean, stable voltage with minimal noise, ideal for sensitive audio or measurement equipment. Switching power supplies offer higher efficiency, lighter weight, and smaller size, making them suitable for portable devices and applications with variable loads. Understanding your device's requirements for noise tolerance, efficiency, and size will help you choose the right power supply for your needs.
linear power supply vs switching power supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com