Transistors offer greater efficiency, smaller size, and increased durability compared to vacuum tubes, which are bulkier, generate more heat, and are less reliable. Discover how these differences impact your electronic devices by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
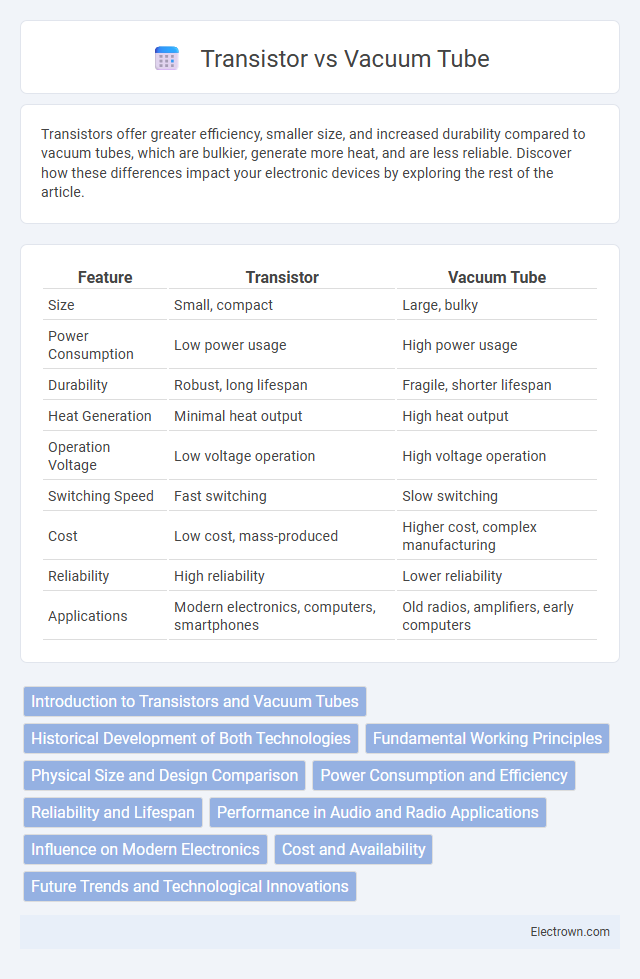
| Feature | Transistor | Vacuum Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Small, compact | Large, bulky |
| Power Consumption | Low power usage | High power usage |
| Durability | Robust, long lifespan | Fragile, shorter lifespan |
| Heat Generation | Minimal heat output | High heat output |
| Operation Voltage | Low voltage operation | High voltage operation |
| Switching Speed | Fast switching | Slow switching |
| Cost | Low cost, mass-produced | Higher cost, complex manufacturing |
| Reliability | High reliability | Lower reliability |
| Applications | Modern electronics, computers, smartphones | Old radios, amplifiers, early computers |
Introduction to Transistors and Vacuum Tubes
Transistors and vacuum tubes are fundamental components in electronic circuits, with transistors being solid-state devices that control current flow using semiconductor materials, while vacuum tubes operate by controlling electron flow in a vacuum between electrodes. Transistors offer greater efficiency, smaller size, and higher reliability compared to vacuum tubes, which were widely used in early electronic devices but are now mostly obsolete due to their bulkiness and energy consumption. Understanding the differences between these technologies is essential for designing modern electronic systems that maximize performance and energy efficiency.
Historical Development of Both Technologies
The historical development of vacuum tubes began in the early 20th century with the invention of the triode by Lee De Forest in 1906, which revolutionized electronics by enabling signal amplification and the birth of radio and early computers. Transistor technology emerged in 1947 at Bell Labs, where John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley developed the first point-contact transistor, leading to smaller, more energy-efficient, and reliable electronic devices. The transition from vacuum tubes to transistors marked a pivotal shift in electronics, facilitating the miniaturization and advancement of modern computing and communication systems.
Fundamental Working Principles
Transistors operate by controlling electron flow through semiconductor materials using electric fields, enabling signal amplification and switching with high efficiency and miniaturization. Vacuum tubes rely on thermionic emission within a vacuum to control electron flow between electrodes, using heated cathodes to release electrons for amplification. Transistors offer greater reliability, lower power consumption, and faster switching compared to vacuum tubes.
Physical Size and Design Comparison
Transistors are significantly smaller than vacuum tubes, allowing for compact and integrated circuit designs in modern electronics. Unlike bulky vacuum tubes that require large glass enclosures and heavy metal components, transistors are solid-state devices fabricated using semiconductor materials, enabling dense packing on microchips. This size and design efficiency contribute to lower power consumption and increased reliability in electronic equipment.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
Transistors consume significantly less power compared to vacuum tubes due to their solid-state design, which allows for greater energy efficiency in electronic circuits. Vacuum tubes require higher voltages to operate and generate substantial heat, leading to increased power waste and reduced overall efficiency. Your choice between these components impacts energy consumption, making transistors the preferred option for low-power, high-efficiency applications.
Reliability and Lifespan
Transistors offer significantly higher reliability and longer lifespan compared to vacuum tubes due to their solid-state construction, which eliminates the fragile glass envelope and filament prone to burnout. Your electronic devices benefit from transistors' enhanced durability, lower power consumption, and resistance to mechanical shock, resulting in fewer failures and extended operational life. Vacuum tubes, by contrast, have a limited lifespan because of filament wear and susceptibility to heat damage.
Performance in Audio and Radio Applications
Transistors provide greater reliability, lower power consumption, and smaller size compared to vacuum tubes, making them ideal for modern audio and radio applications. Vacuum tubes are often favored in high-end audio equipment for their warm sound quality and natural harmonic distortion, which audiophiles prefer. In radio technology, transistors offer faster switching speeds and enhanced frequency response, improving signal amplification and overall performance.
Influence on Modern Electronics
Transistors revolutionized modern electronics by enabling smaller, more reliable, and energy-efficient devices compared to bulky vacuum tubes. Your everyday gadgets, from smartphones to computers, rely on transistors for enhanced performance and longevity. This shift paved the way for rapid advancements in digital technology and miniaturization.
Cost and Availability
Transistors are significantly more cost-effective and widely available compared to vacuum tubes due to advancements in semiconductor manufacturing and mass production techniques. Vacuum tubes remain expensive and harder to source, primarily used in niche applications like high-end audio equipment and certain industrial systems. Your choice in electronics relies heavily on transistors for affordability and accessibility in modern technology.
Future Trends and Technological Innovations
Advancements in transistor technology continue to drive the evolution of electronics, with innovations like silicon carbide and gallium nitride transistors enhancing efficiency and thermal performance in high-frequency and power applications. Emerging research in quantum tunneling transistors and flexible, organic semiconductors promises to revolutionize miniaturization and integration in next-generation devices. Although vacuum tubes are largely obsolete in mainstream electronics, they still find niche applications in high-power radio frequency amplifiers and audiophile equipment, but future trends firmly favor solid-state transistor innovations for scalability and sustainability.
transistor vs vacuum tube Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com