A current source provides a constant current regardless of the voltage across its terminals, while a voltage source delivers a fixed voltage irrespective of the current flowing through it. To understand how these sources impact your electronic circuits and applications, continue reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
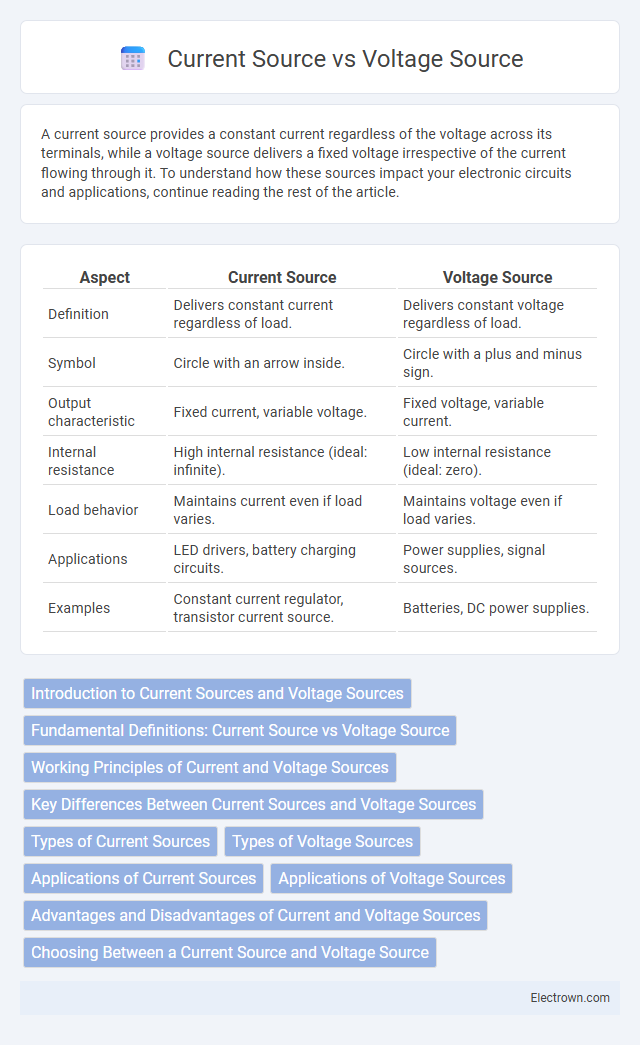
| Aspect | Current Source | Voltage Source |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivers constant current regardless of load. | Delivers constant voltage regardless of load. |
| Symbol | Circle with an arrow inside. | Circle with a plus and minus sign. |
| Output characteristic | Fixed current, variable voltage. | Fixed voltage, variable current. |
| Internal resistance | High internal resistance (ideal: infinite). | Low internal resistance (ideal: zero). |
| Load behavior | Maintains current even if load varies. | Maintains voltage even if load varies. |
| Applications | LED drivers, battery charging circuits. | Power supplies, signal sources. |
| Examples | Constant current regulator, transistor current source. | Batteries, DC power supplies. |
Introduction to Current Sources and Voltage Sources
Current sources deliver a constant current regardless of the voltage across their terminals, making them essential in applications requiring stable current flow. Voltage sources, in contrast, maintain a fixed voltage across their terminals while allowing the current to vary according to the load. Understanding the fundamental differences between ideal current sources and ideal voltage sources is crucial for designing and analyzing electrical circuits efficiently.
Fundamental Definitions: Current Source vs Voltage Source
A current source delivers a constant current regardless of the voltage across its terminals, while a voltage source provides a constant voltage irrespective of the current drawn. Ideal current sources maintain fixed current flow even when the load varies, whereas ideal voltage sources maintain fixed voltage output despite changes in load. Understanding these fundamental definitions helps in designing circuits where precise control of current or voltage is essential for your application.
Working Principles of Current and Voltage Sources
Current sources deliver a constant current regardless of the voltage across their terminals, regulating output by adjusting voltage as needed to maintain steady current flow. Voltage sources maintain a fixed voltage level while allowing the current to vary depending on the load resistance connected to the circuit. Understanding these fundamental working principles helps you select the appropriate source type for applications requiring precise control of either current or voltage.
Key Differences Between Current Sources and Voltage Sources
Current sources deliver a consistent flow of electrical current regardless of the voltage across their terminals, while voltage sources maintain a fixed voltage regardless of the current drawn by the load. The ideal current source has infinite internal resistance, ensuring constant current, whereas the ideal voltage source has zero internal resistance to uphold constant voltage. Understanding these key differences allows you to select the appropriate source type for precise circuit applications and optimal performance.
Types of Current Sources
Types of current sources include ideal and practical current sources, with ideal sources maintaining constant current regardless of load. Practical current sources are often implemented using transistors, current mirrors, and operational amplifiers to regulate output current more accurately. Your choice between current and voltage sources depends on the specific application and load requirements for optimal circuit performance.
Types of Voltage Sources
Voltage sources can be classified into two main types: ideal and practical voltage sources. An ideal voltage source maintains a constant voltage regardless of the current drawn from it, while a practical voltage source has internal resistance that causes voltage to drop under load. Understanding these types helps you select the appropriate voltage source for your electronic circuit design, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Applications of Current Sources
Current sources are essential in applications requiring constant current flow regardless of voltage changes, such as LED driving, battery charging, and transistor biasing. They enable precise control in analog circuits, ensuring stable operation in sensor interfaces and communication systems. Your electronic designs benefit from current sources by maintaining consistent performance under varying load conditions.
Applications of Voltage Sources
Voltage sources are widely used in electronic circuits to provide a stable and constant voltage supply crucial for powering devices such as amplifiers, sensors, and microcontrollers. They are essential in battery-powered systems, regulated power supplies, and signal generators where maintaining a fixed voltage level ensures proper functionality and performance. Voltage sources are integral in automotive electronics, telecommunications, and consumer electronics, enabling reliable operation and consistent energy delivery.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Current and Voltage Sources
Current sources provide constant current regardless of load variations, which ensures predictable circuit behavior, but they can be less efficient and more complex to implement compared to voltage sources. Voltage sources maintain a fixed voltage output, making them ideal for power supply applications, though their performance can degrade significantly under varying load conditions. While current sources excel in driving LEDs and other current-sensitive devices, voltage sources dominate general-purpose power delivery due to simplicity and compatibility with most electronic components.
Choosing Between a Current Source and Voltage Source
Selecting between a current source and a voltage source depends on the application's load characteristics and circuit requirements. Current sources are ideal for driving loads with varying resistance while maintaining a constant current, making them suitable for LED illumination or battery charging. Voltage sources are preferred when a stable voltage is essential across a load, such as in power supplies or signal generation circuits.
current source vs voltage source Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com