VRMS represents the effective value of an AC voltage, reflecting its ability to deliver the same power as a DC voltage, while Vpeak is the maximum instantaneous voltage of the waveform. Understanding the difference between VRMS and Vpeak is crucial for accurately measuring and analyzing electrical signals, so explore the rest of the article to enhance Your electrical knowledge.
Table of Comparison
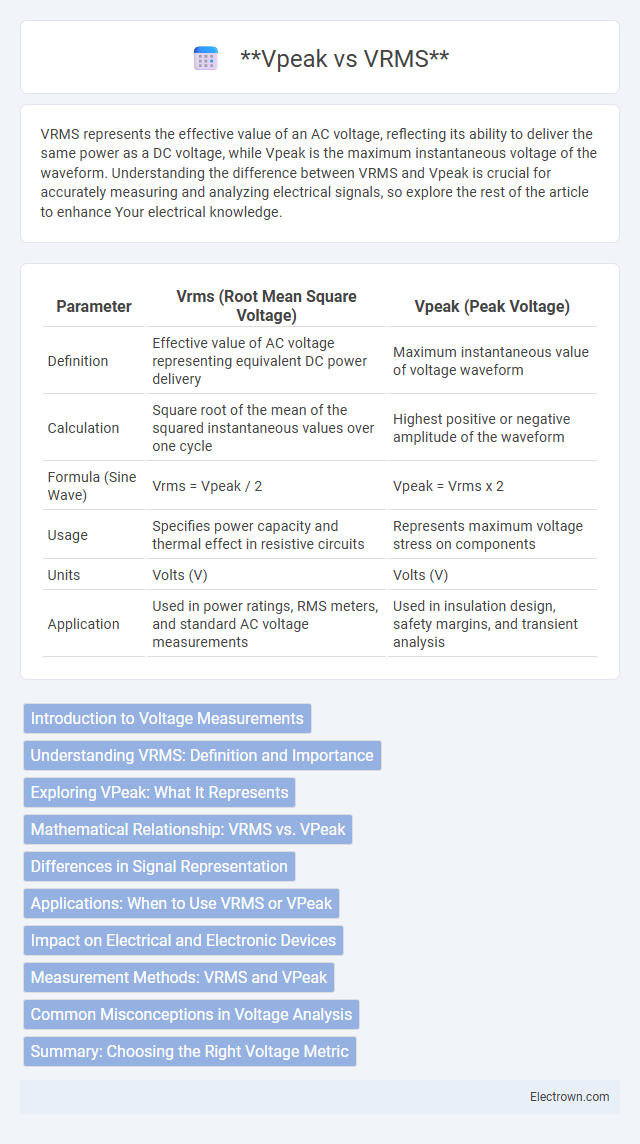
| Parameter | Vrms (Root Mean Square Voltage) | Vpeak (Peak Voltage) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Effective value of AC voltage representing equivalent DC power delivery | Maximum instantaneous value of voltage waveform |
| Calculation | Square root of the mean of the squared instantaneous values over one cycle | Highest positive or negative amplitude of the waveform |
| Formula (Sine Wave) | Vrms = Vpeak / 2 | Vpeak = Vrms x 2 |
| Usage | Specifies power capacity and thermal effect in resistive circuits | Represents maximum voltage stress on components |
| Units | Volts (V) | Volts (V) |
| Application | Used in power ratings, RMS meters, and standard AC voltage measurements | Used in insulation design, safety margins, and transient analysis |
Introduction to Voltage Measurements
Voltage measurements are crucial in electrical engineering, with two primary metrics being VRMS (Root Mean Square Voltage) and Vpeak (Peak Voltage). VRMS represents the effective voltage that delivers the same power as a direct current, making it essential for evaluating AC signals accurately. Vpeak measures the maximum instantaneous voltage value, important for understanding voltage spikes and insulation requirements in circuits.
Understanding VRMS: Definition and Importance
VRMS (Voltage Root Mean Square) measures the effective value of an alternating voltage, representing the equivalent DC voltage that delivers the same power to a load. Understanding VRMS is crucial for accurately assessing electrical systems and ensuring your equipment operates safely under real-world conditions. Unlike Vpeak, which indicates the maximum instantaneous voltage, VRMS provides a practical value for power calculations and system design.
Exploring VPeak: What It Represents
VPeak represents the maximum instantaneous voltage in an electrical waveform, indicating the highest point the voltage reaches during a cycle. In contrast, VRMS (root mean square voltage) reflects the effective voltage or the equivalent DC value delivering the same power to a load. Understanding VPeak is crucial for designing circuits to withstand voltage spikes and ensuring safe voltage ratings for components in your electrical systems.
Mathematical Relationship: VRMS vs. VPeak
The mathematical relationship between VRMS (Root Mean Square Voltage) and VPeak (Peak Voltage) in a sinusoidal waveform is expressed as VRMS = VPeak / 2. This means VRMS value represents the equivalent DC voltage delivering the same power, making it essential for accurate power calculations in AC circuits. You can use this relationship to convert peak voltage readings to RMS values for practical applications like electrical design and measurement.
Differences in Signal Representation
VRMS represents the effective value of an AC signal, reflecting the equivalent DC power, while Vpeak indicates the maximum instantaneous voltage. The RMS value provides a meaningful measure for power calculations and heating effects, as it accounts for the entire waveform over time. Your choice between VRMS and Vpeak impacts how you interpret signal strength and design electrical systems for accurate performance.
Applications: When to Use VRMS or VPeak
VRMS is best used in applications involving power measurement and energy consumption, such as in AC electrical systems and household appliances, where accurate representation of effective voltage is critical. VPeak is crucial in scenarios requiring the assessment of voltage extremes, like surge protection, insulation testing, and signal integrity analysis in electronics, where knowing the maximum voltage level prevents damage. Selecting VRMS or VPeak depends on whether the goal is to understand continuous power delivery or to ensure component safety against voltage spikes.
Impact on Electrical and Electronic Devices
VRMS (root mean square voltage) represents the effective voltage level that electrical and electronic devices experience during operation, ensuring consistent power delivery and reducing thermal stress. Vpeak (peak voltage) indicates the maximum instantaneous voltage that components must withstand, impacting insulation requirements and voltage rating of device parts. Understanding the difference between VRMS and Vpeak is critical for designing circuitry with adequate voltage tolerance, preventing component failure and ensuring long-term reliability.
Measurement Methods: VRMS and VPeak
VRMS (Root Mean Square Voltage) is measured by calculating the square root of the average of the squared instantaneous voltage values over one complete cycle, providing an effective voltage value equivalent to DC that delivers the same power. VPeak represents the maximum instantaneous voltage value reached in the waveform, measured using peak detectors or oscilloscopes capturing the highest point in the signal. Accurate VRMS measurements rely on integrating voltage samples over time, while VPeak requires capturing transient peaks, making the choice of method dependent on application needs such as power calculations or signal peak detection.
Common Misconceptions in Voltage Analysis
Many engineers mistakenly equate VRMS (Root Mean Square voltage) with Vpeak (peak voltage), leading to errors in power calculations and circuit design. VRMS represents the effective voltage that delivers the same power as a DC source, while Vpeak is the maximum instantaneous voltage in a waveform. Confusing these values especially impacts AC circuit analysis, causing inaccuracies in estimating voltage stresses on components and overall system performance.
Summary: Choosing the Right Voltage Metric
Selecting the appropriate voltage metric hinges on the application requirements, where Vpeak represents the maximum instantaneous voltage while VRMS indicates the equivalent heating value in AC circuits. VRMS is preferred for power calculations and comparing AC signals to DC equivalents, as it reflects the effective voltage that delivers power. Vpeak is crucial for ensuring component voltage tolerance and avoiding insulation breakdown during voltage surges.
vrms vs vpeak Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com