Horn tweeters deliver high efficiency and focused sound dispersion, making them ideal for large venues requiring powerful projection, while planar tweeters provide smoother, more detailed audio with wider dispersion, perfect for critical listening environments. Explore the article to discover which tweeter type suits Your audio setup best.
Table of Comparison
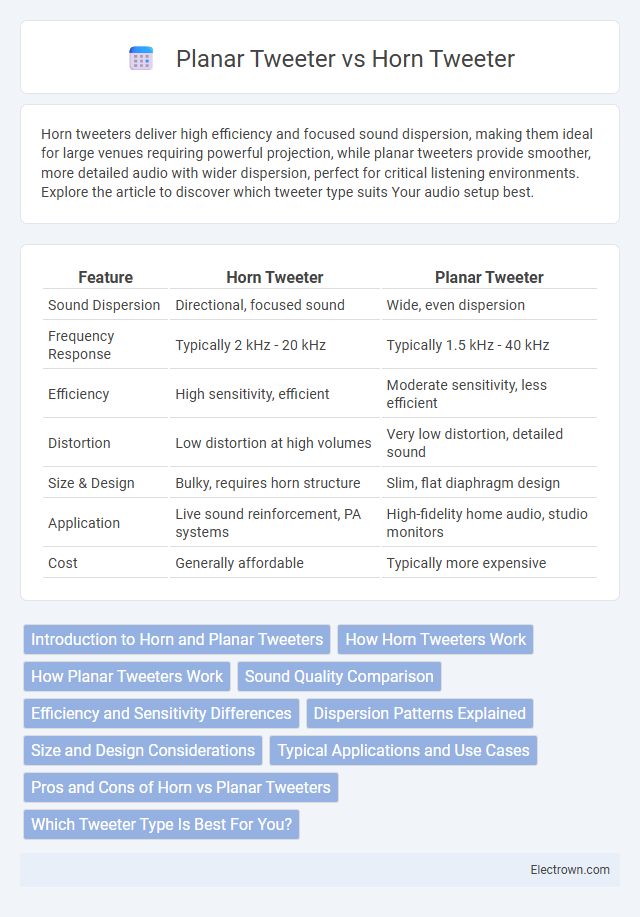
| Feature | Horn Tweeter | Planar Tweeter |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Dispersion | Directional, focused sound | Wide, even dispersion |
| Frequency Response | Typically 2 kHz - 20 kHz | Typically 1.5 kHz - 40 kHz |
| Efficiency | High sensitivity, efficient | Moderate sensitivity, less efficient |
| Distortion | Low distortion at high volumes | Very low distortion, detailed sound |
| Size & Design | Bulky, requires horn structure | Slim, flat diaphragm design |
| Application | Live sound reinforcement, PA systems | High-fidelity home audio, studio monitors |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Typically more expensive |
Introduction to Horn and Planar Tweeters
Horn tweeters utilize a flared acoustic waveguide to amplify sound efficiency and directivity, providing higher sensitivity and greater output levels ideal for large venues. Planar tweeters rely on a thin, lightweight diaphragm suspended in a magnetic field, producing precise, low-distortion high frequencies with broad dispersion. The choice between horn and planar tweeters impacts sound reproduction quality, power handling, and application suitability in audio systems.
How Horn Tweeters Work
Horn tweeters operate by coupling a small driver diaphragm to a flared horn structure, which efficiently directs high-frequency sound waves into the listening environment. This design increases acoustic output and improves sensitivity by amplifying the driver's sound energy while controlling dispersion patterns, resulting in clearer and more focused high-frequency reproduction. Your audio setup can benefit from horn tweeters when seeking enhanced clarity and higher efficiency in delivering detailed treble response.
How Planar Tweeters Work
Planar tweeters use a thin, flat diaphragm suspended within a magnetic field, which moves uniformly to produce sound waves with minimal distortion. Unlike horn tweeters that rely on acoustic loading and directional control, planar tweeters offer fast transient response and a wide, even dispersion pattern. Their technology excels in delivering clear, detailed high frequencies, making them ideal for audiophiles seeking precise sound reproduction.
Sound Quality Comparison
Horn tweeters deliver higher sound pressure levels and enhanced directivity, resulting in more focused and efficient high-frequency reproduction ideal for large venues. Planar tweeters offer exceptionally smooth, natural, and detailed sound with low distortion, providing a more accurate and immersive listening experience suited for critical home audio applications. The choice between the two depends on the listener's preference for either dynamic projection or refined tonal clarity.
Efficiency and Sensitivity Differences
Horn tweeters generally offer higher efficiency and sensitivity compared to planar tweeters due to their design, which uses a horn structure to amplify the sound output with less power. You can expect horn tweeters to deliver louder sound levels at lower input power, making them ideal for high-volume applications. Planar tweeters usually have lower sensitivity but provide smoother and more detailed high-frequency reproduction with less distortion.
Dispersion Patterns Explained
Horn tweeters feature highly directional dispersion patterns that concentrate sound energy into a narrow beam, enhancing efficiency and projection at higher frequencies. Planar tweeters, with their flat diaphragm design, offer wider and more uniform dispersion across a broader listening area, delivering smoother off-axis response and more natural sound imaging. Understanding the dispersion patterns is crucial for selecting the appropriate tweeter based on room acoustics and desired soundstage characteristics.
Size and Design Considerations
Horn tweeters generally require larger enclosures due to their flared shape, which influences the overall size of your speaker system and its placement options. Planar tweeters feature a flat, compact diaphragm that allows for a slimmer, more minimalistic design ideal for space-conscious setups. Your choice depends on balancing the physical footprint with the desired dispersion and acoustic output characteristics.
Typical Applications and Use Cases
Horn tweeters excel in large venues, outdoor concerts, and public address systems due to their high efficiency and ability to project sound over long distances with minimal distortion. Planar tweeters are commonly used in high-end home audio systems, studio monitors, and audiophile headphones for their precise sound reproduction and wide frequency response. Your choice between these tweeters should consider whether you need powerful sound projection or detailed, accurate audio in controlled environments.
Pros and Cons of Horn vs Planar Tweeters
Horn tweeters deliver high sensitivity and directional sound projection, making them ideal for large venues and outdoor use, but they often produce coloration and distortion at high volumes. Planar tweeters offer a smooth, detailed, and natural sound with low distortion and wide dispersion, yet their lower sensitivity requires more amplification and they tend to be less efficient in handling high power. Choosing between horn and planar tweeters depends on application needs, balancing sound precision against efficiency and environmental factors.
Which Tweeter Type Is Best For You?
Horn tweeters deliver high efficiency and directional sound, making them ideal for large venues or outdoor use where volume and projection are priorities. Planar tweeters provide smoother, more detailed high-frequency response with lower distortion, perfect for audiophiles seeking precise, natural sound in controlled listening environments. Your choice depends on whether you value powerful sound reinforcement or accurate, refined audio reproduction.
horn vs planar tweeter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com