Phantom power provides a consistent 48V supply through an audio cable, ideal for condenser microphones, while battery power offers portable, self-contained energy for devices requiring mobility. Explore the detailed comparison to determine which power source best suits Your audio equipment needs.
Table of Comparison
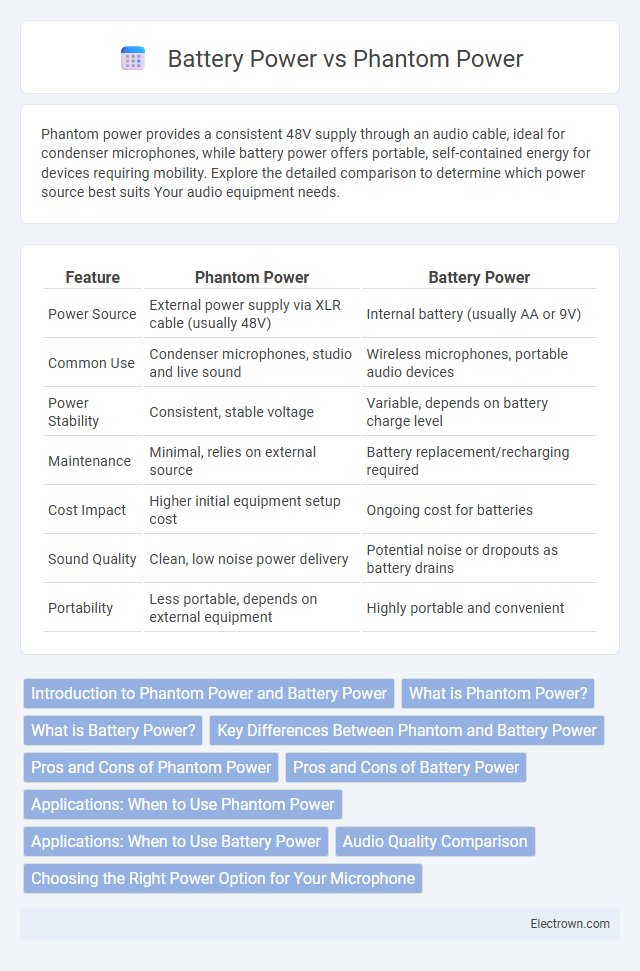
| Feature | Phantom Power | Battery Power |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | External power supply via XLR cable (usually 48V) | Internal battery (usually AA or 9V) |
| Common Use | Condenser microphones, studio and live sound | Wireless microphones, portable audio devices |
| Power Stability | Consistent, stable voltage | Variable, depends on battery charge level |
| Maintenance | Minimal, relies on external source | Battery replacement/recharging required |
| Cost Impact | Higher initial equipment setup cost | Ongoing cost for batteries |
| Sound Quality | Clean, low noise power delivery | Potential noise or dropouts as battery drains |
| Portability | Less portable, depends on external equipment | Highly portable and convenient |
Introduction to Phantom Power and Battery Power
Phantom power is a method of supplying DC voltage, typically 48 volts, through microphone cables to power condenser microphones and active DI boxes without needing batteries. Battery power provides an independent, portable energy source for audio devices, offering flexibility but requiring regular monitoring and replacement. Understanding the benefits and limitations of each power type is essential for optimizing audio equipment performance.
What is Phantom Power?
Phantom power is a method of supplying DC voltage, typically 48 volts, through microphone cables to power condenser microphones and active DI boxes without needing batteries. It enables high-quality audio capture by energizing the microphone's internal electronics while maintaining a balanced audio signal path. This technique is widely used in professional recording studios and live sound setups for its convenience and reliability.
What is Battery Power?
Battery power refers to the use of chemical energy stored in batteries to provide electrical energy for devices like microphones, enabling portable and independent operation without reliance on external power sources. It offers consistent voltage output and is essential for powering condenser microphones when phantom power is unavailable. Unlike phantom power, battery power allows for flexible placement of audio equipment without the constraints of cable length or compatibility with mixing consoles.
Key Differences Between Phantom and Battery Power
Phantom power supplies a stable 48 volts through XLR cables to condenser microphones, enabling consistent audio performance without the need for internal batteries. Battery power relies on individual cells within the microphone or device, offering portability and use in situations where phantom power is unavailable but requiring regular replacement or charging. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the ideal power source for your recording setup, balancing convenience, reliability, and audio quality.
Pros and Cons of Phantom Power
Phantom power provides a consistent, reliable voltage (usually 48V) essential for condenser microphones, eliminating the need for batteries and reducing downtime during recordings. Its main drawback is the incompatibility with some vintage or ribbon microphones, which can be damaged if phantom power is applied improperly. You benefit from phantom power's convenience and durability, although battery-powered microphones offer portability and independence from external power sources.
Pros and Cons of Battery Power
Battery power offers portability and independence from external power sources, making it ideal for remote or mobile audio equipment. However, battery life is limited and requires regular replacement or recharging, which can interrupt usage and increase operational costs. Your choice depends on whether convenience and mobility outweigh the need for continuous, reliable power.
Applications: When to Use Phantom Power
Phantom power is ideal for professional studio microphones and condenser mics requiring a constant 48V supply for optimal performance and minimal noise interference. Battery power suits portable recording devices and dynamic microphones in fieldwork or live settings where mobility and independence from external power sources are crucial. Choosing phantom power is essential in controlled environments demanding high-fidelity audio capture, while battery power is preferable for versatility and convenience in on-the-go applications.
Applications: When to Use Battery Power
Battery power is ideal for applications requiring portability and independence from external power sources, such as wireless microphones, field recorders, and outdoor audio equipment. It ensures consistent performance in environments where phantom power supply is unavailable or unreliable. For lightweight, mobile devices, batteries provide essential power without the need for bulky cables or external power phantom power supplies.
Audio Quality Comparison
Phantom power delivers a consistent and noise-free voltage to condenser microphones, resulting in clearer and more detailed audio quality compared to battery power, which can sometimes introduce hiss or signal degradation as the battery drains. Unlike batteries, phantom power supplies a stable current that maintains microphone performance over extended recording sessions without compromising sound fidelity. This consistency makes phantom-powered microphones preferable in professional audio settings where optimal audio clarity is essential.
Choosing the Right Power Option for Your Microphone
Selecting the appropriate power source for your microphone depends on its type and usage context. Condenser microphones typically require phantom power (48V) supplied through an audio interface or mixer, ensuring consistent and clean audio performance for studio or live settings. Battery power suits wireless or portable microphones, offering mobility but necessitating regular monitoring to avoid interruptions during recordings or broadcasts.
phantom power vs battery power Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com