Class D amplifiers offer high efficiency and compact size, making them ideal for portable and battery-powered devices, while Class AB amplifiers provide superior sound quality with lower distortion, favored in high-fidelity audio systems. Explore the rest of the article to understand which amplifier best suits your audio needs and preferences.
Table of Comparison
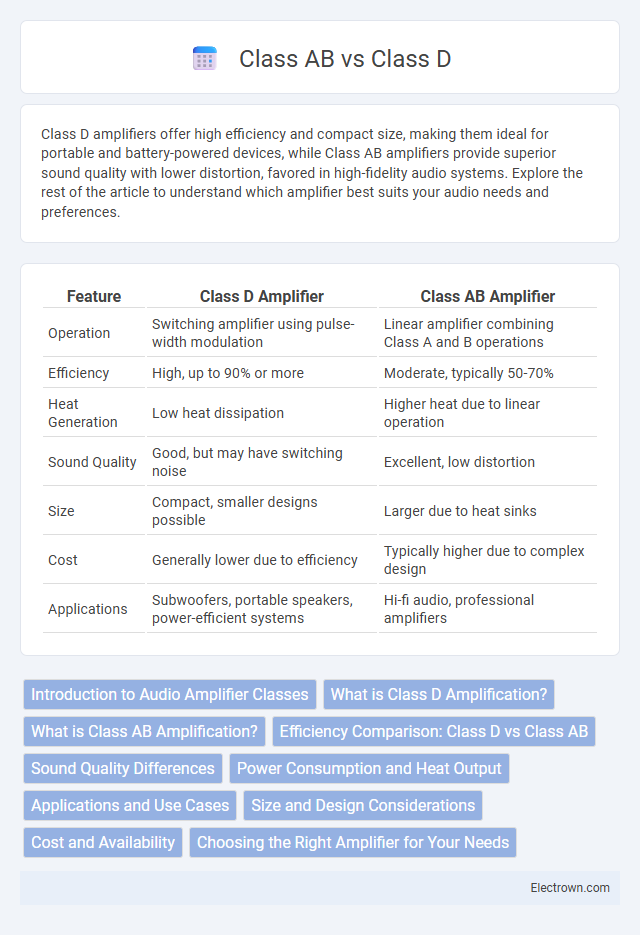
| Feature | Class D Amplifier | Class AB Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Switching amplifier using pulse-width modulation | Linear amplifier combining Class A and B operations |
| Efficiency | High, up to 90% or more | Moderate, typically 50-70% |
| Heat Generation | Low heat dissipation | Higher heat due to linear operation |
| Sound Quality | Good, but may have switching noise | Excellent, low distortion |
| Size | Compact, smaller designs possible | Larger due to heat sinks |
| Cost | Generally lower due to efficiency | Typically higher due to complex design |
| Applications | Subwoofers, portable speakers, power-efficient systems | Hi-fi audio, professional amplifiers |
Introduction to Audio Amplifier Classes
Class D amplifiers use pulse-width modulation to achieve high efficiency and minimal heat dissipation, making them ideal for portable and compact audio devices. Class AB amplifiers combine the low distortion of Class A with the improved efficiency of Class B, offering a balanced audio performance favored in high-fidelity home and professional audio systems. The choice between Class D and Class AB depends on trade-offs in power efficiency, sound quality, and application requirements.
What is Class D Amplification?
Class D amplification utilizes pulse-width modulation to switch transistors between fully on and fully off states, resulting in high efficiency and reduced heat generation compared to linear amplifiers. This switching mechanism allows Class D amplifiers to deliver greater power output in compact, lightweight designs, making them ideal for portable audio devices and subwoofers. Despite earlier concerns about audio fidelity, modern Class D technology achieves sound quality comparable to Class AB amplifiers while maintaining superior energy efficiency.
What is Class AB Amplification?
Class AB amplification combines the efficiency of Class B amplifiers with the low distortion of Class A designs by using two transistors operating in a push-pull configuration. This method reduces crossover distortion commonly found in Class B amplifiers while maintaining better power efficiency compared to pure Class A amplification. Your audio system benefits from Class AB amps by delivering clear sound quality with moderate heat generation and energy consumption.
Efficiency Comparison: Class D vs Class AB
Class D amplifiers achieve efficiency levels of up to 90%, significantly surpassing Class AB amplifiers, which typically operate around 50-70%. This higher efficiency in Class D reduces heat generation and power consumption, making them ideal for portable and battery-powered devices. Your choice between these classes will depend on the need for power efficiency versus audio fidelity, as Class AB often delivers better sound quality at the expense of higher energy use.
Sound Quality Differences
Class D amplifiers offer high efficiency and compact design but tend to produce more harmonic distortion and noise compared to Class AB, which delivers smoother and warmer sound with lower total harmonic distortion (THD). Class AB amplifiers excel in reproducing subtle audio details and maintaining linearity at moderate power levels, making them ideal for audiophiles prioritizing sound fidelity. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize energy efficiency or premium audio quality in sound reproduction.
Power Consumption and Heat Output
Class D amplifiers consume significantly less power due to their high efficiency, often exceeding 90%, which results in reduced heat output and minimal energy loss. Class AB amplifiers, while offering high audio fidelity, generally operate at lower efficiency levels around 50-70%, leading to greater power consumption and increased heat dissipation. The lower heat generation in Class D designs allows for smaller heat sinks and more compact, lightweight amplifier units compared to Class AB models.
Applications and Use Cases
Class D amplifiers excel in applications requiring high efficiency and compact size, such as portable audio devices, subwoofers, and car audio systems. Class AB amplifiers are preferred in high-fidelity audio equipment and professional sound systems where audio quality and low distortion are critical. The choice depends on balancing power efficiency with sound fidelity demands in specific use cases.
Size and Design Considerations
Class D amplifiers are significantly smaller and more compact due to their high efficiency and minimal heat dissipation needs, allowing for sleek, portable designs ideal for modern audio systems. Class AB amplifiers require larger heat sinks and more space to manage heat generated from their linear operation, resulting in bulkier, heavier units. This fundamental difference in size and design impacts installation flexibility and application, with Class D favored in space-constrained environments.
Cost and Availability
Class D amplifiers are generally more cost-effective and widely available due to their simpler design and efficient power usage, making them popular for budget-conscious consumers and compact applications. In contrast, Class AB amplifiers tend to be pricier because of their more complex circuitry and traditional analog design, which often limits their availability to premium audio markets. The mass production and growing demand for Class D technology have driven down prices and increased accessibility compared to the relatively niche Class AB models.
Choosing the Right Amplifier for Your Needs
Class D amplifiers offer high efficiency and compact design, making them ideal for portable and energy-conscious applications. Class AB amplifiers deliver superior audio fidelity and lower distortion, preferred for critical listening environments like home theaters and professional audio. Understanding your priority between power efficiency and sound quality helps determine the best amplifier class for your needs.
class d vs class ab Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com