Tube amplifiers deliver warm, rich tones favored by many musicians for their natural compression and harmonic distortion, while solid state amps offer reliable, lightweight, and low-maintenance performance with clear and consistent sound. Discover which amp suits your playing style and needs by exploring the detailed comparison in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
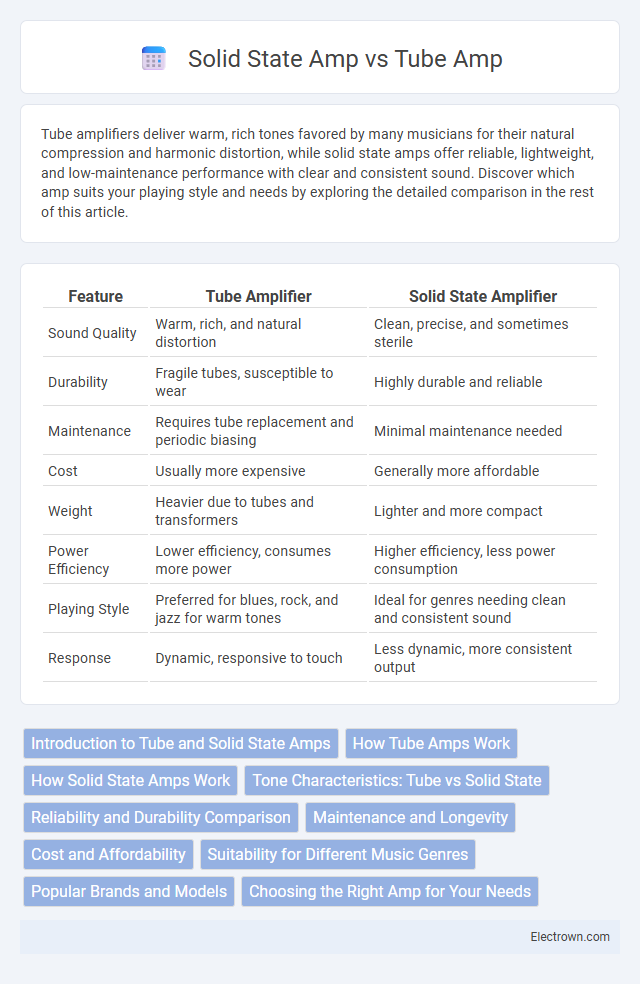
| Feature | Tube Amplifier | Solid State Amplifier |
|---|---|---|
| Sound Quality | Warm, rich, and natural distortion | Clean, precise, and sometimes sterile |
| Durability | Fragile tubes, susceptible to wear | Highly durable and reliable |
| Maintenance | Requires tube replacement and periodic biasing | Minimal maintenance needed |
| Cost | Usually more expensive | Generally more affordable |
| Weight | Heavier due to tubes and transformers | Lighter and more compact |
| Power Efficiency | Lower efficiency, consumes more power | Higher efficiency, less power consumption |
| Playing Style | Preferred for blues, rock, and jazz for warm tones | Ideal for genres needing clean and consistent sound |
| Response | Dynamic, responsive to touch | Less dynamic, more consistent output |
Introduction to Tube and Solid State Amps
Tube amplifiers use vacuum tubes to amplify sound, producing warm, rich tones favored by many musicians for their natural distortion and dynamic response. Solid state amplifiers rely on semiconductor transistors, offering greater reliability, lighter weight, and cleaner sound with less maintenance. The choice between tube and solid state amps depends on desired tonal characteristics, durability, and specific use cases.
How Tube Amps Work
Tube amps operate by using vacuum tubes to amplify audio signals, where the tubes control electron flow between electrodes in a vacuum, creating a warm and harmonically rich sound. The tubes introduce natural distortion and compression as they reach their saturation point, often preferred by musicians for its organic tonal qualities. This analog process contrasts with solid-state amps, which use transistors to amplify signals more linearly and with less coloration.
How Solid State Amps Work
Solid state amps use semiconductor transistors to amplify the electrical signal, converting the input from your instrument into a stronger output without relying on vacuum tubes. These amps offer consistent tone, greater reliability, and lower maintenance due to their solid components. Your sound benefits from precise, efficient amplification that is less susceptible to heat and wear compared to tube technology.
Tone Characteristics: Tube vs Solid State
Tube amplifiers deliver warm, rich, and dynamic tones with natural compression and harmonic distortion that enhance musical expressiveness. Solid state amps offer clean, crisp, and consistent sound with high reliability and lower maintenance, making them ideal for precise, transparent tone reproduction. Your choice depends on whether you prefer the organic warmth of tubes or the clarity and durability of solid-state technology.
Reliability and Durability Comparison
Tube amplifiers generally require more frequent maintenance due to their vacuum tubes, which have a limited lifespan and are sensitive to heat and physical shock. Solid-state amplifiers use transistor circuits, making them more reliable and durable for long-term use with less need for replacement parts. The robust build and resistance to wear make solid-state amps ideal for rigorous touring and everyday use.
Maintenance and Longevity
Tube amplifiers require regular maintenance such as tube replacement and bias adjustments to maintain optimal performance and can experience gradual wear impacting longevity. Solid state amplifiers, built with transistors, typically offer longer lifespan with minimal upkeep due to their durable and stable electronic components. Users seeking low-maintenance solutions often prefer solid state amps, while tube amps attract those valuing tonal characteristics despite increased maintenance demands.
Cost and Affordability
Tube amplifiers generally come with a higher price tag due to their complex vacuum tube components and vintage craftsmanship, making them less affordable for budget-conscious musicians. Solid state amps offer a more cost-effective solution with durable semiconductor circuits that require less maintenance and provide consistent performance over time. The lower manufacturing costs and widespread availability of solid state amps make them the preferred choice for beginners and those seeking reliable gear without a significant financial investment.
Suitability for Different Music Genres
Tube amplifiers deliver warm, rich tones ideal for blues, jazz, and classic rock, enhancing expressive guitar nuances with natural harmonic distortion. Solid-state amps provide tighter, cleaner sounds favored in genres like metal, punk, and pop, offering high reliability and consistency for high-gain settings. Your choice depends on the tonal characteristics suited to your preferred music style and performance needs.
Popular Brands and Models
Popular tube amplifier brands include Marshall, Fender, and Vox, renowned for models like the Marshall Plexi, Fender Deluxe Reverb, and Vox AC30 that deliver warm, rich tones favored by rock and blues guitarists. Solid state amps from brands such as Roland, Peavey, and Line 6 offer reliable, lightweight options with models like the Roland JC-120, Peavey Bandit, and Line 6 Spider, known for versatile sound presets and durability. Musicians often choose tube amps for vintage sound quality and solid state amps for affordability and low maintenance.
Choosing the Right Amp for Your Needs
Tube amps deliver warm, rich tones favored by blues and rock guitarists, while solid state amps offer reliability, lighter weight, and affordability, ideal for beginners and gigging musicians. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize vintage sound quality and natural distortion or versatility, durability, and low maintenance. Consider the specific genres you play, your budget, and how often you'll transport your equipment to select the perfect amplifier for your setup.
tube vs solid state amp Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com