Constant voltage speakers maintain a fixed voltage level across the speaker terminals, ensuring consistent sound output regardless of the load, while constant current speakers deliver a steady current, optimizing performance in long cable runs and preventing losses due to impedance changes. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right speaker system for your audio setup; continue reading to explore the advantages and applications of each type.
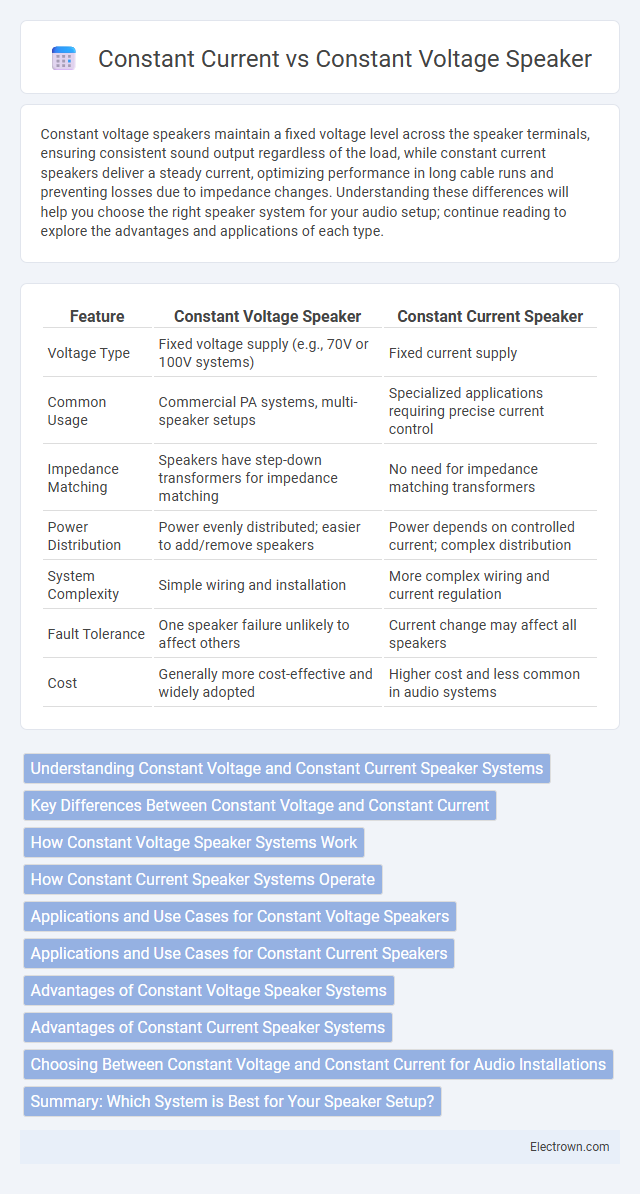
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Constant Voltage Speaker | Constant Current Speaker |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Type | Fixed voltage supply (e.g., 70V or 100V systems) | Fixed current supply |
| Common Usage | Commercial PA systems, multi-speaker setups | Specialized applications requiring precise current control |
| Impedance Matching | Speakers have step-down transformers for impedance matching | No need for impedance matching transformers |
| Power Distribution | Power evenly distributed; easier to add/remove speakers | Power depends on controlled current; complex distribution |
| System Complexity | Simple wiring and installation | More complex wiring and current regulation |
| Fault Tolerance | One speaker failure unlikely to affect others | Current change may affect all speakers |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective and widely adopted | Higher cost and less common in audio systems |
Understanding Constant Voltage and Constant Current Speaker Systems
Constant voltage speaker systems use transformers to step up voltage levels, enabling efficient long-distance audio signal transmission with minimal power loss. Constant current speaker systems regulate the current rather than voltage, providing consistent power delivery regardless of impedance variations in the speaker line. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing audio performance in commercial and distributed sound environments.
Key Differences Between Constant Voltage and Constant Current
Constant voltage speaker systems use 70V or 100V transformers to distribute audio signals efficiently over long distances with minimal loss, making them ideal for large-scale installations. Constant current speakers, on the other hand, rely on uniform current flow to maintain consistent audio levels across each speaker, typically used in specialized or industrial environments. The primary difference lies in load management: constant voltage systems handle varying speaker loads by adjusting voltage, while constant current systems maintain constant current regardless of load changes.
How Constant Voltage Speaker Systems Work
Constant voltage speaker systems operate by using a step-up transformer to increase the amplifier voltage, allowing multiple speakers to be connected in parallel without significantly affecting the overall impedance. Each speaker contains a matching transformer that steps the voltage down to a usable level, ensuring consistent power distribution regardless of the number of speakers. This method reduces power loss over long cable runs and simplifies system scalability in commercial audio installations.
How Constant Current Speaker Systems Operate
Constant current speaker systems operate by maintaining a fixed current flow through the speaker circuit, regardless of variations in speaker impedance or cable length. This approach ensures consistent audio performance and volume levels across multiple speakers connected in parallel, commonly used in large-scale public address systems. Your sound system benefits from reduced signal loss and easier impedance matching, resulting in clearer and more reliable audio distribution.
Applications and Use Cases for Constant Voltage Speakers
Constant voltage speakers are ideal for large-scale audio distribution systems such as public address, paging, and background music in commercial buildings, schools, and stadiums. Their ability to transmit audio signals over long distances with minimal loss makes them suitable for multi-speaker setups where uniform volume and simple wiring are essential. You benefit from efficient power delivery and scalability in environments requiring multiple audio zones and consistent sound quality.
Applications and Use Cases for Constant Current Speakers
Constant current speakers are ideal for large-scale public address systems where long cable runs require consistent audio quality and power distribution, such as in stadiums, airports, and shopping malls. They enable easy expansion of speaker arrays without significant power loss, making them suitable for emergency notification systems and zoning applications. Your system benefits from simplified wiring and enhanced fault tolerance, ensuring reliable audio performance in complex installations.
Advantages of Constant Voltage Speaker Systems
Constant voltage speaker systems offer the advantage of simplified wiring, allowing multiple speakers to be connected over long distances with minimal power loss and impedance matching issues. These systems provide flexibility in adjusting speaker volume individually through transformers, ensuring consistent sound quality across various zones. Your audio setup benefits from ease of expansion and reduced risk of amplifier overload, making constant voltage ideal for large or distributed audio installations.
Advantages of Constant Current Speaker Systems
Constant current speaker systems offer superior impedance matching, reducing power loss and enabling longer cable runs without signal degradation. These systems simplify multi-speaker installations by maintaining consistent voltage across speakers, ensuring uniform sound levels. Enhanced system reliability and easier troubleshooting are achieved due to standardized current flow, which minimizes the risk of overloads and component failures.
Choosing Between Constant Voltage and Constant Current for Audio Installations
Selecting between constant voltage and constant current for audio installations depends on system size and wiring complexity, with constant voltage (commonly 70V or 100V systems) preferred for longer cable runs and multiple speakers due to minimal power loss and simpler impedance matching. Constant current systems offer precise power distribution and are less common in standard audio setups, typically used in specialized applications requiring uniform power delivery regardless of cable length. For typical public address or distributed audio, constant voltage systems provide cost-effective scalability and easier installation.
Summary: Which System is Best for Your Speaker Setup?
Constant voltage speaker systems are ideal for large installations requiring long cable runs and multiple speakers, as they minimize power loss and simplify wiring. Constant current systems provide precise control over speaker output, ensuring uniform sound levels in environments with variable impedance. Choosing the best system depends on your setup size, wiring complexity, and desired sound consistency.
constant voltage vs constant current speaker Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com