Microphonic tubes tend to pick up mechanical vibrations and convert them into electrical signals, causing unwanted noise or feedback in audio equipment, whereas non-microphonic tubes are designed to resist this sensitivity. Understanding the differences between microphonic and non-microphonic tubes can help you choose the right components for clearer, more reliable sound performance--read on to discover how these tube types impact your audio setup.
Table of Comparison
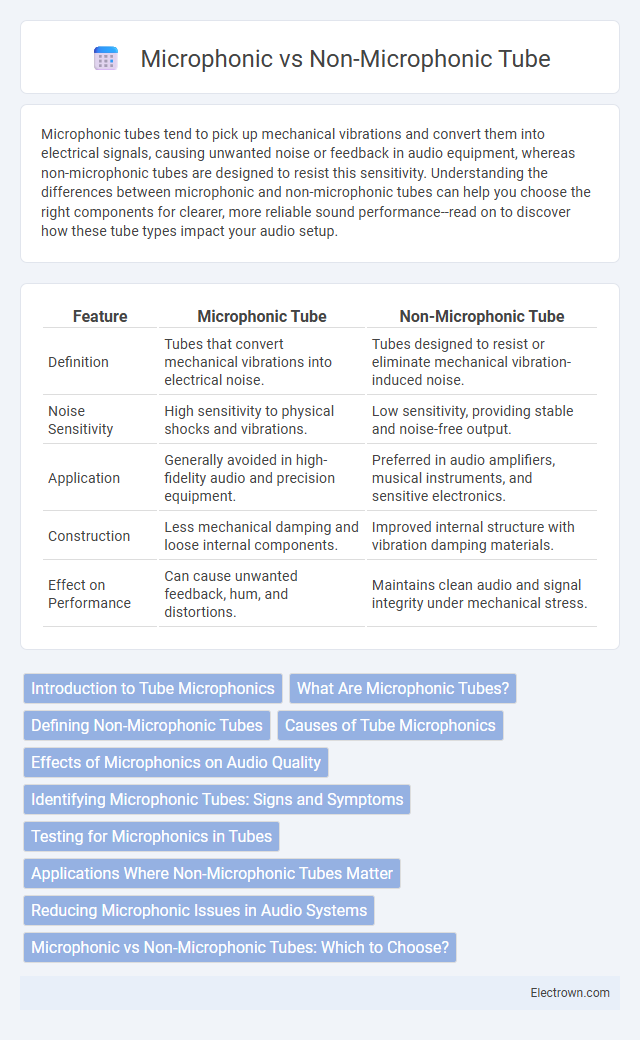
| Feature | Microphonic Tube | Non-Microphonic Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tubes that convert mechanical vibrations into electrical noise. | Tubes designed to resist or eliminate mechanical vibration-induced noise. |
| Noise Sensitivity | High sensitivity to physical shocks and vibrations. | Low sensitivity, providing stable and noise-free output. |
| Application | Generally avoided in high-fidelity audio and precision equipment. | Preferred in audio amplifiers, musical instruments, and sensitive electronics. |
| Construction | Less mechanical damping and loose internal components. | Improved internal structure with vibration damping materials. |
| Effect on Performance | Can cause unwanted feedback, hum, and distortions. | Maintains clean audio and signal integrity under mechanical stress. |
Introduction to Tube Microphonics
Tube microphonics occur when vacuum tubes convert mechanical vibrations into electrical noise, affecting audio quality in sensitive equipment such as amplifiers. Microphonic tubes produce unwanted sounds caused by internal components reacting to physical shocks, whereas non-microphonic tubes are designed with robust construction to minimize this effect. Understanding the difference helps you choose tubes that maintain clean signal integrity in high-fidelity audio applications.
What Are Microphonic Tubes?
Microphonic tubes are vacuum tubes that convert mechanical vibrations into electrical signals, causing unwanted noise or feedback in audio equipment. These tubes are particularly sensitive to physical impacts or movement, making them less ideal for high-fidelity sound applications. Understanding whether your equipment uses microphonic or non-microphonic tubes can significantly affect audio clarity and performance.
Defining Non-Microphonic Tubes
Non-microphonic tubes are vacuum tubes specifically designed to minimize microphonic effects, which occur when mechanical vibrations cause unwanted noise or signal distortion. These tubes feature reinforced internal structures and specialized materials to reduce sensitivity to physical vibrations, ensuring clearer audio output in sensitive applications like guitar amplifiers and high-fidelity audio equipment. Choosing non-microphonic tubes enhances performance by maintaining signal integrity and reducing feedback caused by tube movement or handling noise.
Causes of Tube Microphonics
Tube microphonics occur when mechanical vibrations cause internal components--such as the cathode, grid, or plate--to physically move and generate unwanted electrical signals. These vibrations can be triggered by external sources like speaker feedback, handling noise, or environmental vibrations. Your amplifier's performance is affected because microphonic tubes convert mechanical energy into electrical noise, while non-microphonic tubes have robust construction and damping materials to minimize this effect.
Effects of Microphonics on Audio Quality
Microphonic tubes cause unwanted noise and vibrations that degrade audio quality by introducing hums, crackles, and distortion into the sound signal. Non-microphonic tubes maintain cleaner and clearer audio reproduction by minimizing mechanical vibrations and interference. Choosing non-microphonic tubes ensures Your audio equipment delivers higher fidelity and preserves the integrity of the original sound.
Identifying Microphonic Tubes: Signs and Symptoms
Microphonic tubes generate unwanted noise and vibrations that can cause popping, crackling, or ringing sounds in audio equipment. Identifying microphonic tubes involves tapping the tube gently while the device is on and listening for amplified noises or distortion through the speakers. Ensuring your tubes are non-microphonic improves sound clarity and overall audio performance, making it crucial to recognize these symptoms early.
Testing for Microphonics in Tubes
Testing for microphonics in tubes involves tapping the tube gently while monitoring the audio output for unwanted noise or feedback, indicating internal mechanical vibrations. A dedicated tube tester with vibration sensitivity or using an oscilloscope can help identify microphonic behavior, as these tools detect variations caused by physical movement inside the tube. Non-microphonic tubes maintain stable audio signals without generating noise when subjected to such tests, making them ideal for high-fidelity audio equipment.
Applications Where Non-Microphonic Tubes Matter
Non-microphonic tubes are crucial in high-fidelity audio systems, sensitive radio receivers, and precision measurement equipment, where mechanical vibrations can degrade sound quality or signal integrity. Your audio experience or signal accuracy benefits significantly from non-microphonic tubes, as these components minimize noise and unwanted feedback caused by physical movement. In professional recording studios or critical communication devices, using non-microphonic tubes ensures cleaner, more reliable performance.
Reducing Microphonic Issues in Audio Systems
Reducing microphonic issues in audio systems involves selecting non-microphonic tubes designed with internal structures that minimize mechanical vibrations and noise interference. Using shock-mounted tube sockets, vibration-damping materials, and isolating tubes from physical shocks further decreases microphonic effects, enhancing audio clarity. Regularly testing tubes for microphonics and replacing those exhibiting excessive noise ensures consistent, high-quality sound performance in professional audio equipment.
Microphonic vs Non-Microphonic Tubes: Which to Choose?
Microphonic tubes generate unwanted noise by converting vibrations into electrical signals, making them less ideal for sensitive audio applications like high-gain preamps or guitar amplifiers. Non-microphonic tubes feature internal structures designed to minimize mechanical resonance, providing cleaner sound quality and improved signal fidelity in professional audio equipment. Selecting non-microphonic tubes is crucial for audiophiles and musicians seeking low noise floor and stable performance under physical movement.
microphonic vs non-microphonic tube Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com