Analog gauges display measurements through a continuous needle movement, providing an intuitive view of trends and changes, while digital gauges offer precise numerical readings for exact data analysis. Explore the detailed comparison to discover which gauge best suits your needs and enhances your measurement accuracy.
Table of Comparison
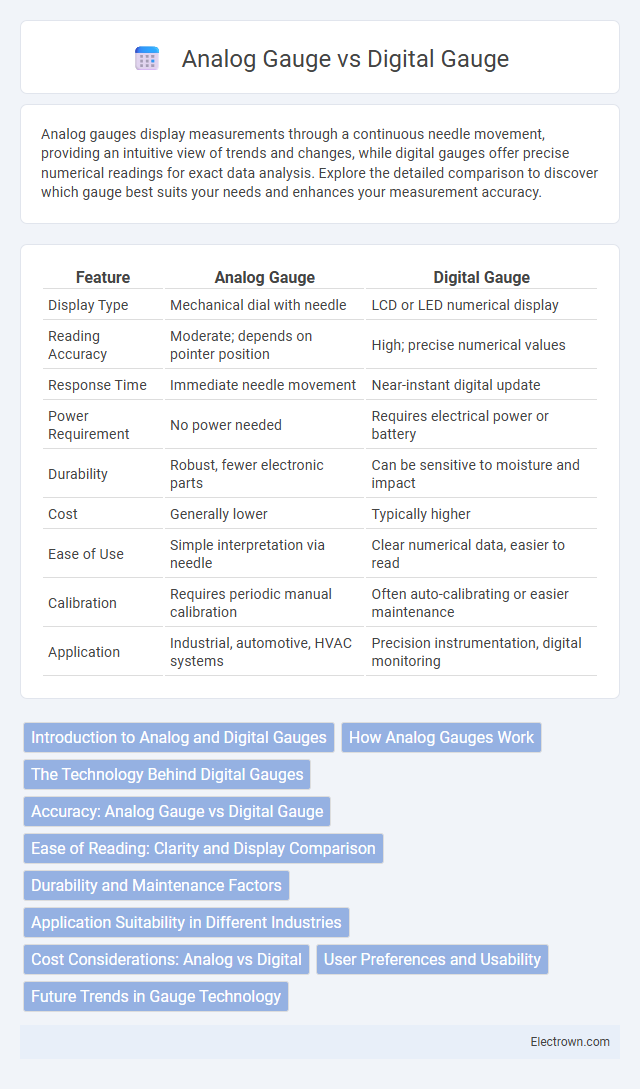
| Feature | Analog Gauge | Digital Gauge |
|---|---|---|
| Display Type | Mechanical dial with needle | LCD or LED numerical display |
| Reading Accuracy | Moderate; depends on pointer position | High; precise numerical values |
| Response Time | Immediate needle movement | Near-instant digital update |
| Power Requirement | No power needed | Requires electrical power or battery |
| Durability | Robust, fewer electronic parts | Can be sensitive to moisture and impact |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Ease of Use | Simple interpretation via needle | Clear numerical data, easier to read |
| Calibration | Requires periodic manual calibration | Often auto-calibrating or easier maintenance |
| Application | Industrial, automotive, HVAC systems | Precision instrumentation, digital monitoring |
Introduction to Analog and Digital Gauges
Analog gauges use a mechanical needle to display measurements on a dial, providing real-time, continuous data readings ideal for quick visual assessments. Digital gauges convert sensor input into numerical values displayed on an electronic screen, offering higher precision and easier readability, especially in low-light conditions. Your choice between these gauges depends on the need for accuracy, display clarity, and environmental factors influencing gauge performance.
How Analog Gauges Work
Analog gauges operate by measuring physical parameters through mechanical means, often using a needle that moves along a calibrated dial in response to pressure, temperature, or voltage changes. The needle's position correlates proportionally to the measured value, allowing users to interpret real-time data visually without digital processing. Understanding how your analog gauge functions can help ensure accurate monitoring in environments where immediate analog feedback is essential.
The Technology Behind Digital Gauges
Digital gauges utilize microprocessor-based sensors that convert physical input signals such as pressure, temperature, or speed into digital data, enabling precise and real-time measurements. Advanced components like MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) sensors and LCD or LED displays provide accurate readouts with minimal lag, enhancing reliability over traditional analog gauges. The integration of wireless connectivity and data logging capabilities further elevates digital gauges for modern applications in automotive, industrial, and aerospace sectors.
Accuracy: Analog Gauge vs Digital Gauge
Digital gauges provide higher accuracy with precise numerical readouts, reducing human error common in analog gauge readings. Analog gauges rely on needle positioning, which can be affected by parallax and mechanical wear, leading to less precise measurements. For critical applications demanding exact data, digital gauges offer superior reliability and consistency in accuracy.
Ease of Reading: Clarity and Display Comparison
Analog gauges feature a needle moving over a graduated scale, offering quick visual trends but can be harder to read precise values, especially in low light or from a distance. Digital gauges provide exact numerical readings with backlit displays, enhancing clarity and reducing reading errors in various lighting conditions. The choice depends on the need for immediate trend visualization versus exact numerical precision.
Durability and Maintenance Factors
Analog gauges typically offer greater durability in harsh environments due to their mechanical construction, making them less susceptible to electronic failures. Maintenance for analog gauges is often simpler, involving occasional calibration and physical inspection, while digital gauges may require software updates and battery replacements. Digital gauges provide precise readings but can be more sensitive to moisture, electrical interference, and impact damage, potentially increasing maintenance frequency.
Application Suitability in Different Industries
Analog gauges excel in industries such as manufacturing and aviation due to their simplicity, durability, and real-time needle movement that offers quick visual inspection under harsh conditions. Digital gauges are preferred in sectors like pharmaceuticals and electronics, where high precision, data logging, and integration with automated systems enhance process control and quality assurance. Each gauge type aligns with industry needs based on accuracy, environmental resilience, and the requirement for data analytics or manual monitoring.
Cost Considerations: Analog vs Digital
Analog gauges typically have lower upfront costs compared to digital gauges, making them a budget-friendly choice for basic measurement needs. Digital gauges often involve higher initial investment due to advanced features and precision technology but can offer long-term savings through enhanced accuracy and reduced maintenance. Your decision should weigh the balance between cost and performance based on application requirements.
User Preferences and Usability
Analog gauges provide a clear, continuous visual representation that many users find intuitive for quickly assessing trends and relative values, especially in environments where rapid, at-a-glance readings are essential. Digital gauges deliver precise numerical data, enhancing accuracy and ease of monitoring exact measurements, which benefits users requiring detailed information for analysis or control. Your choice between analog and digital gauges should consider whether ease of trend recognition or precision measurement aligns better with your specific usability needs and preferences.
Future Trends in Gauge Technology
Future trends in gauge technology emphasize enhanced accuracy, real-time data integration, and IoT connectivity, driving the evolution from traditional analog gauges to advanced digital gauges. Digital gauges offer superior precision and remote monitoring capabilities, enabling You to optimize system performance and predictive maintenance. Innovations in wireless technology and AI-driven analytics will further revolutionize gauge functionality, making digital solutions the industry standard.
Analog gauge vs Digital gauge Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com